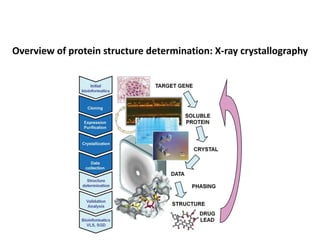
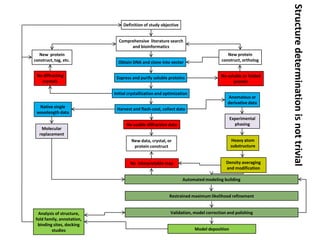
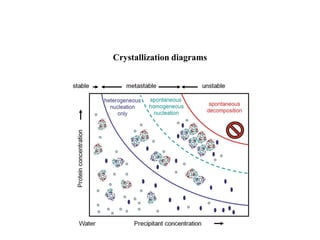
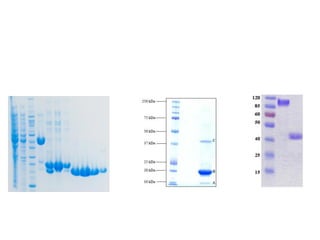
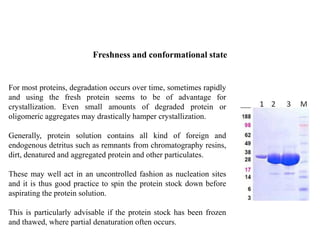
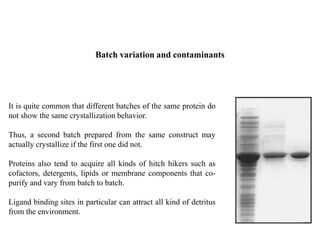
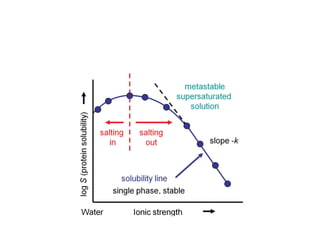
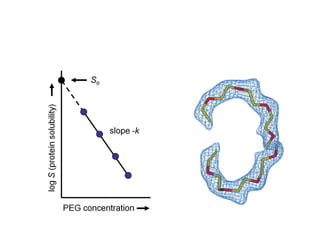
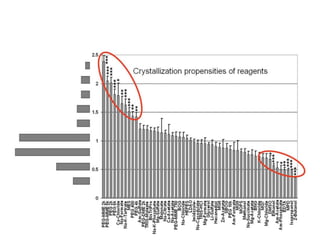
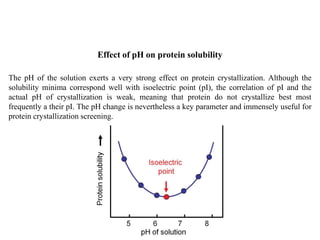
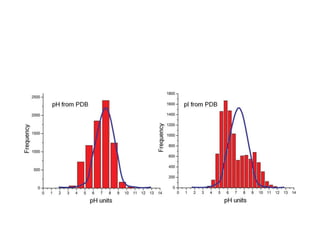
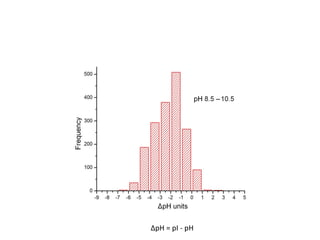
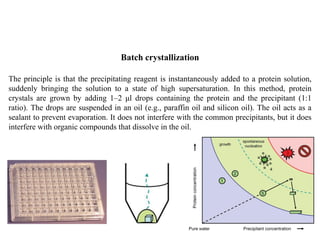
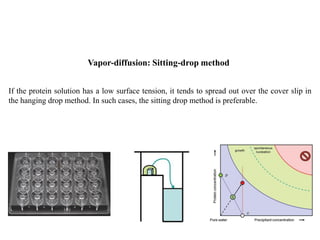
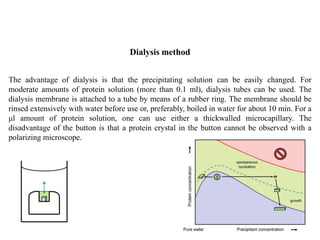
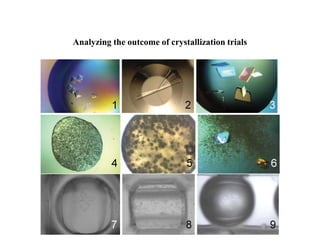
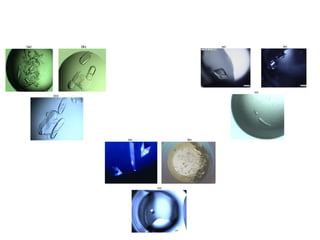
Crystallizing proteins involves obtaining pure protein, determining initial crystallization conditions through trials, and optimizing crystals for diffraction analysis. Key factors that affect crystallization include protein purity and concentration, pH, temperature, buffers, and precipitation techniques such as vapor diffusion. Lysozyme is commonly used to optimize crystallization methods due to its low cost and ease of obtaining crystals under various conditions including salts or polymers. The goal is to produce well-diffracting crystals to determine the 3D protein structure.