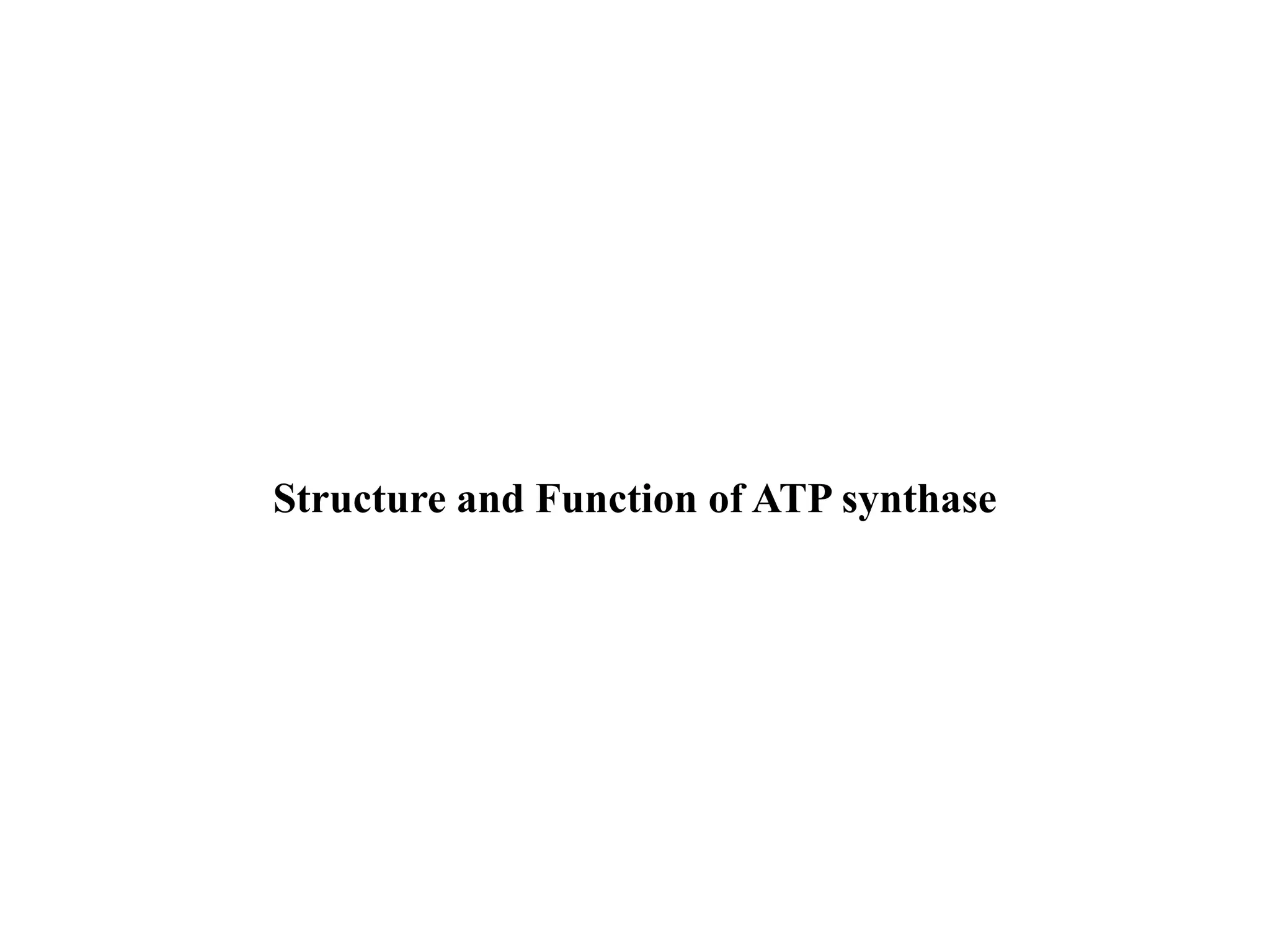
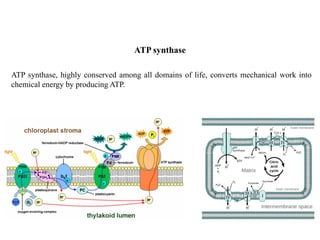
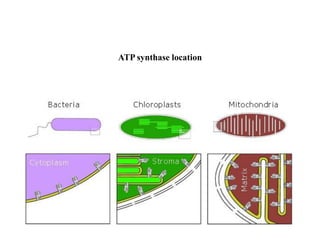
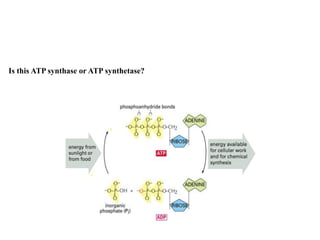
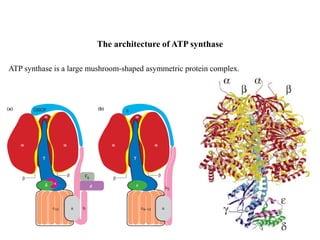
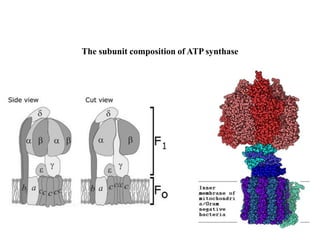
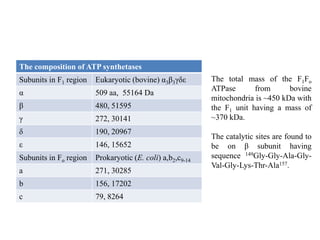
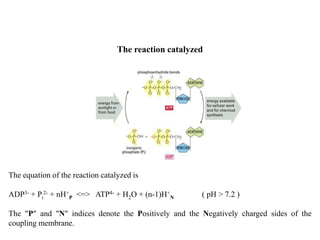
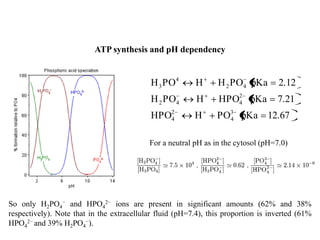
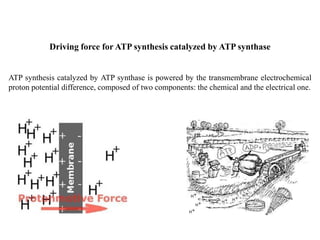
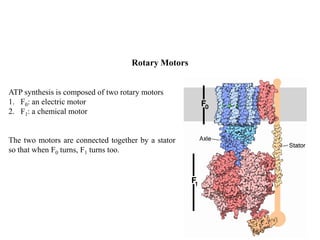
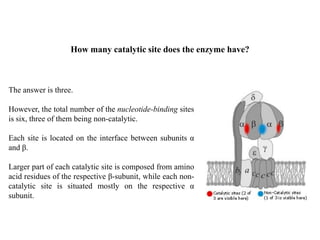
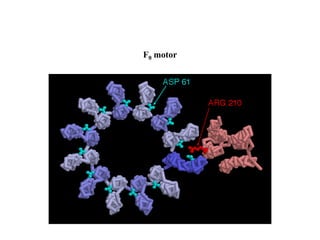
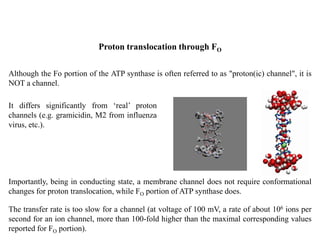
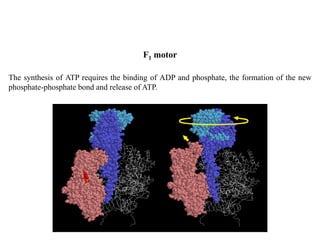
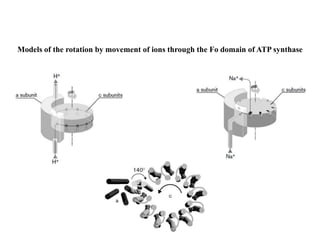
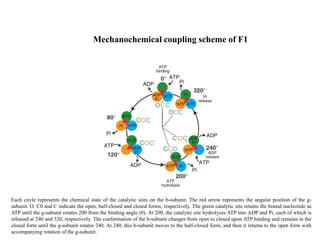
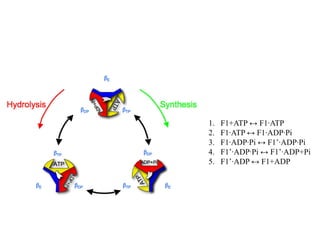
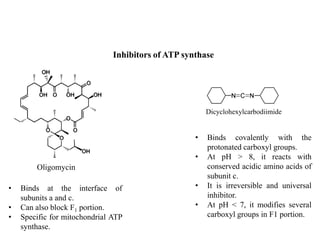
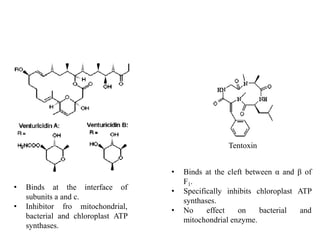
ATP synthase is an enzyme that generates ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate using energy from the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. It consists of two main parts - F0, which forms a channel for protons to pass through, and F1, which contains the catalytic sites to synthesize ATP. The passage of protons through F0 powers the rotation of F1, which facilitates the formation of ATP from ADP and phosphate at three catalytic binding sites. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase couples proton translocation across the membrane to ATP synthesis, and is essential for energy production in cells.