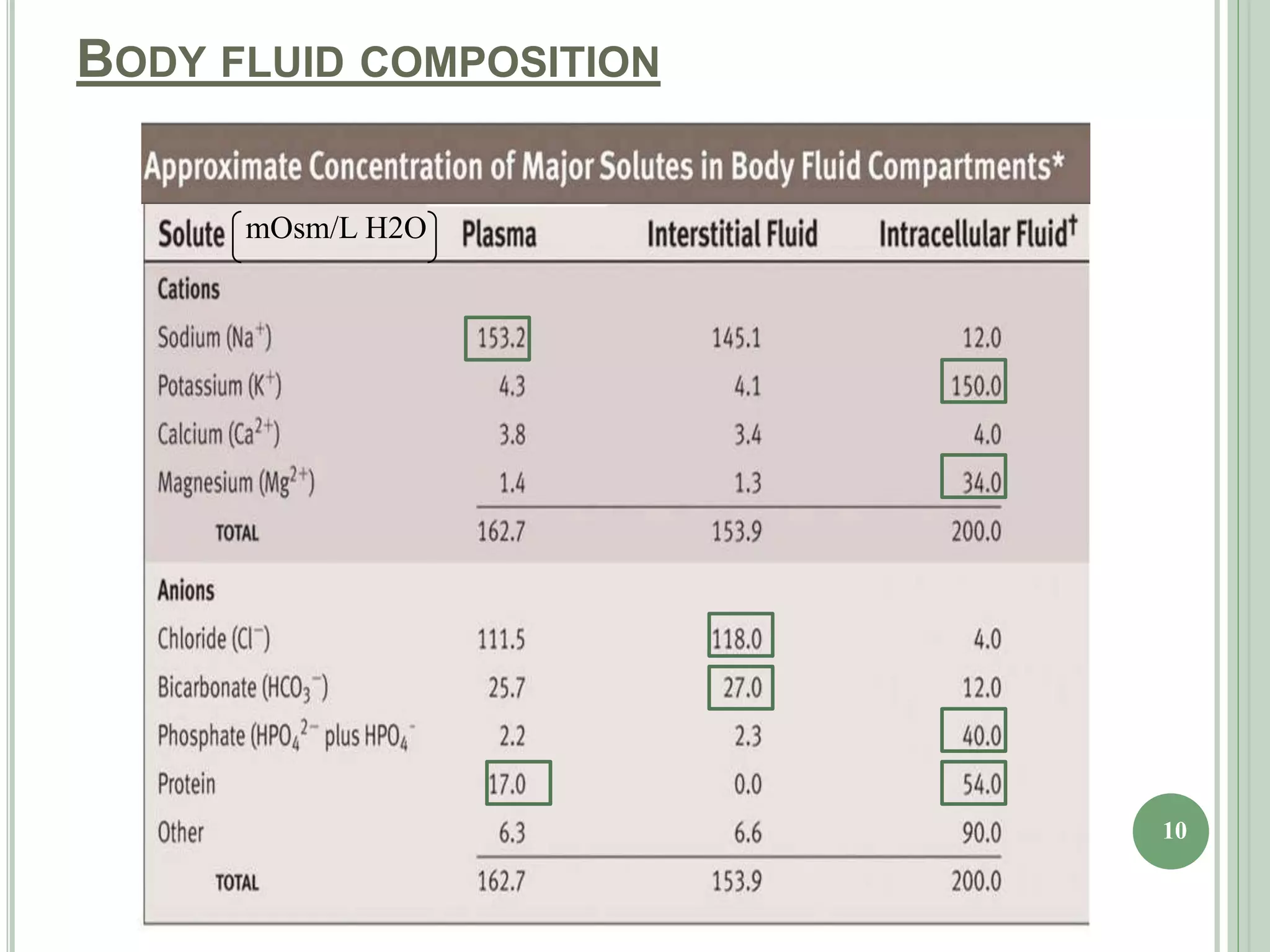
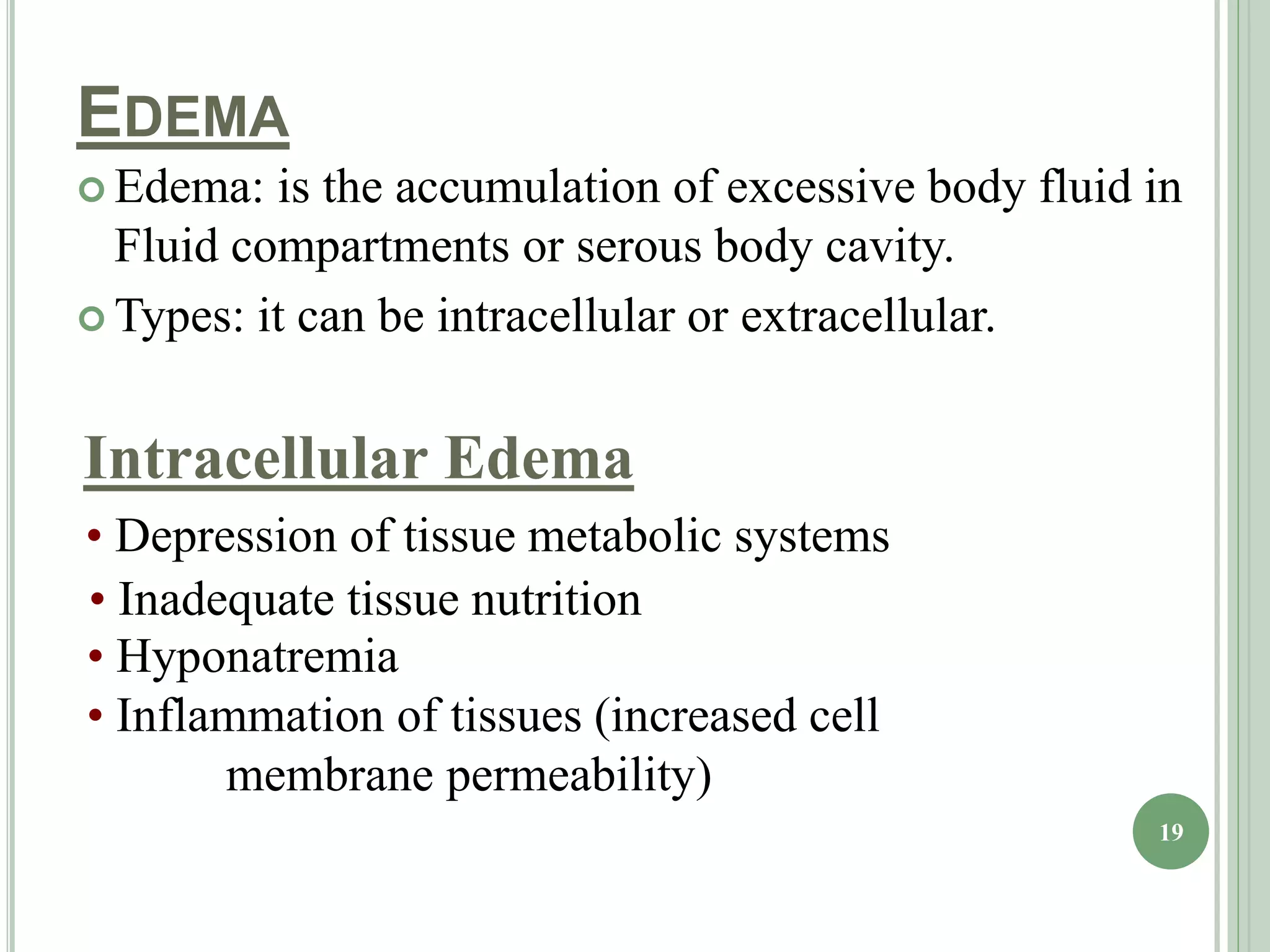
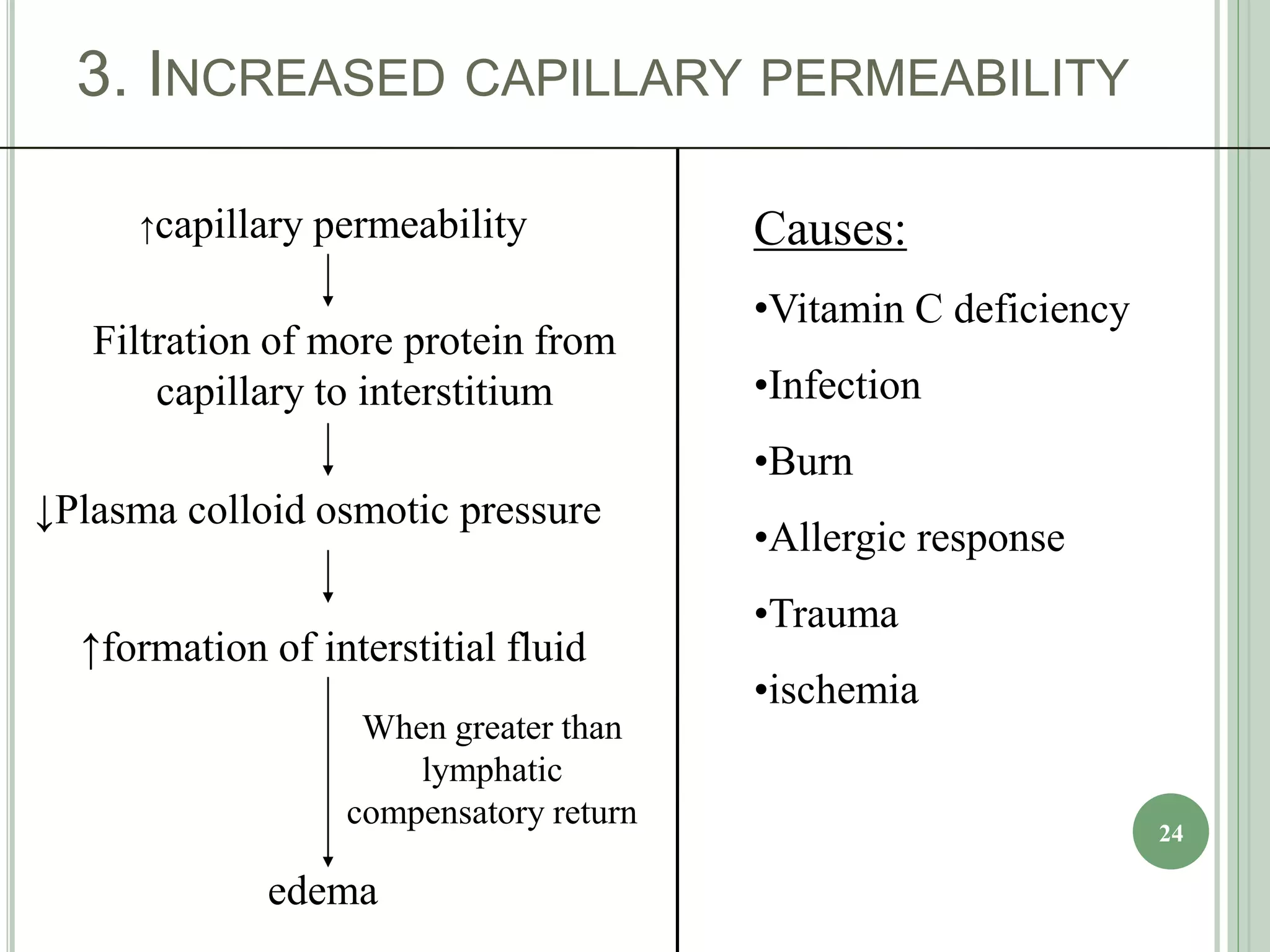
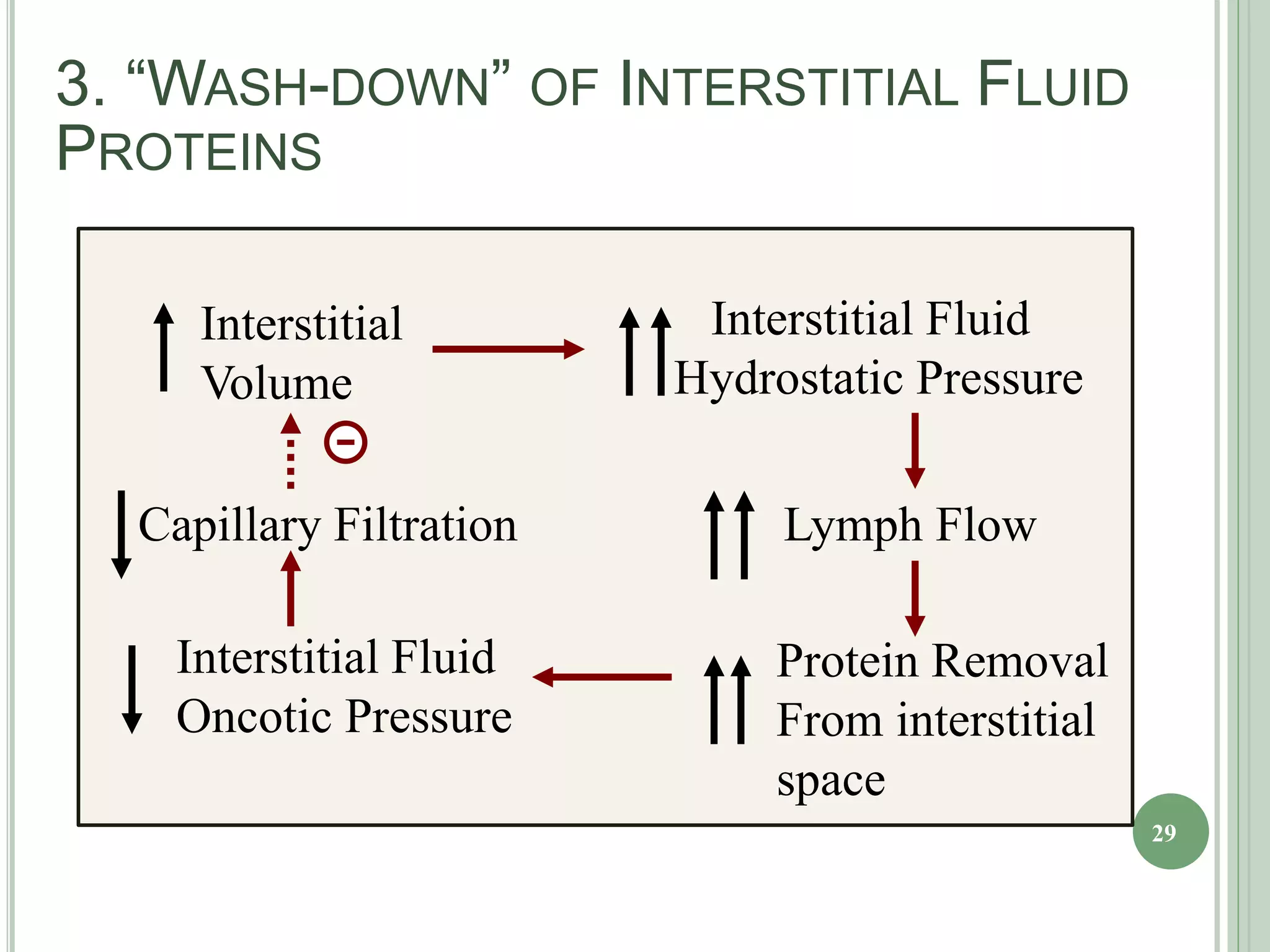
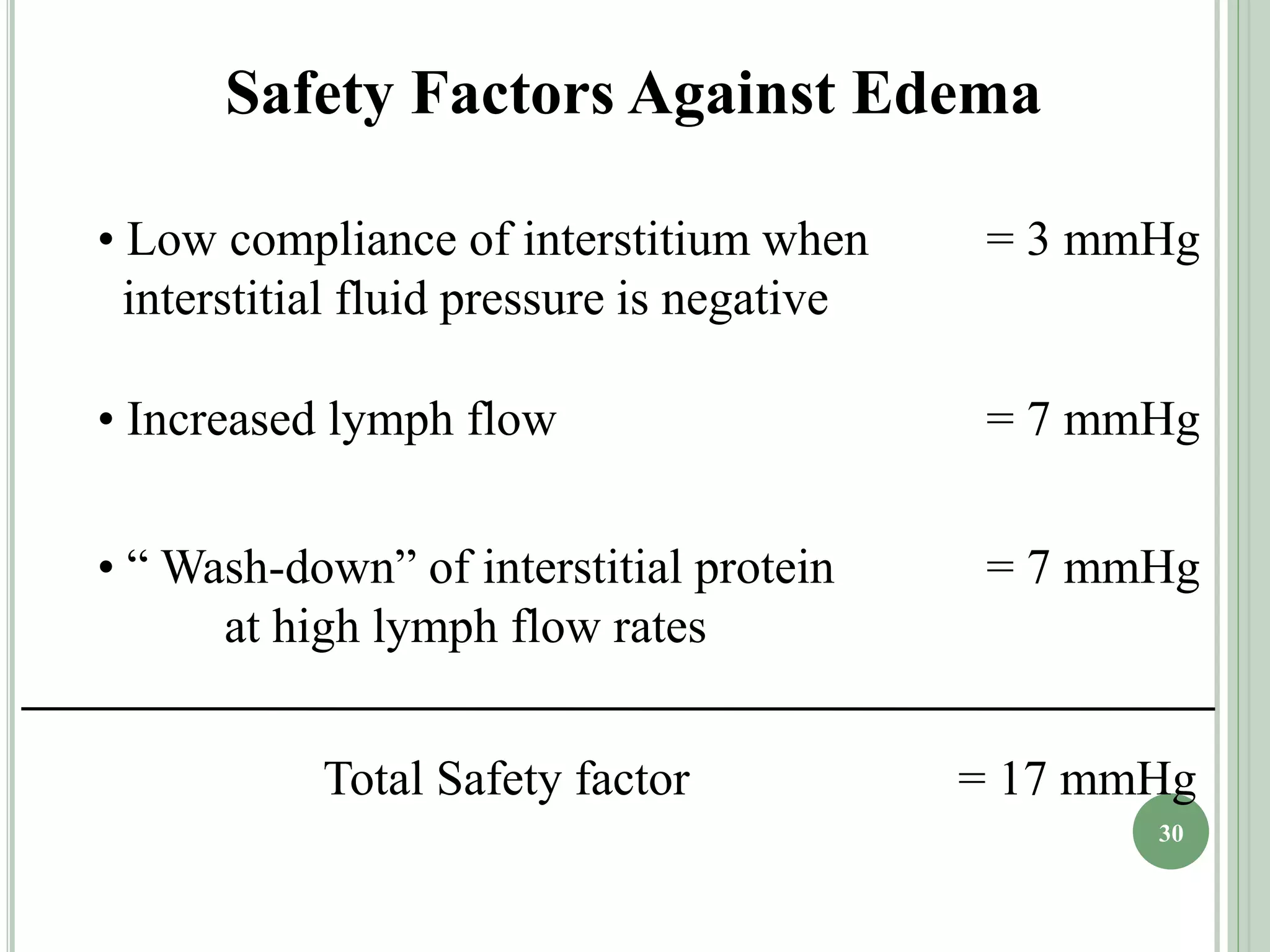
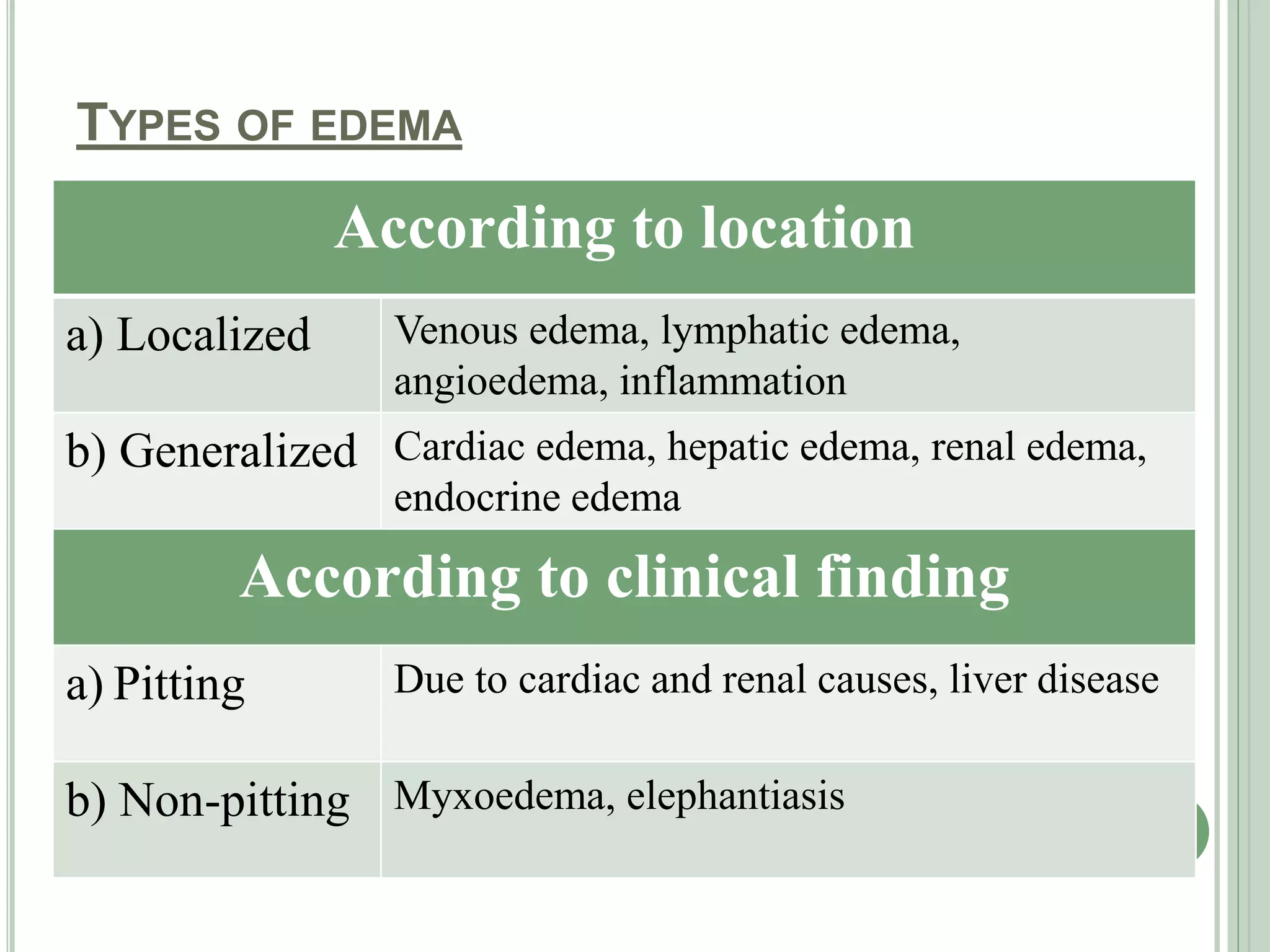
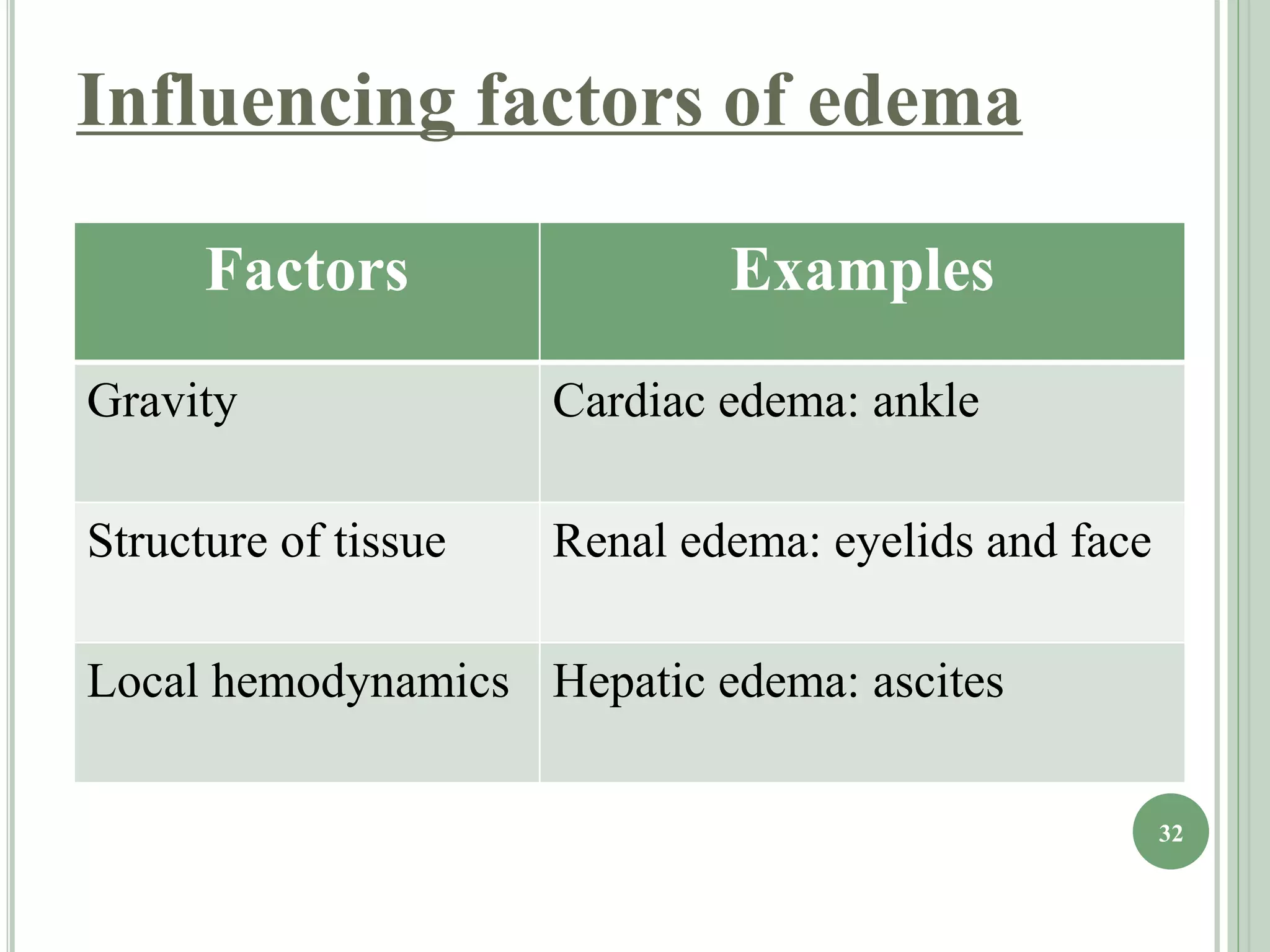
The document discusses body fluids, fluid compartments, and edema. It notes that total body water is about 60% of body weight in adult males and 55% in females. Fluid balance is maintained through daily intake and output of water. The extracellular fluid volume makes up about 1/3 of total body water and is divided between interstitial fluid and plasma. Edema occurs when there is fluid accumulation from increased capillary pressure, decreased plasma oncotic pressure, increased capillary permeability, or lymphatic obstruction. Safety factors prevent edema from low tissue compliance, increased lymph flow, and washdown of interstitial proteins. Types of edema are classified by location such as generalized or localized edema.