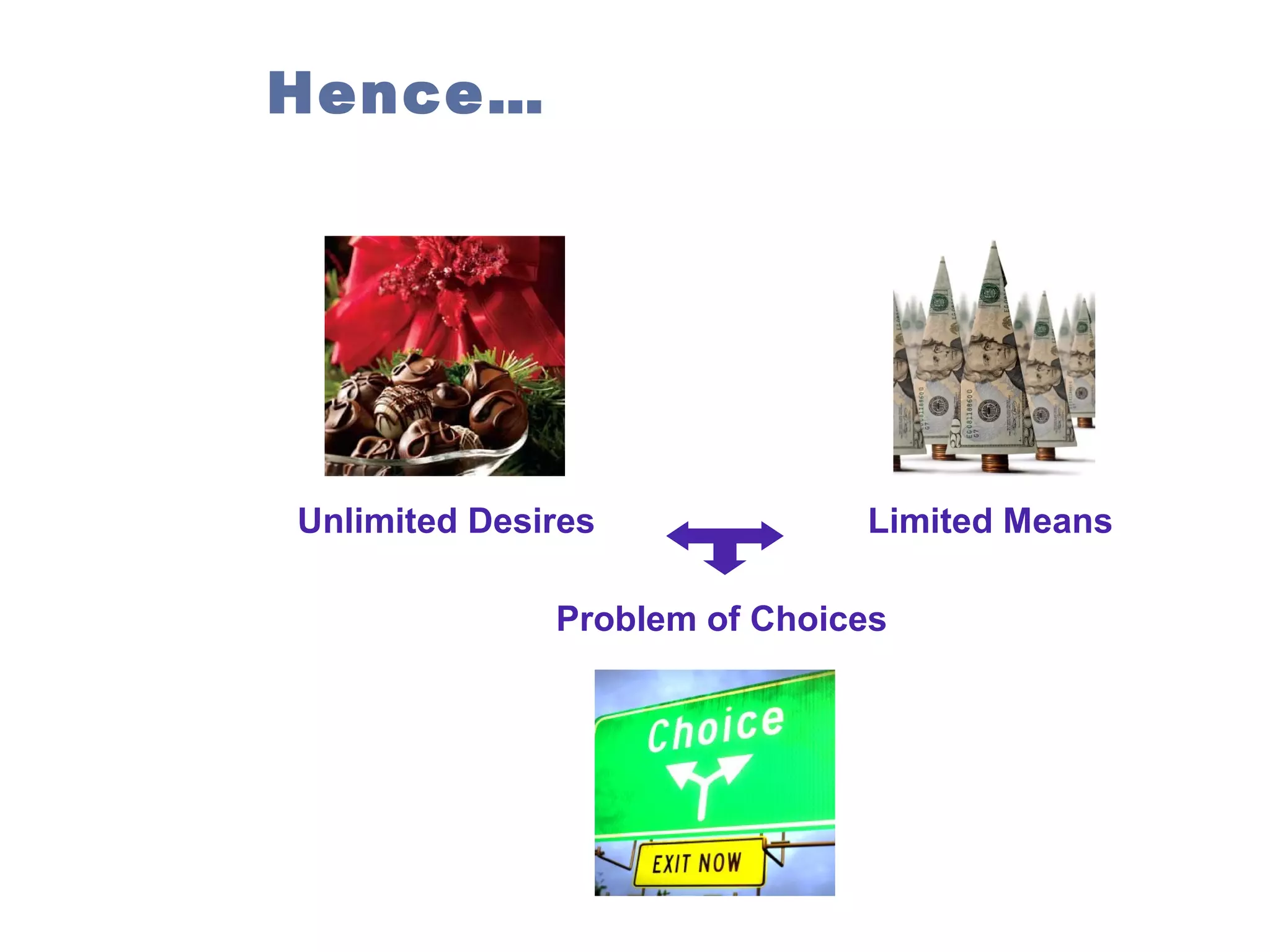
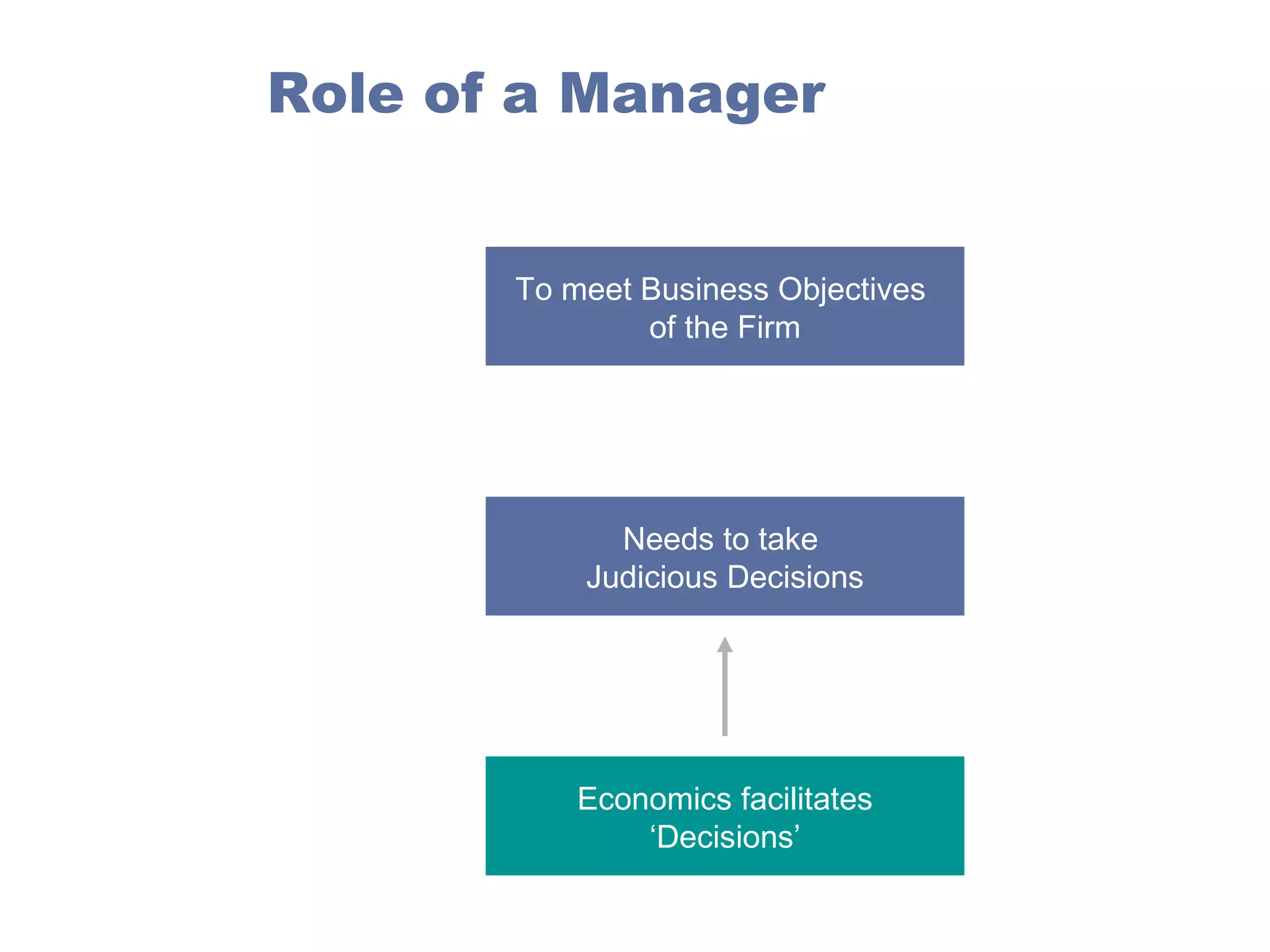
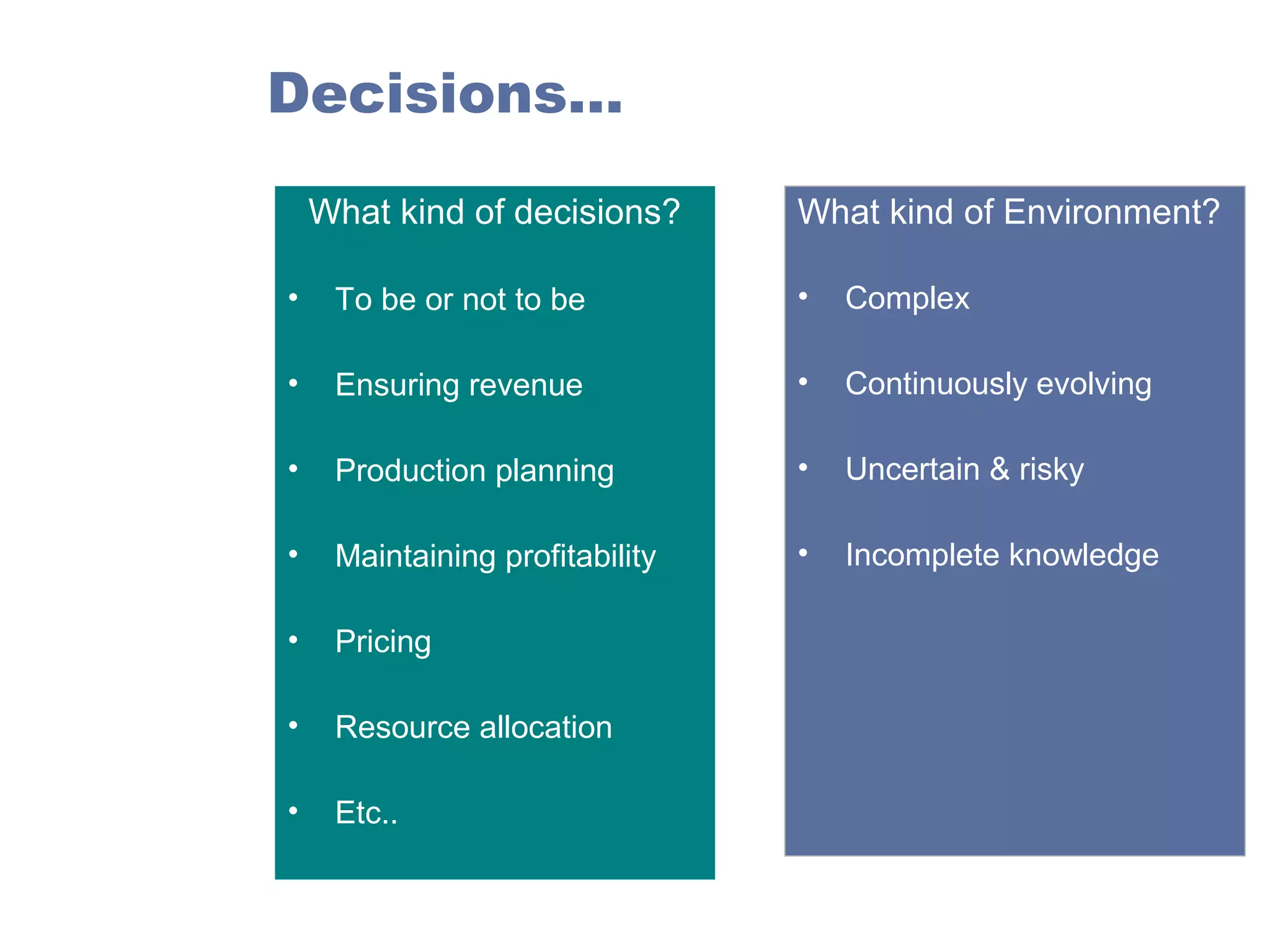
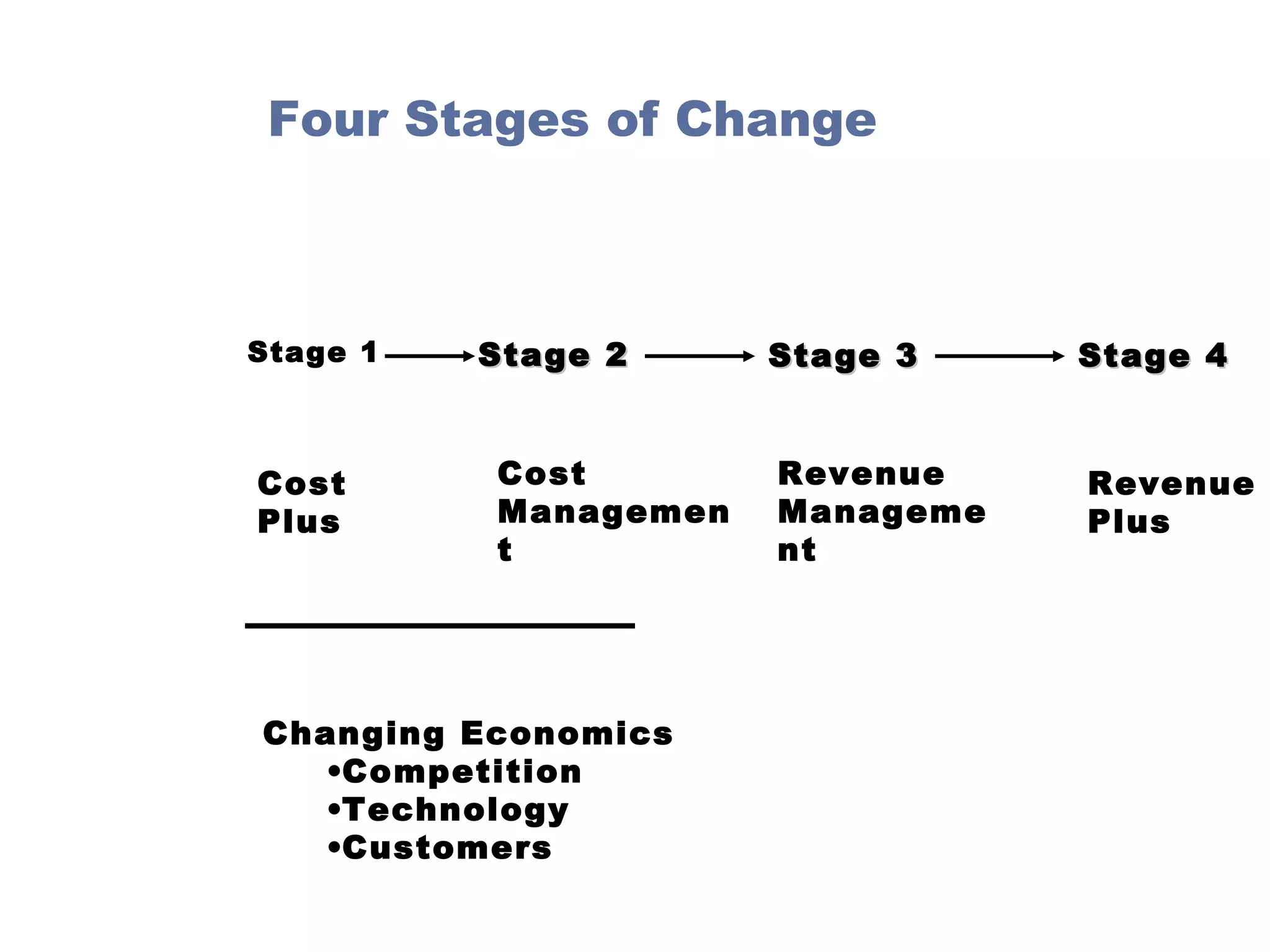
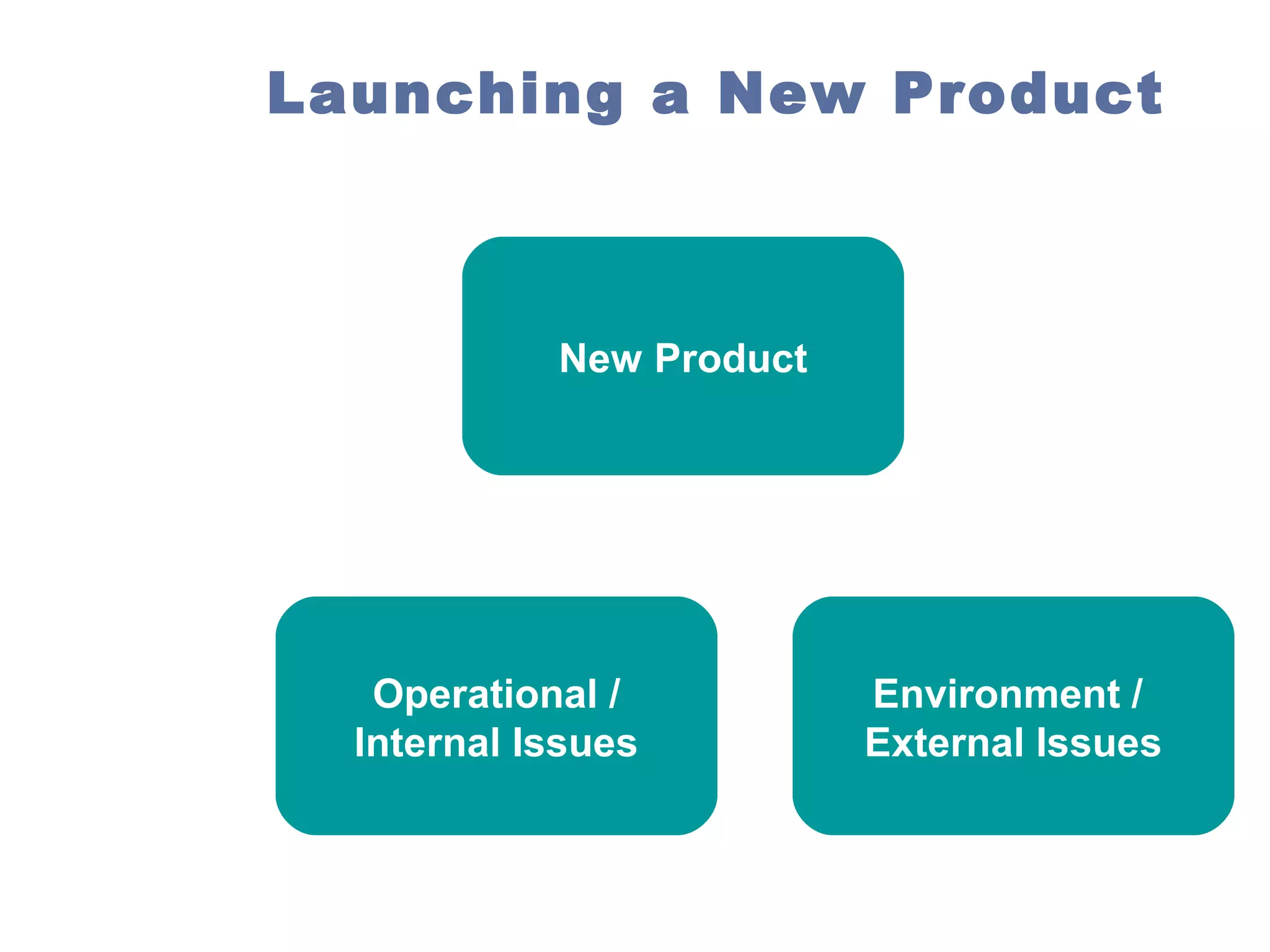
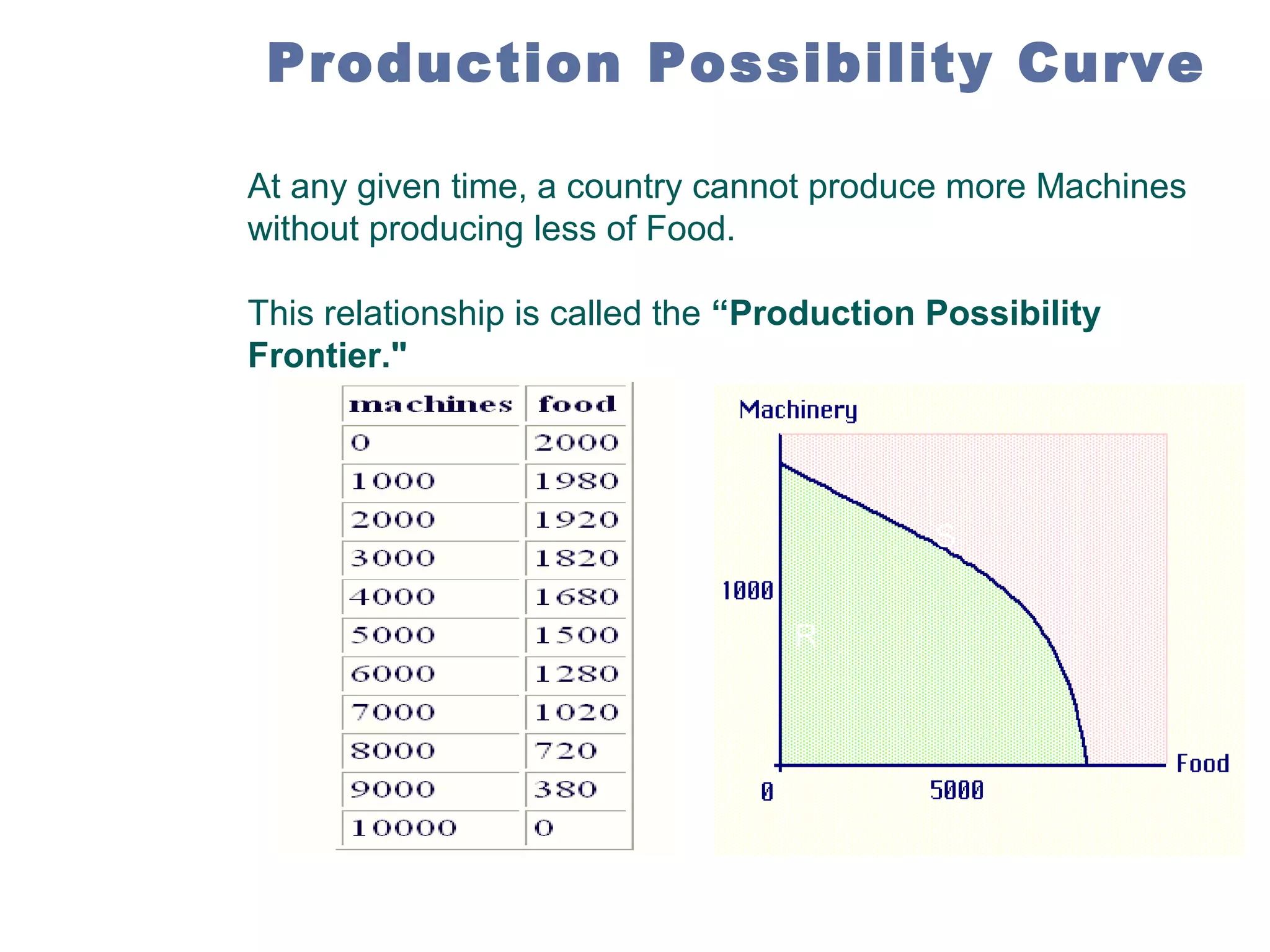
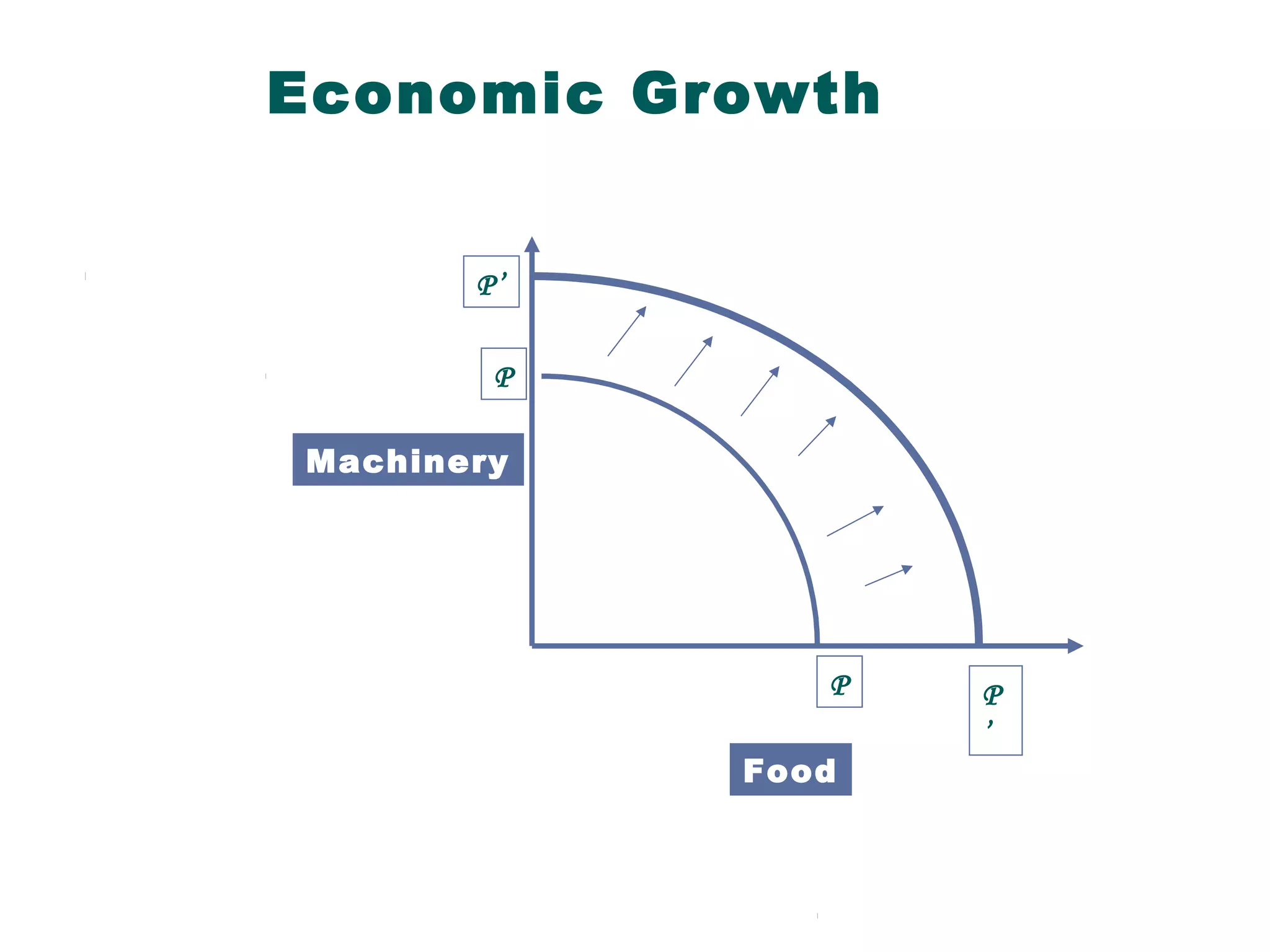
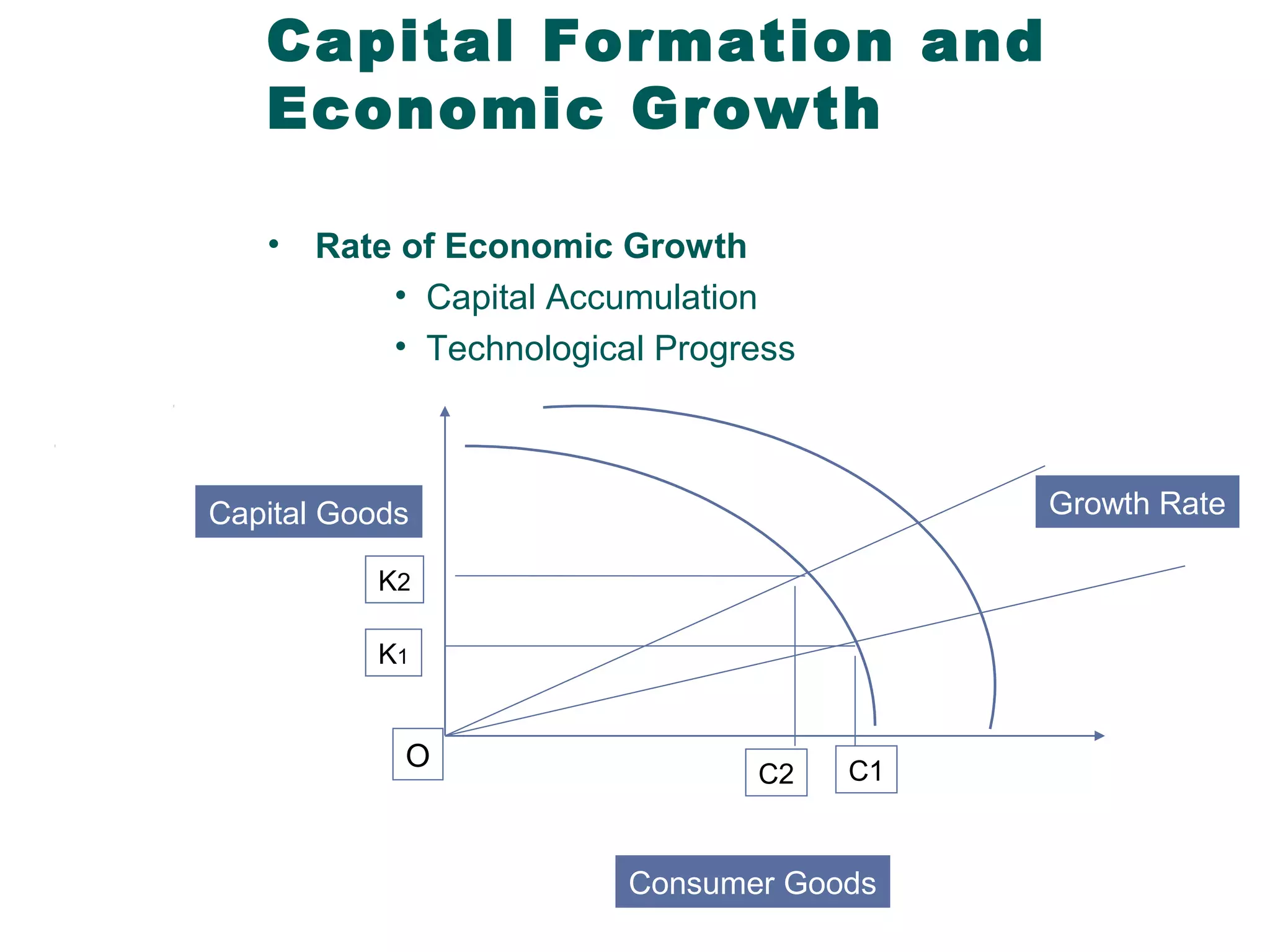
Managerial economics is the study of how people and societies choose to employ scarce resources to produce goods and services over time and how to distribute them for consumption. It involves analyzing operational/internal issues like production, costs, and pricing using microeconomics and environmental/external issues like the economy, policies, and markets using macroeconomics. The key questions addressed are what and how to produce and for whom, from both a country and company perspective. Resources are scarce so there is a need to allocate them efficiently, which involves opportunity costs and maintaining a balance shown by the production possibility curve. Economic growth requires capital accumulation and technological progress through investing in capital goods rather than immediate consumption.