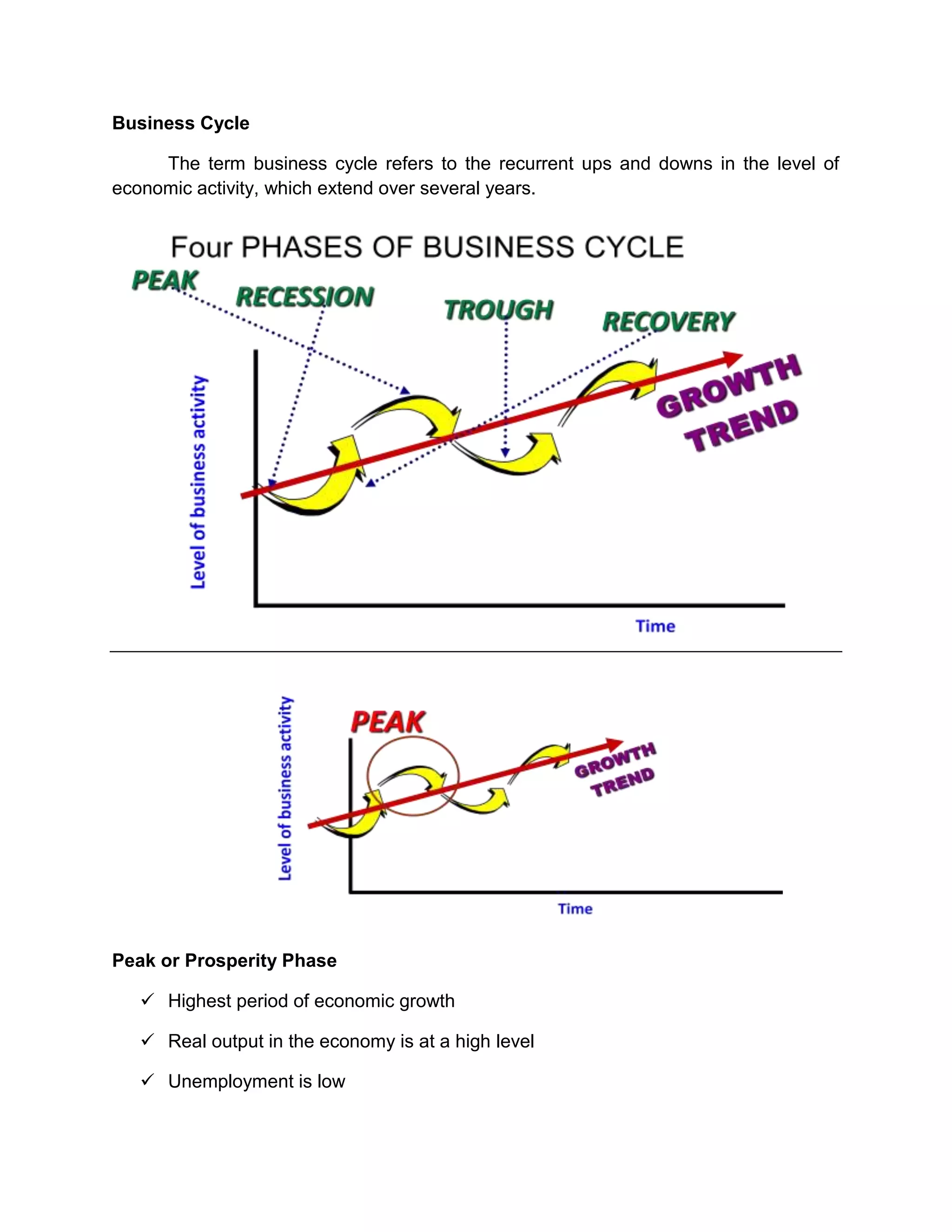
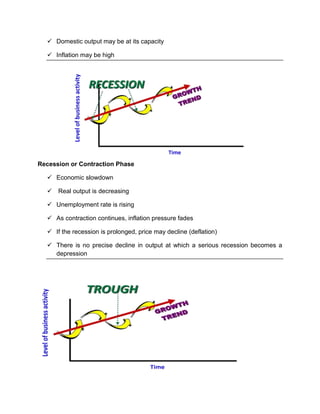
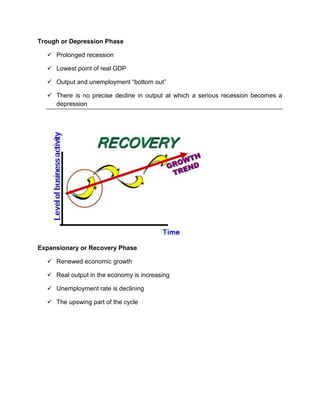
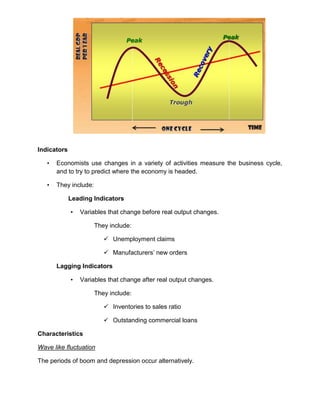
The business cycle refers to recurring periods of economic growth (peak/prosperity phase) and contraction (recession/contraction phase) that can last for years. During the peak, economic growth is highest, output and employment are at their maximum levels, and inflation may be high. In the recession, economic growth declines, output and employment decrease, and unemployment rises. The cycle bottoms out in the trough/depression phase, then enters a recovery/expansionary phase where growth resumes. Economists use indicators like unemployment claims and inventory levels to track changes in the business cycle and predict economic trends.