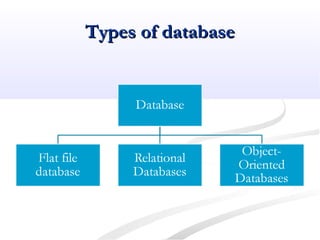
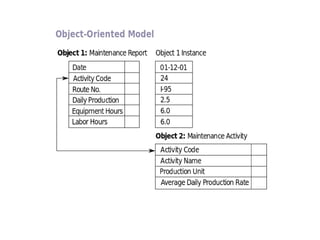
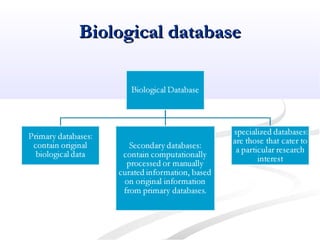
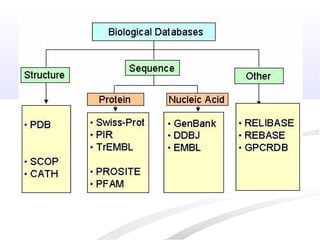
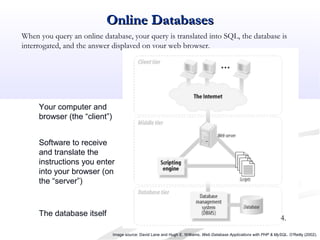
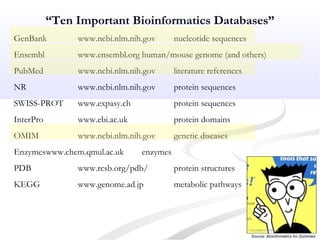
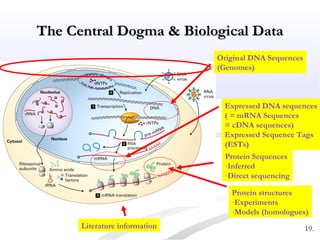
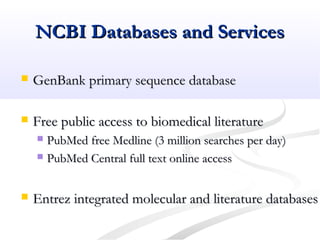
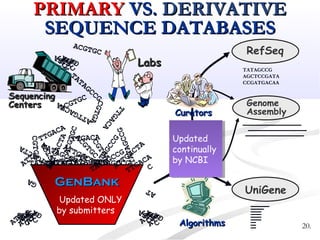
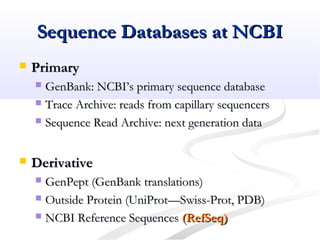
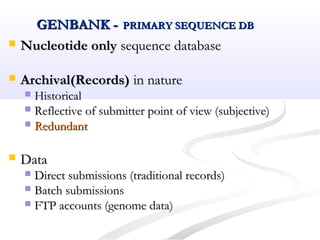
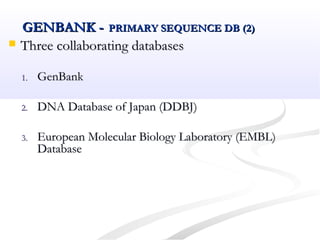
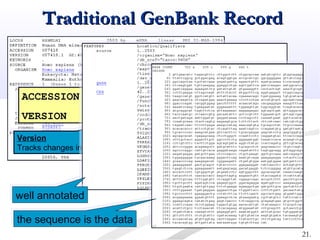
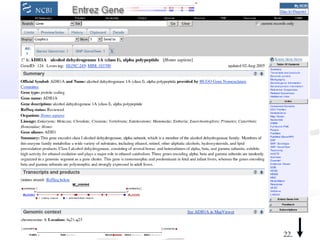
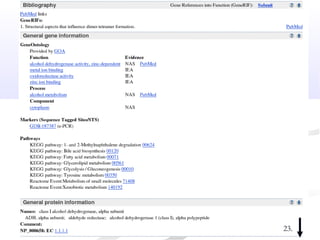
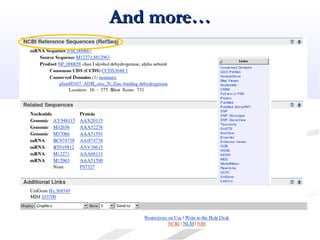
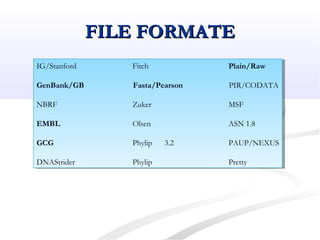
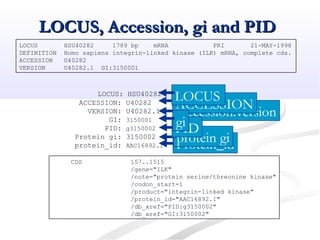
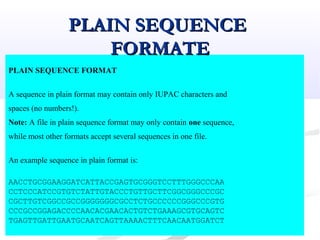
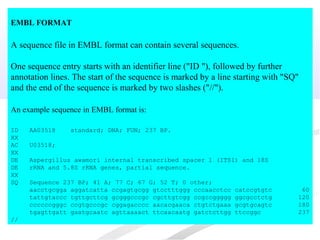
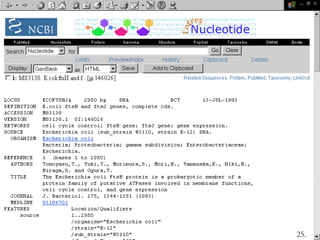
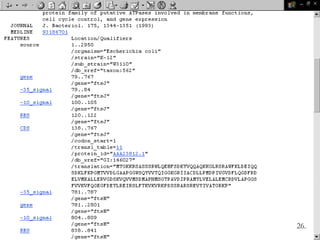
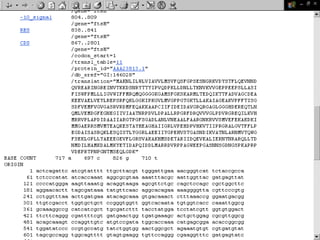
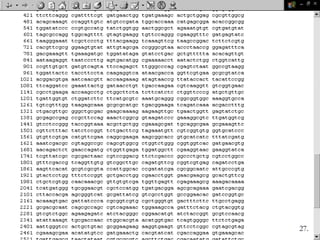
Biological databases are collections of experimental and theoretical biological data that are organized so their contents can be easily accessed, managed, updated, and retrieved. The activity of preparing a database can be divided into collecting data in an accessible form and making it available to a multi-user system. Two important biological databases are GenBank, which contains publicly available nucleotide and protein sequences, and the Protein Data Bank, which houses 3D structures of proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates.