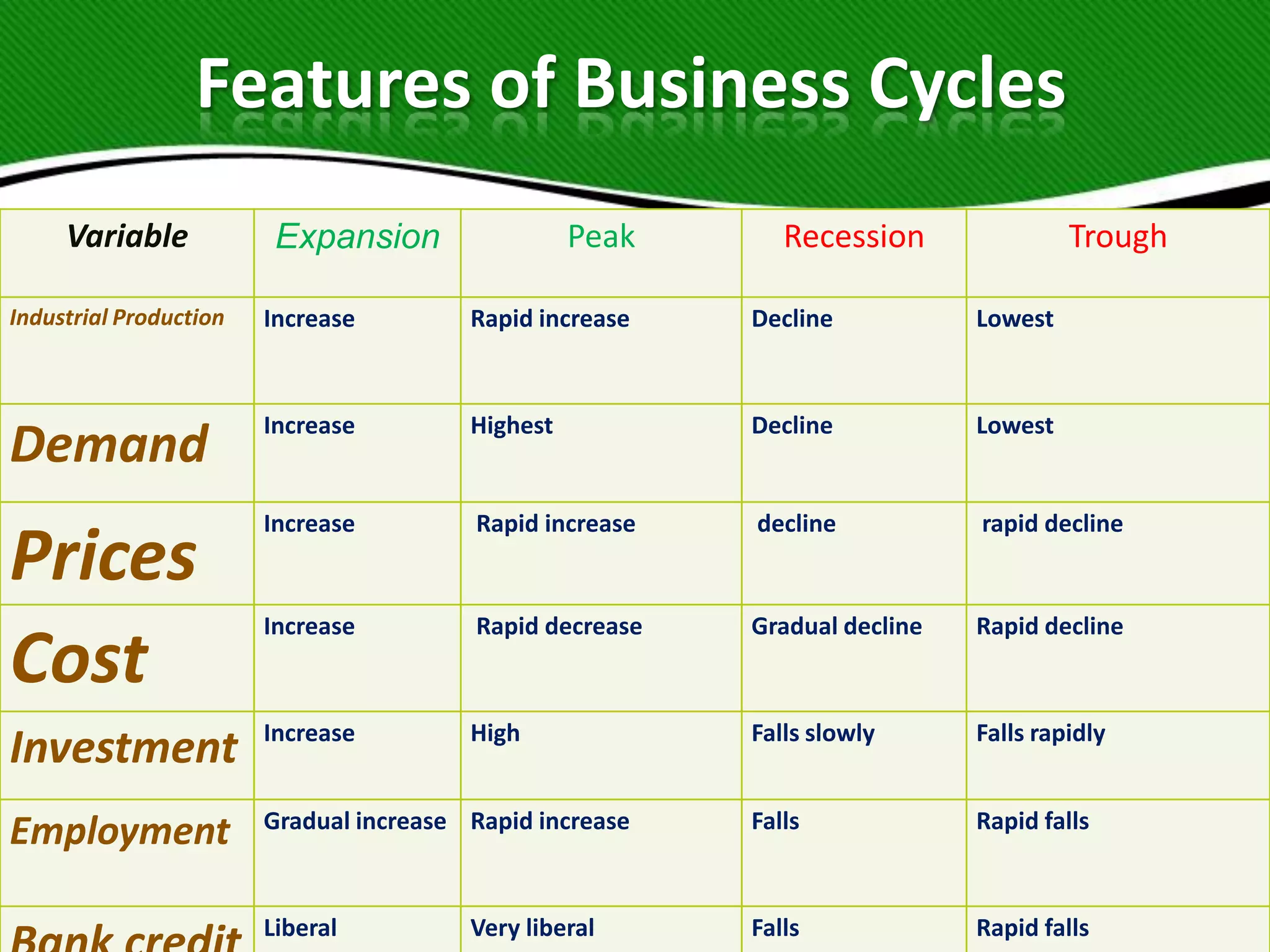
The document outlines the concept of business cycles, which are periodic rises and falls in economic activity comprising four main phases: expansion, peak, recession, and trough. It discusses the characteristics of each phase, indicators that predict changes in the business cycle, and the role of government fiscal and monetary policies in stabilizing the economy. Additionally, it includes a case study of PepsiCo's performance in India during various business cycle phases.