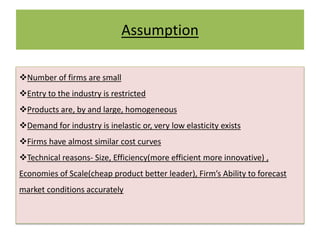
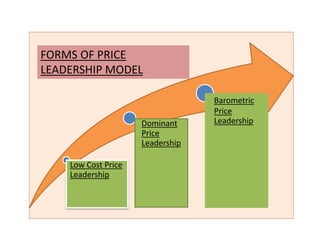
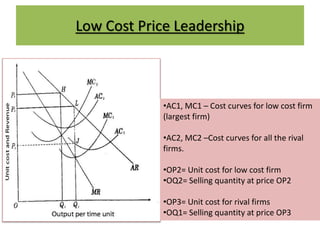
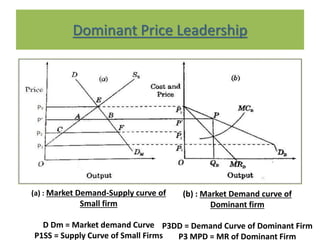
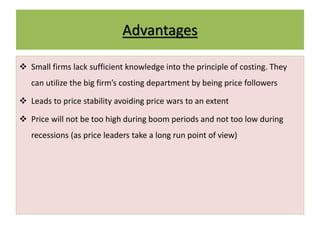
This document discusses price leadership models in oligopolistic markets. It defines price leadership as a situation where one dominant firm sets prices that other competitors feel compelled to match. There are three forms of price leadership discussed: low-cost price leadership, where the lowest cost firm leads prices; dominant price leadership, where the firm with the largest market share sets prices; and barometric price leadership, where the most reliable firm acts as a barometer of market conditions. Price leadership can provide price stability and prevent price wars while allowing smaller firms to benefit from a larger firm's cost information. However, price leadership is regulated to prevent illegal practices under India's MRTP Act.