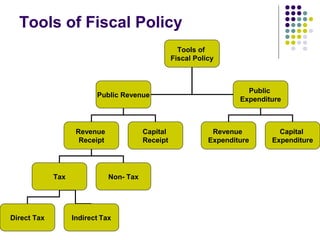
Fiscal policy refers to a government's spending and tax policies to influence macroeconomic conditions. The document discusses different aspects of fiscal policy including:
- Countercyclical fiscal policy aims to stabilize the economy by increasing government spending and reducing taxes during recessions, and reducing spending and raising taxes during expansions.
- Discretionary fiscal policy is used purposefully by governments to achieve macroeconomic goals like reducing inflation or boosting growth. Tools include changing spending, taxes, and borrowing.
- Non-discretionary or automatic fiscal policy relies on built-in stabilizers like income taxes that automatically influence demand over the business cycle.
- Large fiscal deficits can adversely impact growth by reducing funds for