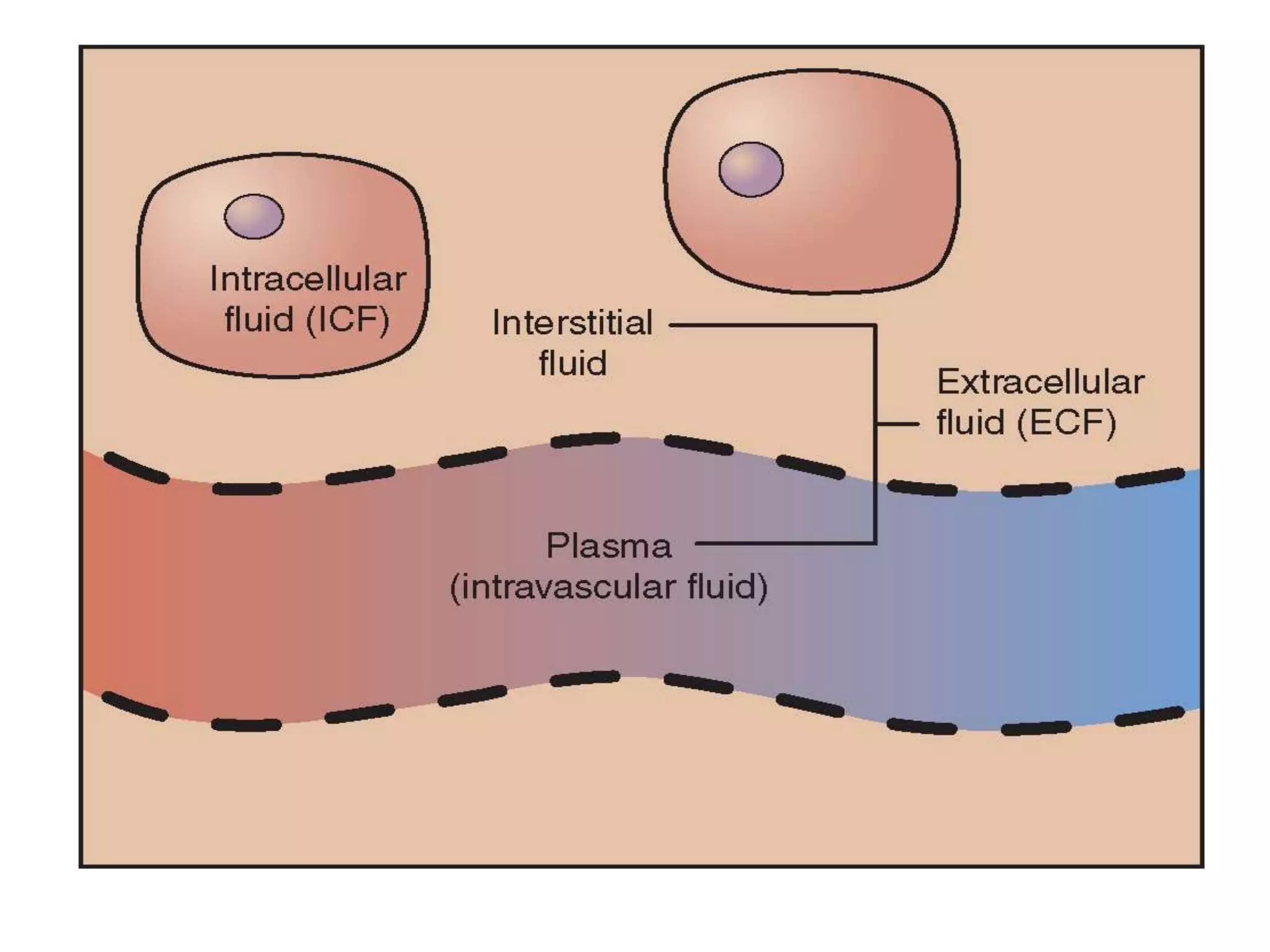
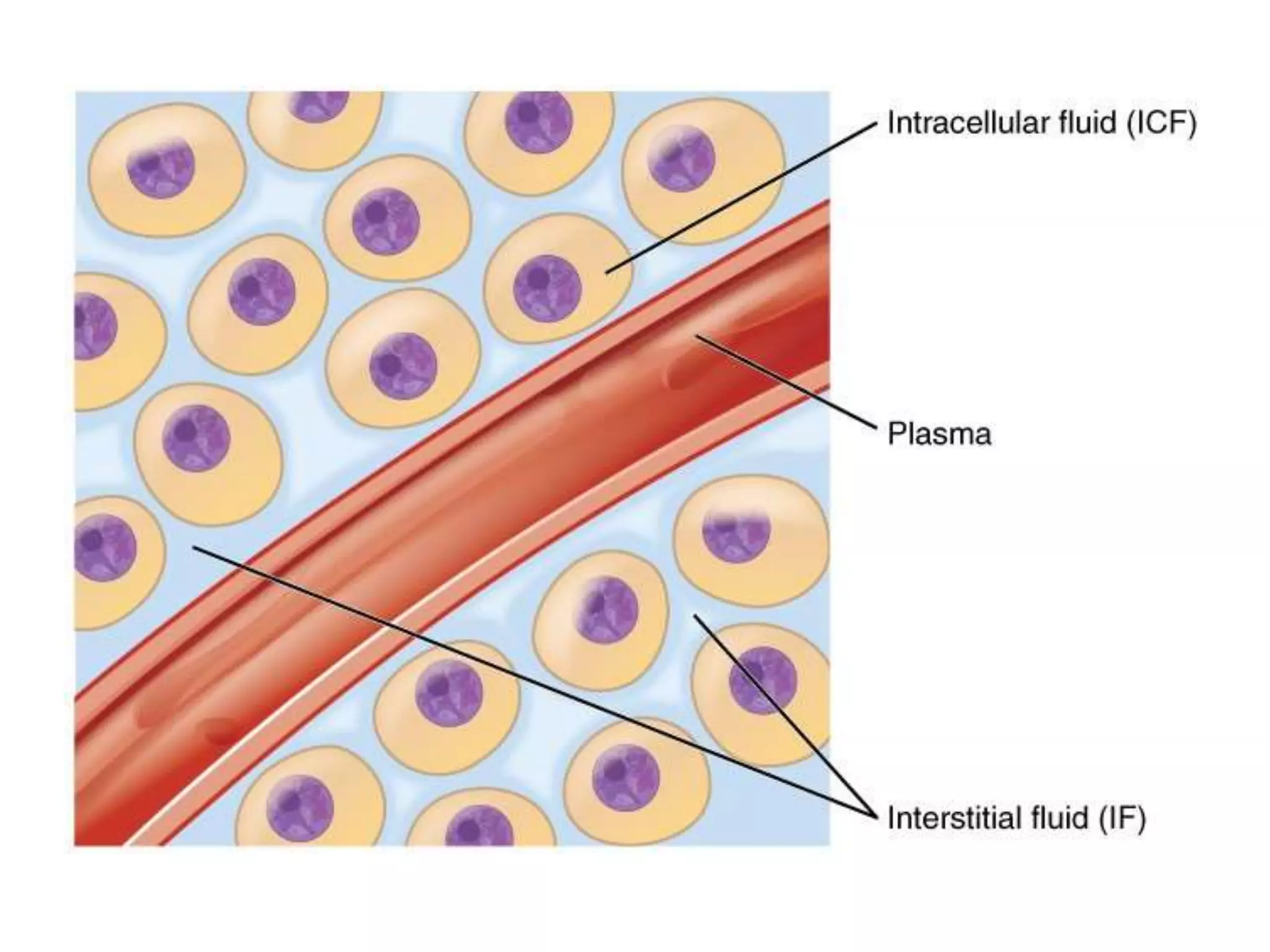
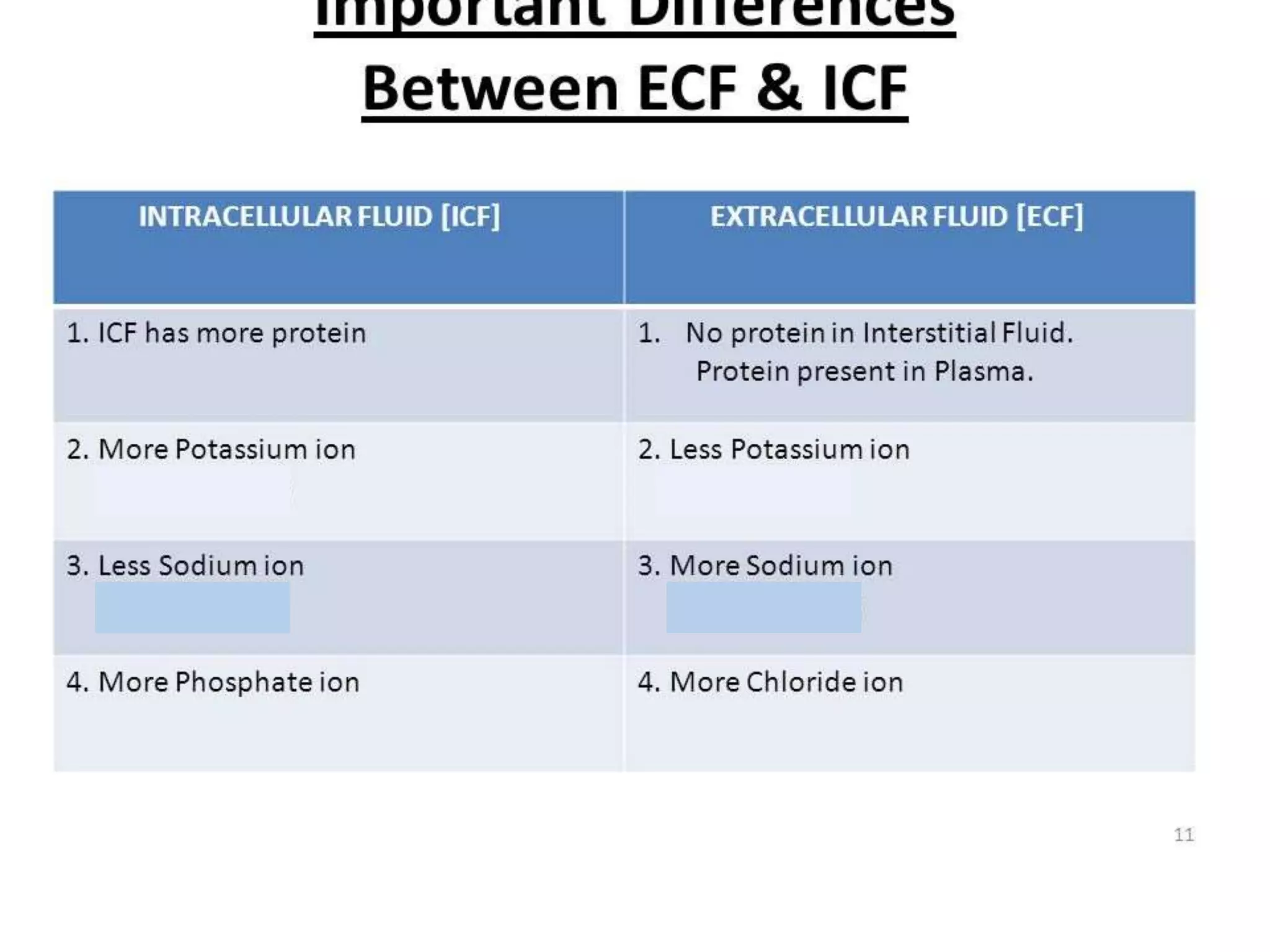
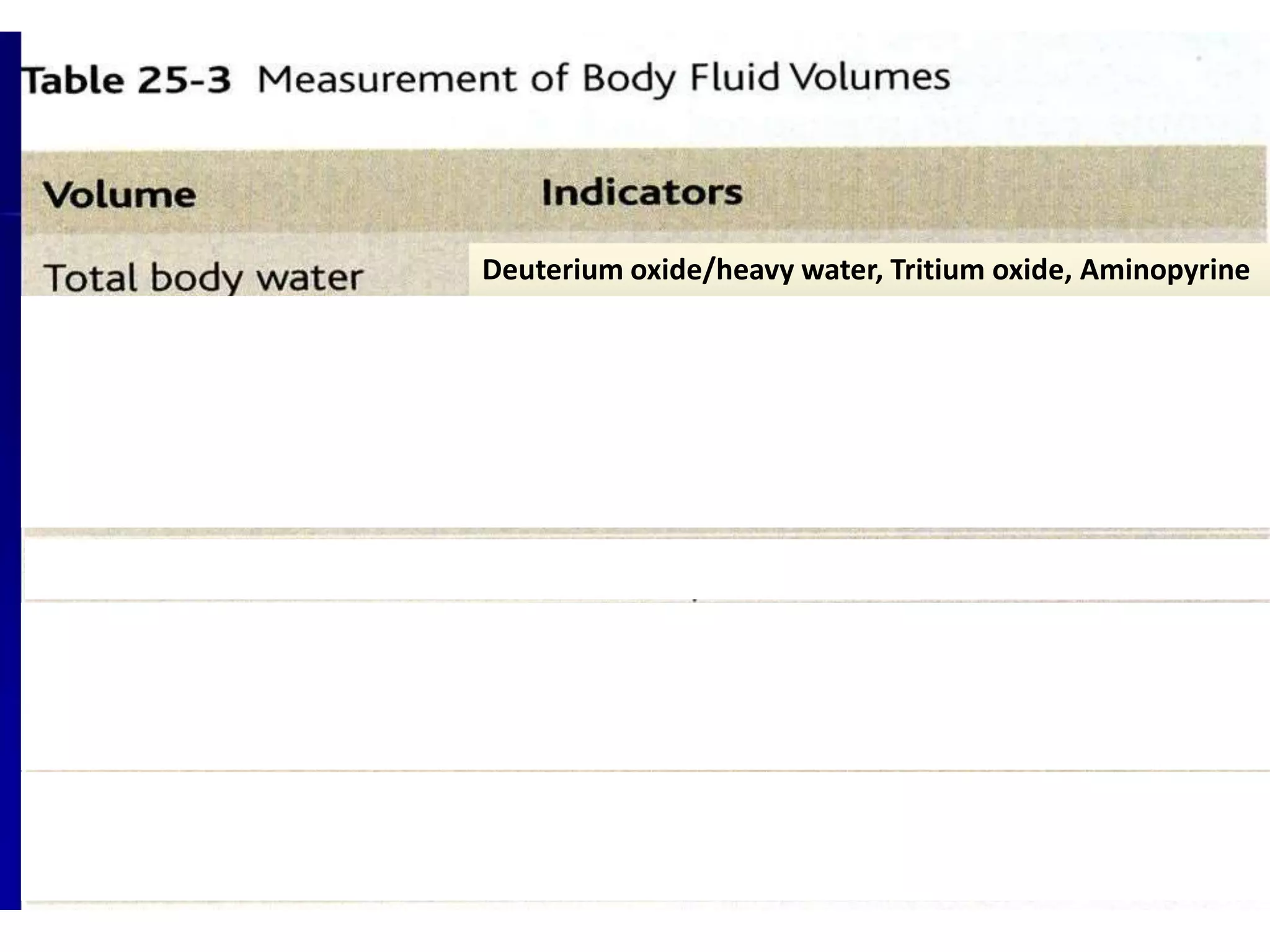
The human body is composed primarily of fluids, with water making up about two-thirds of the total body weight. The body's fluids are divided into two main compartments: intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF). ICF makes up about 40% of total body water and is contained within cells, while ECF comprises around 20% and includes interstitial fluid, plasma, and transcellular fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid. ECF volume can be measured using substances that remain in the extracellular space, while total body water and plasma volume are determined through the dilution of markers distributed throughout the body's water compartments. Proper fluid balance is essential for acid-base regulation, electrolyte levels