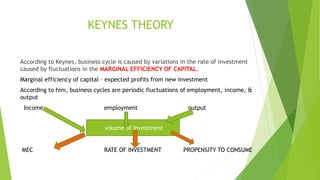
The business cycle refers to the periodic fluctuations in economic activity, measured by variables such as GDP, employment, and prices. There are four main phases of the business cycle: boom, recession, depression, and recovery. During a boom, economic activity peaks as GDP, employment, incomes, and prices are highest. A recession is a period of declining economic activity marked by falling GDP, incomes, and employment. A depression is a more prolonged and severe recession with a sharp drop in economic activity. Recovery begins as the economy starts to grow again, GDP and employment increase from their lows. The causes of business cycles include fluctuations in demand and supply, capital and consumer goods, purchasing power, population changes, and human psychology. Governments