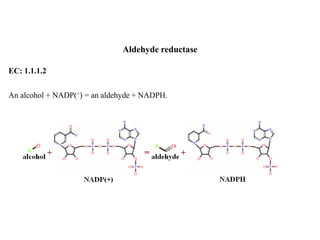
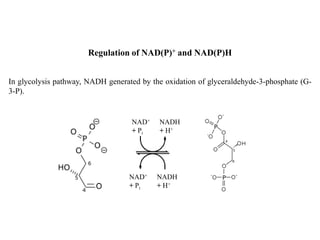
Dehydrogenases are oxidoreductase enzymes that catalyze the removal of hydrogen from substrates through oxidation-reduction reactions. They transfer hydrogen from substrates to acceptors like NAD+/NADP+ or flavin enzymes. There are several classes of dehydrogenases that act on different substrate groups like alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, etc. Alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the interconversion of alcohol and aldehyde with NAD+/NADH involved. It has important roles in metabolism and toxin removal in organisms. Excessive ethanol consumption can disrupt metabolic pathways and cause dangerous conditions due to changes in NADH and lactate levels.