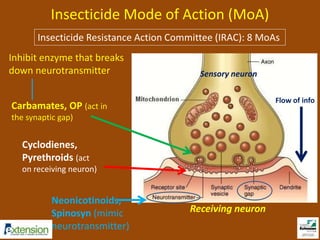
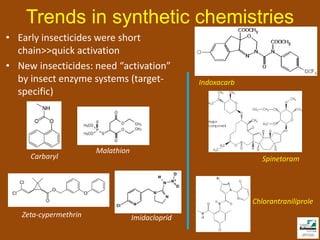
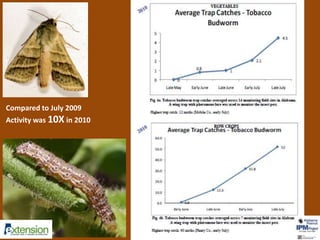
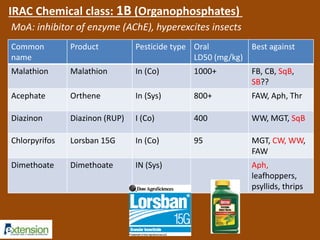
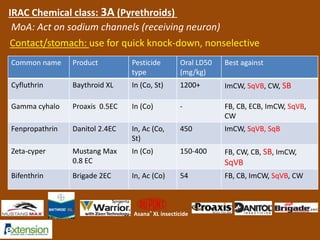
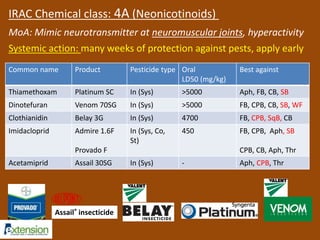
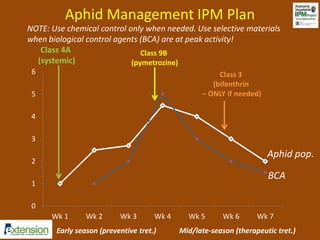
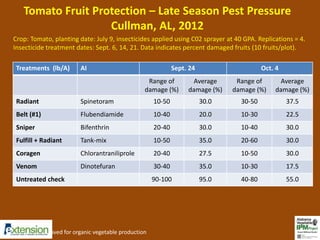
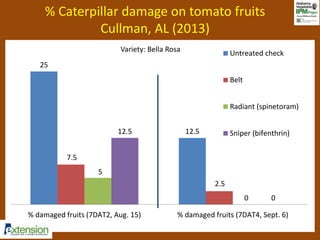
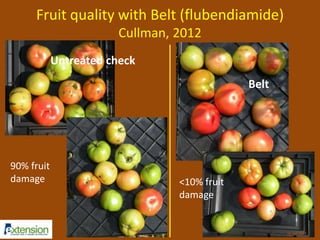
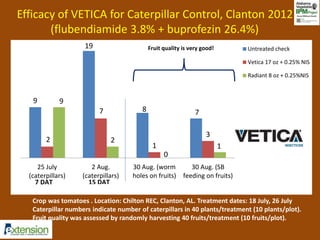
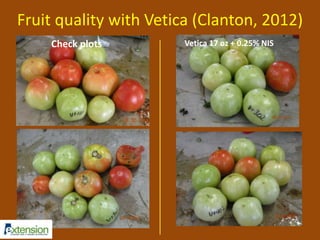
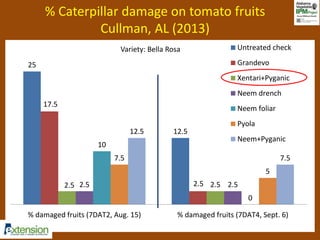
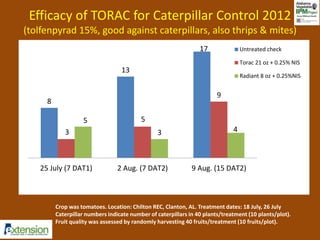
The document discusses integrated pest management (IPM) strategies and new insecticide options for managing pests in peanuts and vegetables. It highlights the importance of early detection, proper insecticide use to prevent resistance, and careful pest identification to enhance effectiveness. Additionally, it provides detailed insecticide recommendations and emphasizes the potential negative impacts of certain insecticides on beneficial species.