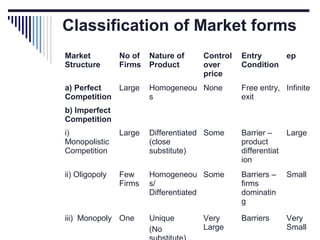
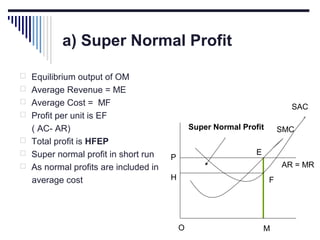
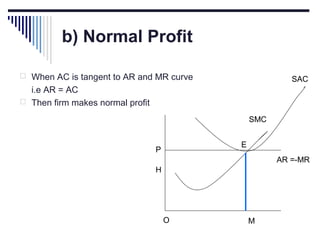
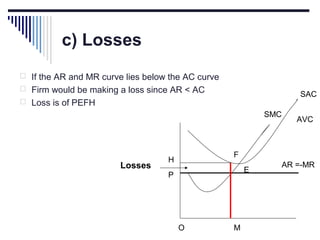
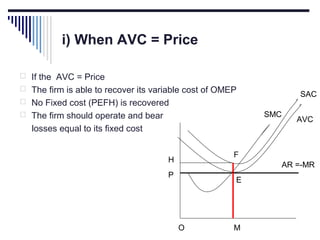
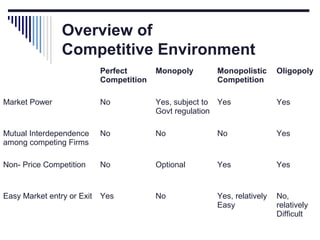
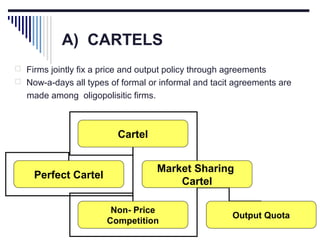
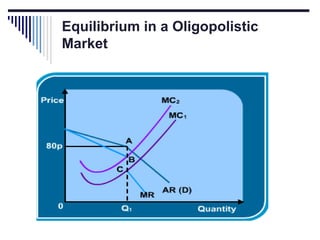
- A market is defined as the interaction between buyers and sellers of a product where the price tends to be uniform. Market structure depends on the number of firms, nature of products, barriers to entry, and degree of price control.
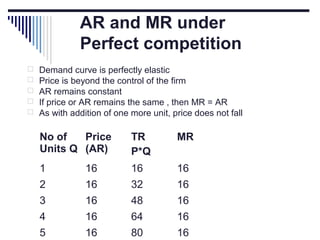
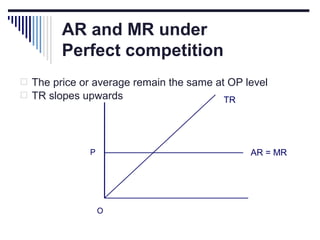
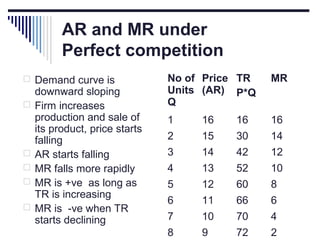
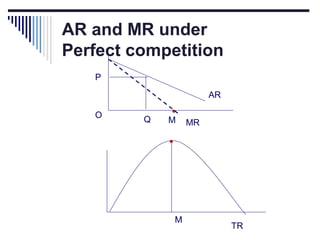
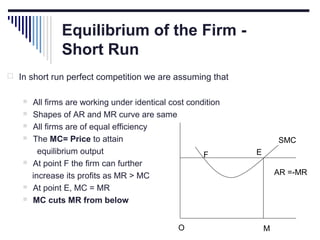
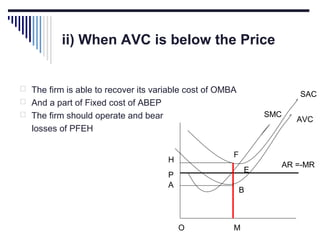
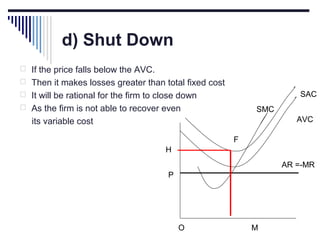
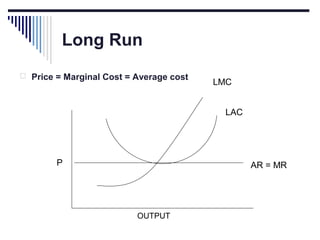
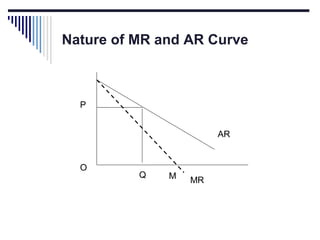
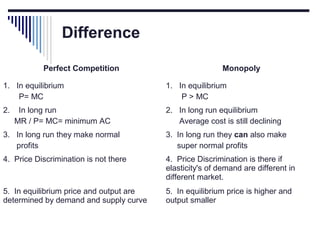
- Under perfect competition there are many small firms, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and no single firm can influence price. Equilibrium occurs where marginal cost equals price.
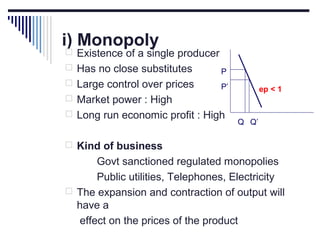
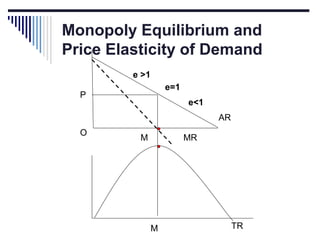
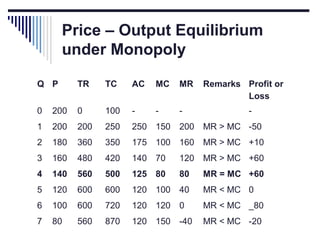
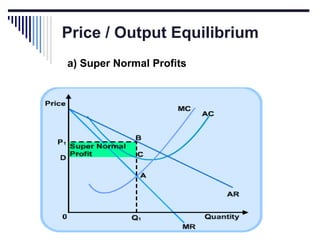
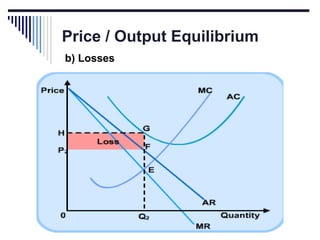
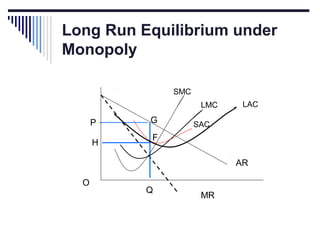
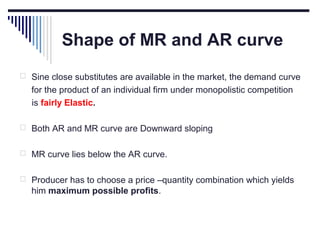
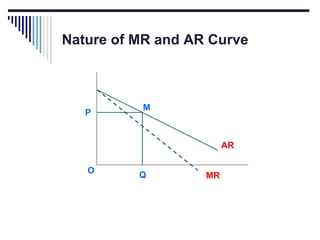
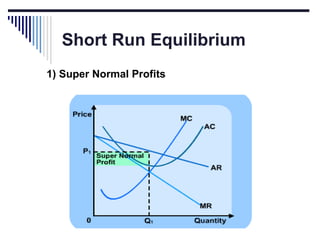
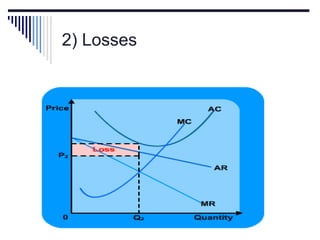
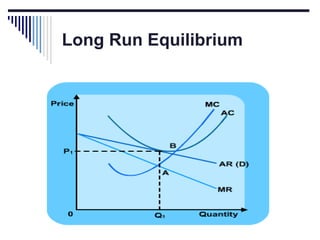
- Monopoly is characterized by a single firm, no close substitutes, and high barriers to entry. The monopolist's equilibrium occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price is above marginal cost.