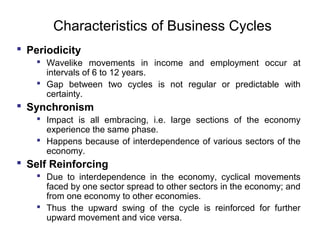
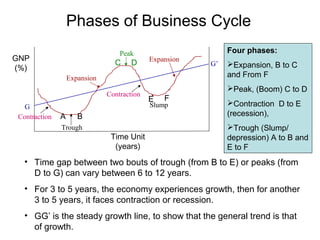
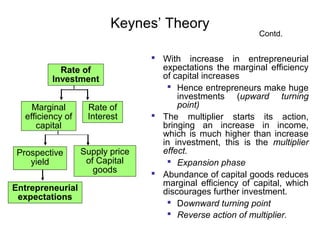
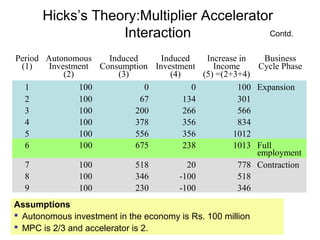
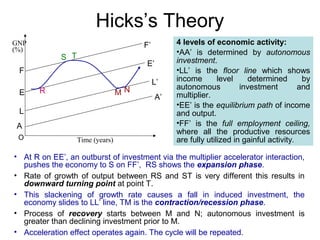
Business cycles show periodic fluctuations in economic activity, measured by indicators like production, employment, and income. There are four phases of a business cycle: expansion, peak, contraction/recession, and trough. Expansions involve growth while contractions involve declines. Business cycles are caused by factors like changes in investment levels, consumer and business expectations, and technological innovations. Theories like Keynes' emphasize how fluctuations in investment can drive cycles, while real business cycle theory sees cycles arising from supply-side shocks. Cycles affect the economy through impacts on areas like growth, inflation, and unemployment. Policy tools can help control the amplitude of cycles.