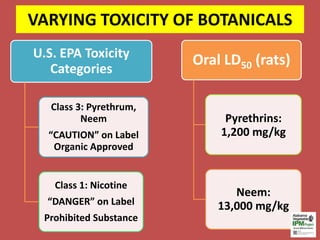
This document provides an overview of botanical insecticides for vegetable production, detailing their sources, applications, and effectiveness against target pests. Key insecticides discussed include pyrethrin, neem, rotenone, and sabadilla, each with specific usage guidelines and potential toxicity to non-target organisms. Recommendations for managing non-target effects include rotating products and careful application timing.













![• Insecticides for Organic Commercial and
Backyard Vegetable Production, ANR-
1428. [Online]
http://www.aces.edu/pubs/docs/A/ANR
-1428/ANR-1428.pdf
• Pest Management in High Tunnel Crop
Production, ANR-1432. [Online]
http://www.aces.edu/pubs/docs/A/ANR
-1432/ANR-1432.pdf
• Consult a Regional Extension Agent for
designing an optimal trap cropping
system with accurate pest insect
identification.
Additional Publications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/botanicalinsecticides2013-130619055724-phpapp01/85/Botanical-Insecticides-version-2013-15-320.jpg)

