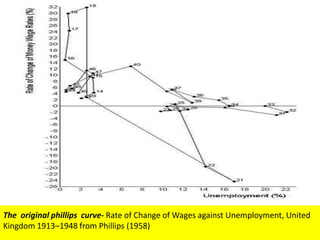
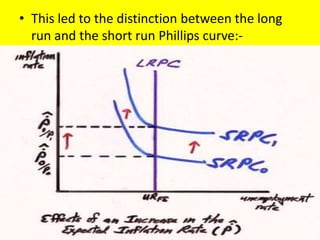
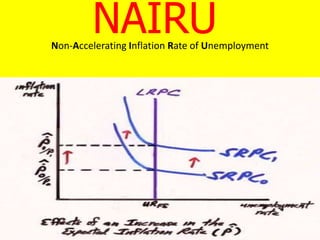
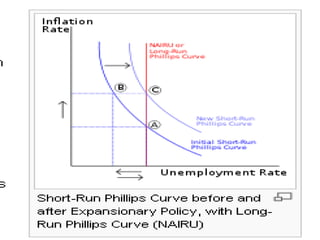
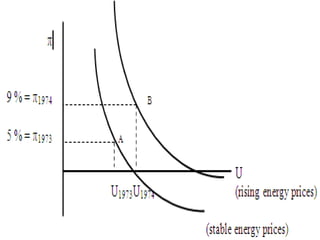
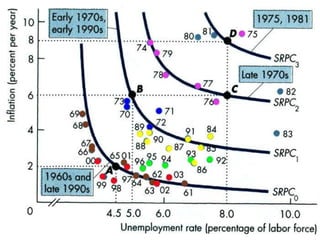
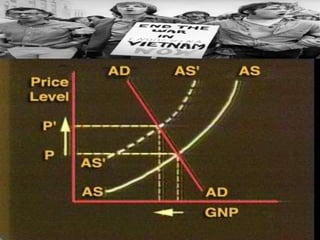
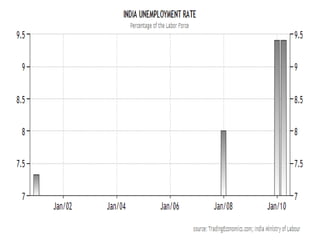
The Phillips curve describes an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation, such that lower unemployment is associated with higher inflation. While observed to be stable in the short-run, it does not hold in the long-run. The document discusses the origins of the Phillips curve from William Phillips' 1958 paper and subsequent modifications by economists like Friedman and Phelps who argued it does not reflect long-run economic realities. It also examines shifts to the Phillips curve from supply shocks and how the relationship between unemployment and inflation is now understood with incorporation of inflation expectations.