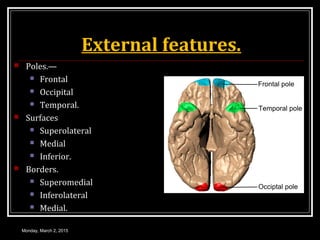
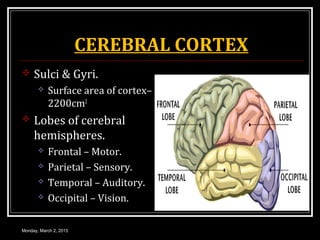
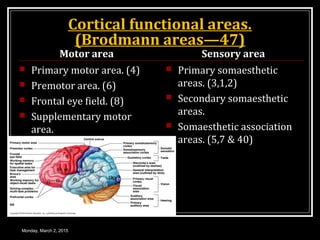
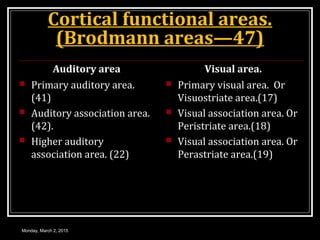
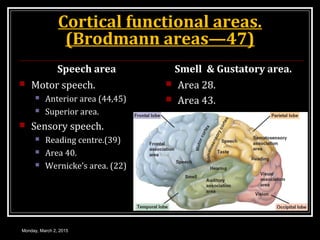
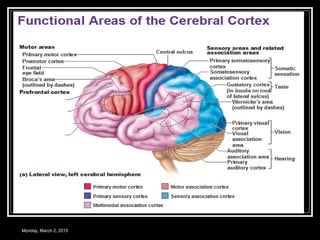
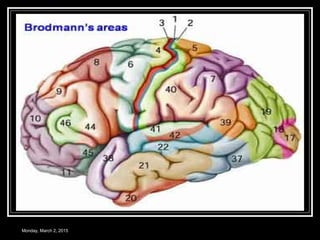
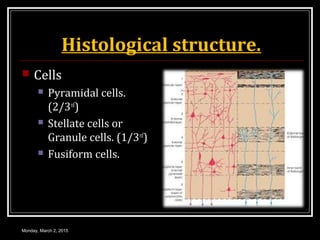
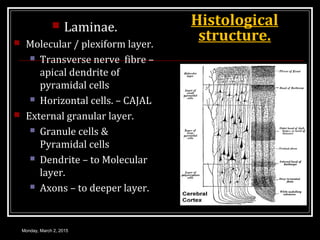
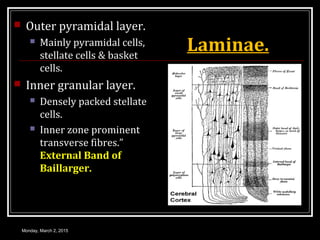
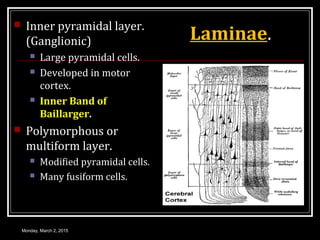
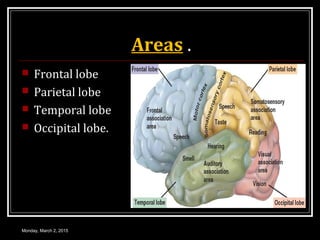
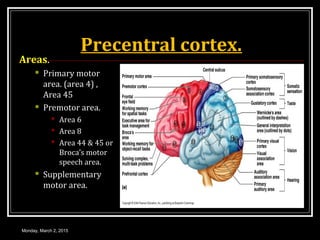
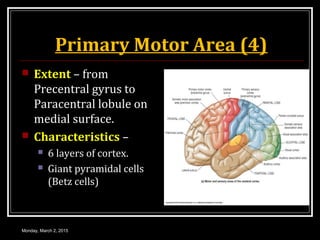
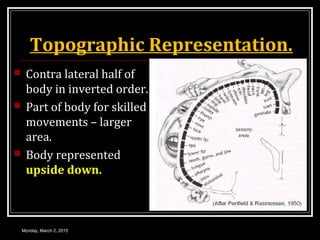
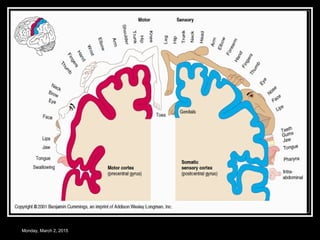
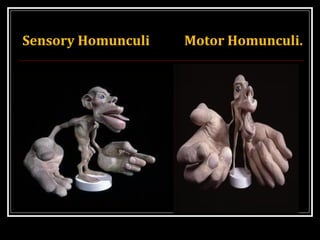
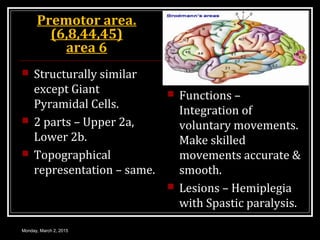
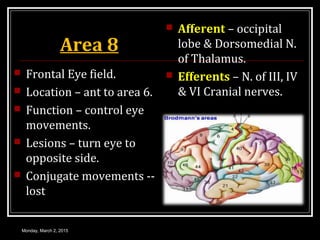
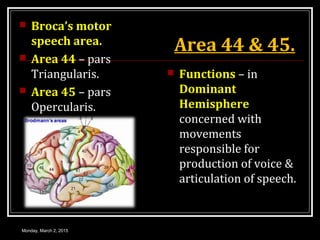
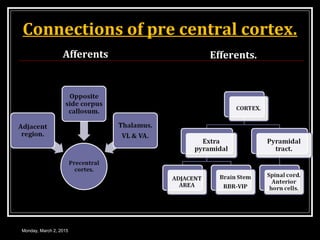
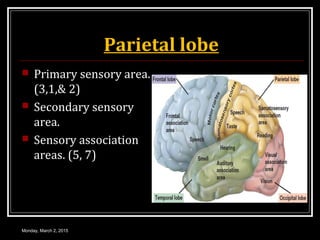
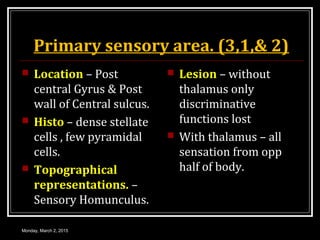
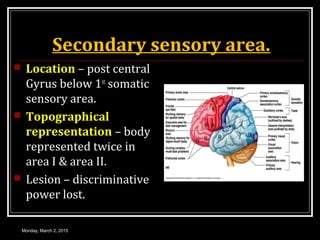
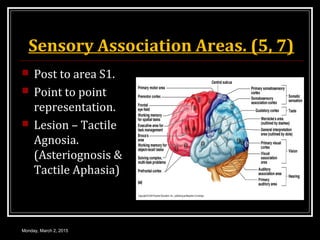
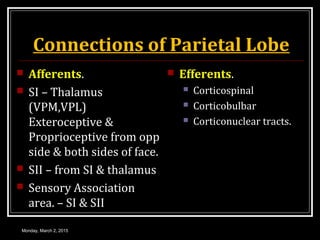
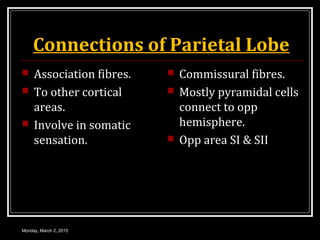
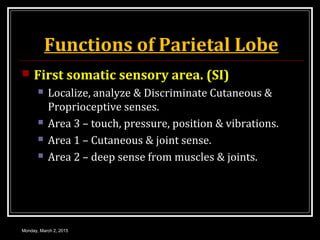
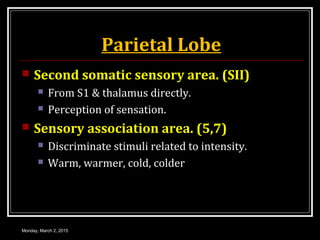
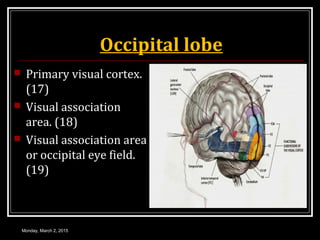
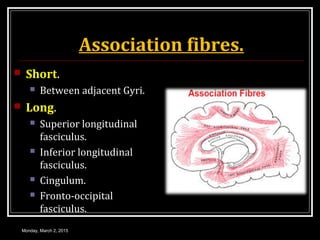
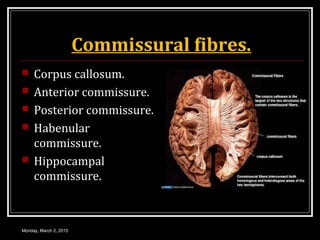
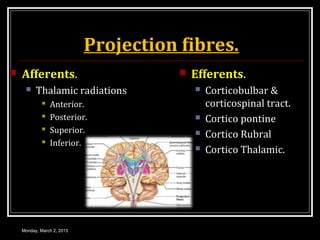
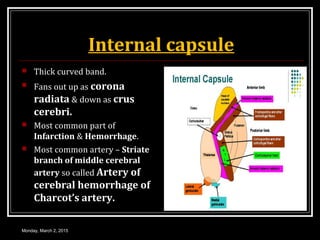
This document provides an overview of the cerebral cortex, including its external features, functional areas, lobes, connections, and histological structure. It discusses the different areas of the cortex such as the frontal lobe (including the precentral, premotor, and prefrontal cortex), parietal lobe (primary and secondary sensory areas), temporal lobe (primary auditory and association areas), occipital lobe, and their functions. It also covers applied aspects like frontal lobe syndrome and temporal lobe syndrome.