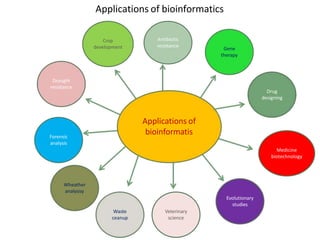
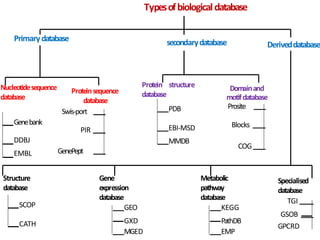
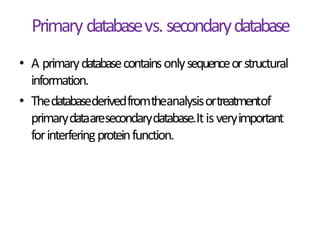
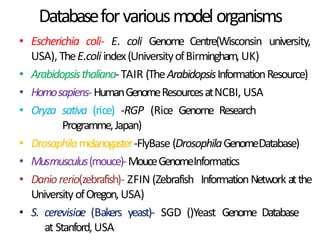
This document provides an introduction to bioinformatics and biological databases. It defines bioinformatics as the use of computers to analyze biological data like DNA sequences. The aims of bioinformatics include developing databases of all biological information and software for tasks like drug design. Biological databases store complex biological data and can be primary databases containing raw sequences/structures or secondary databases containing derived data. Examples of primary databases include GenBank, EMBL, Swiss-Prot and PDB, while secondary databases include motif, domain, gene expression and metabolic pathway databases. Maintaining accurate, up-to-date biological databases is important for biological research and applications.