This document provides an overview of basic neuroanatomy, including:
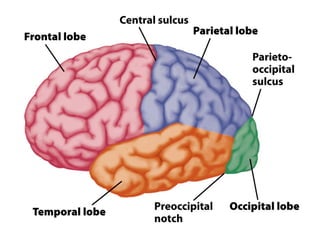
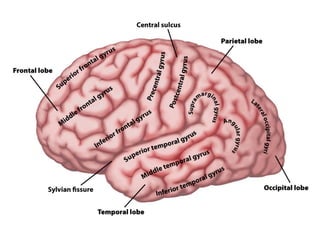
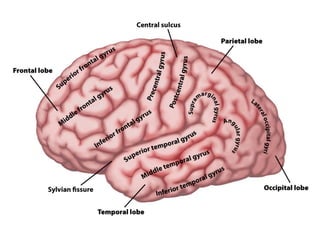
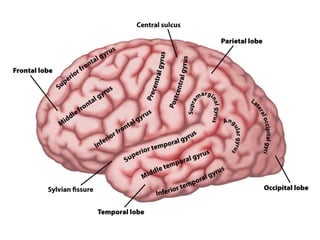
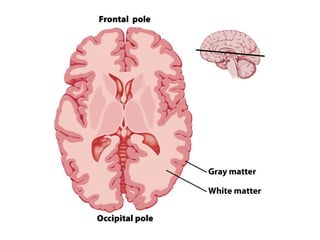
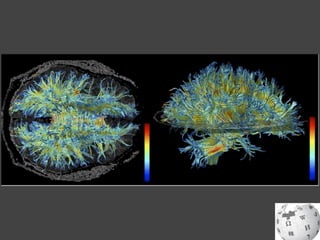
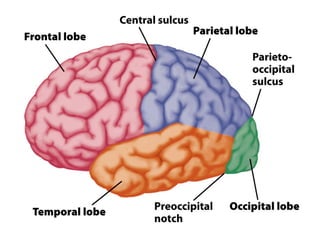
- Gross anatomy sections on gyri, sulci, fissures, grey and white matter, and fiber tracts.
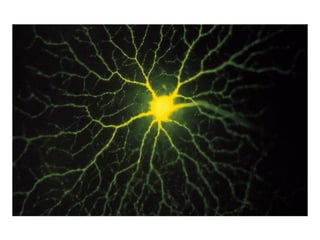
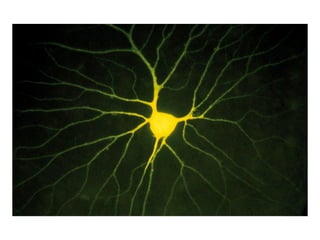
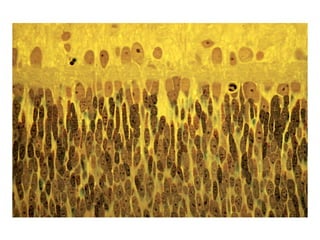
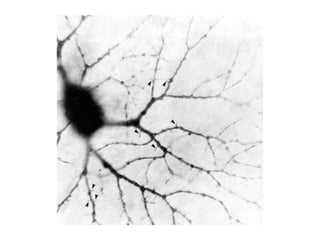
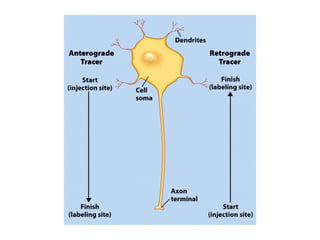
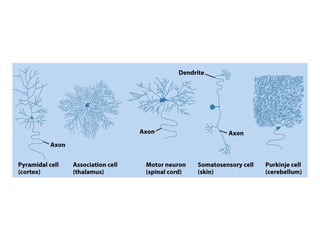
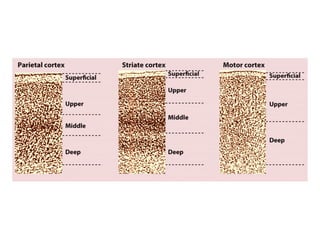
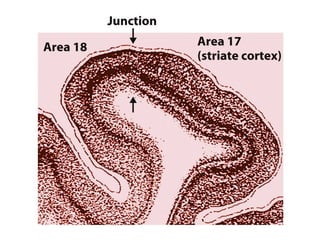
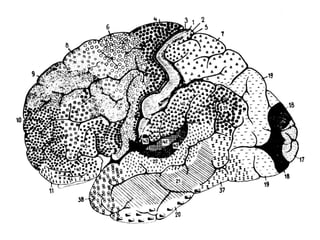
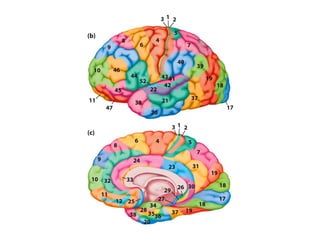
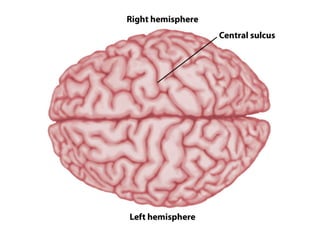
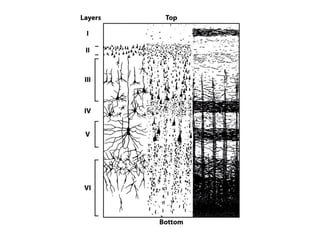
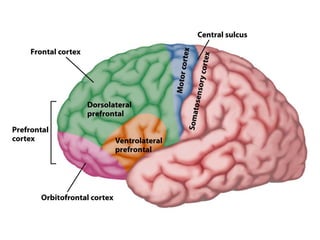
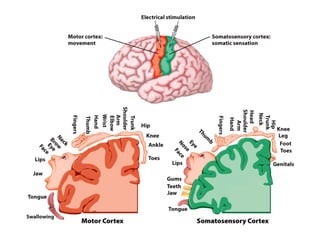
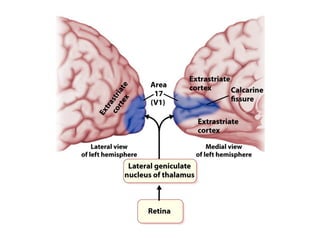
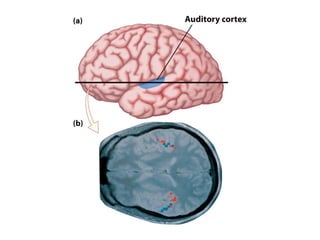
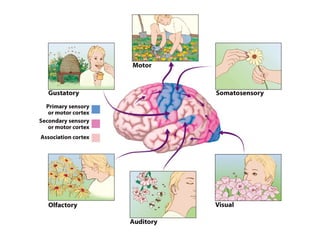
- Descriptions of the cerebral cortex as the outer wrinkled surface, with neocortex as the outer layer and cortical layers and functional divisions.
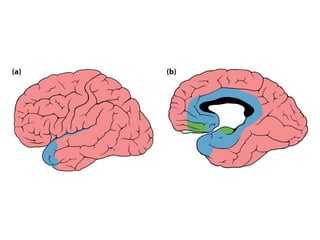
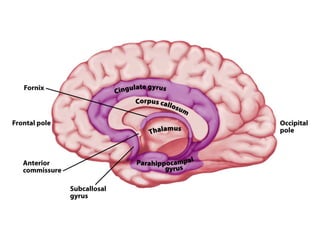
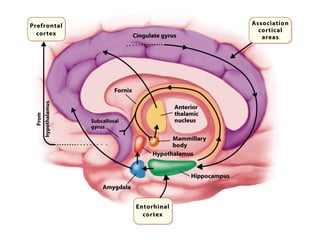
- The limbic system participates in emotion, learning, and memory, and includes structures like the cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, and amygdala.
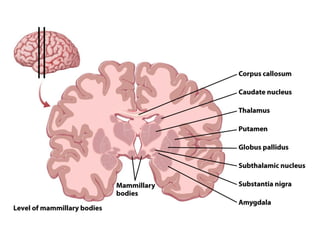
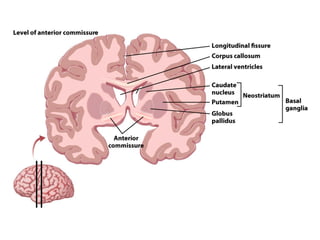
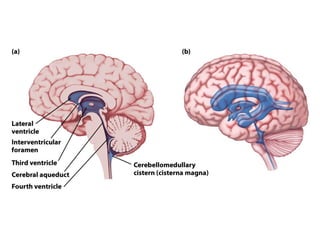
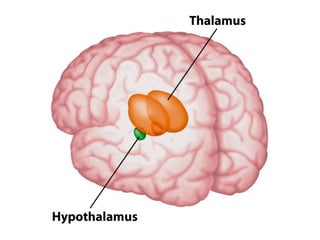
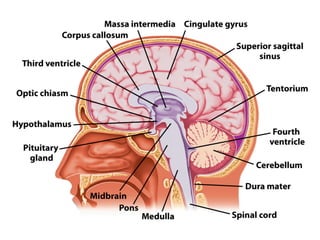
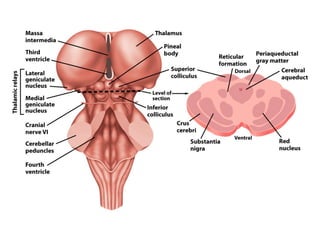
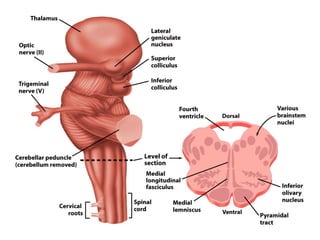
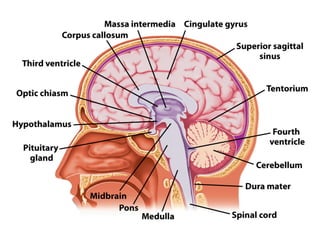
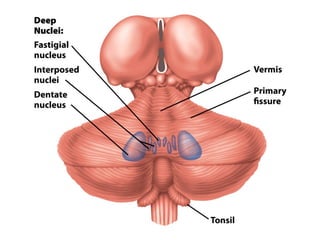
- Other areas discussed include the basal ganglia, ventricles, diencephalon, thalamus, hypothalamus, brainstem, midbrain, pons