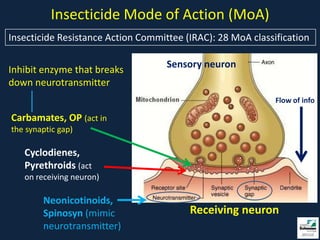
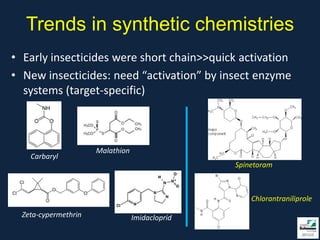
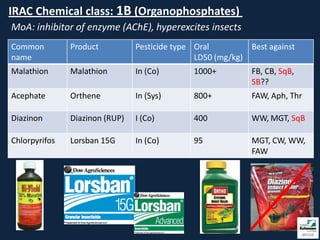
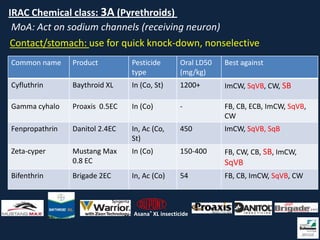
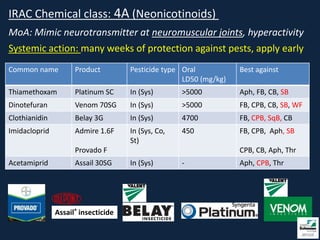
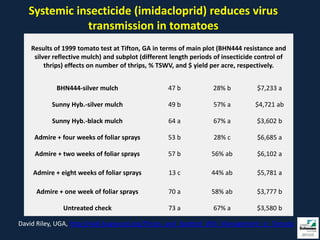
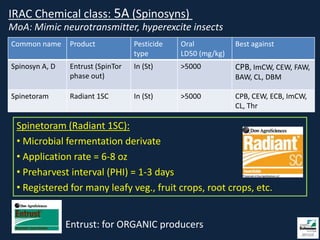
This document provides information on insect pests and their management in tomatoes and peppers. It discusses key pests such as aphids, thrips, flea beetles, Colorado potato beetle, stink bugs, caterpillars, and others. For each pest, it describes monitoring and scouting techniques, host plants, and economic thresholds. It also reviews various insecticide options organized by mode of action, including newer products and those approved for organic production. Overall, the document emphasizes integrated pest management approaches like cultural controls, resistant varieties, and judicious use of insecticides.