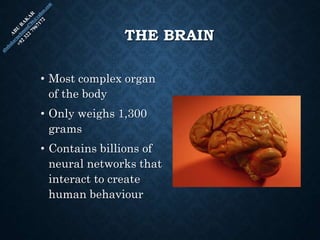
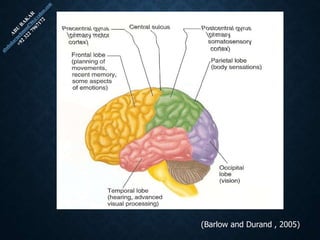
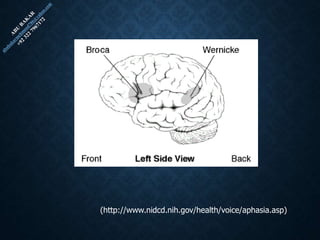
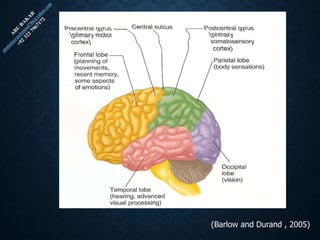
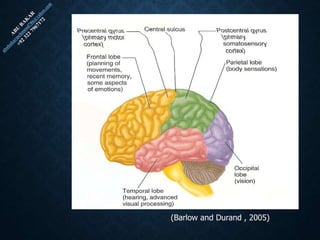
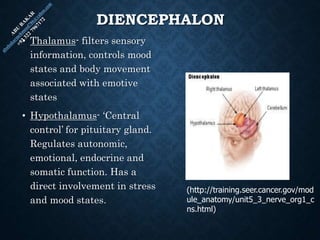
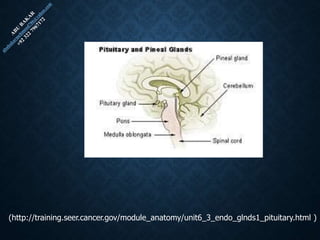
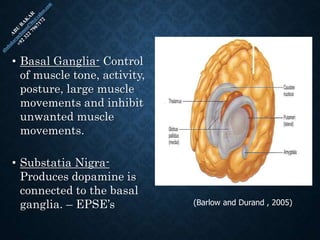
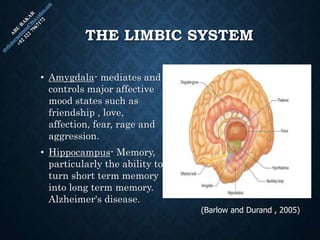
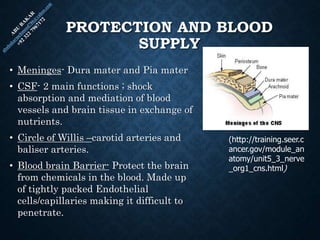
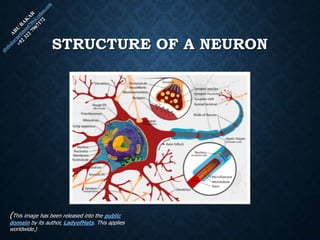
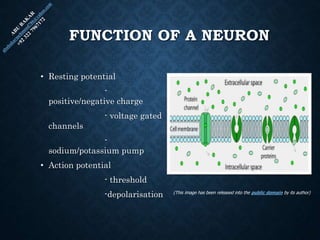
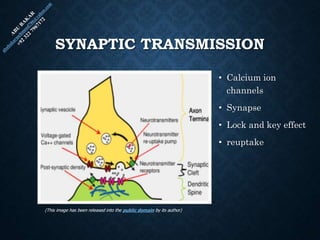
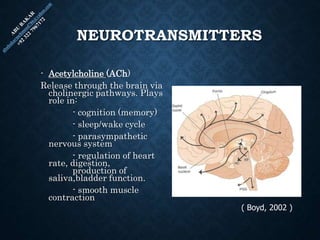
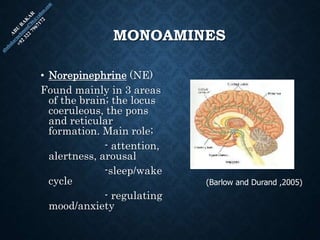
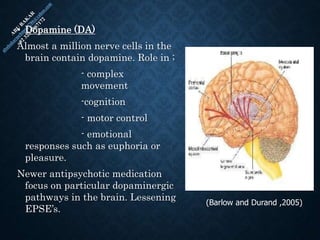
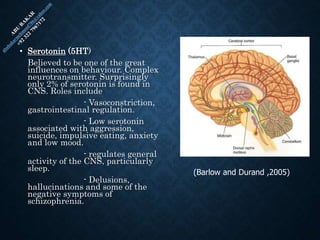
The document provides an overview of brain structure and function, detailing the roles of different lobes and areas such as the forebrain, hindbrain, and limbic system. It discusses various aspects of neurons, synaptic transmission, and neurotransmitters, highlighting their importance in cognition, mood regulation, and behavior. Additionally, it mentions protective mechanisms and blood supply to the brain, relevant anatomy, and neurotransmitter functions associated with mental health.