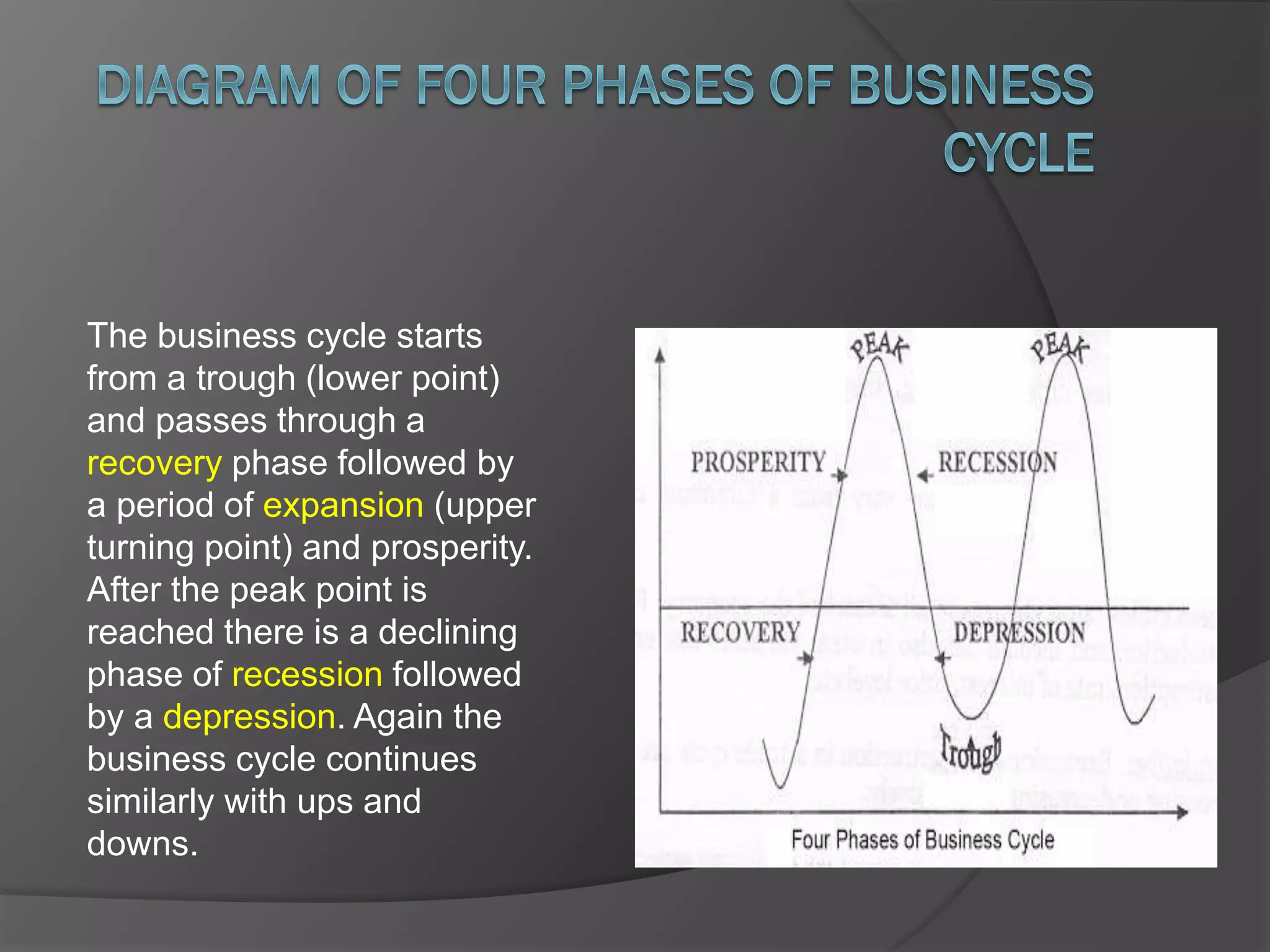
The document discusses business cycles, also known as trade cycles. It defines them as alternating periods of economic expansion and contraction. Expansion periods are times of high income, output, and employment, also called prosperity. Contraction periods are times of low income, output, and employment, also called recessions. The business cycle involves four phases - prosperity, recession, depression, and recovery - as the economy fluctuates between expansion and contraction over time.