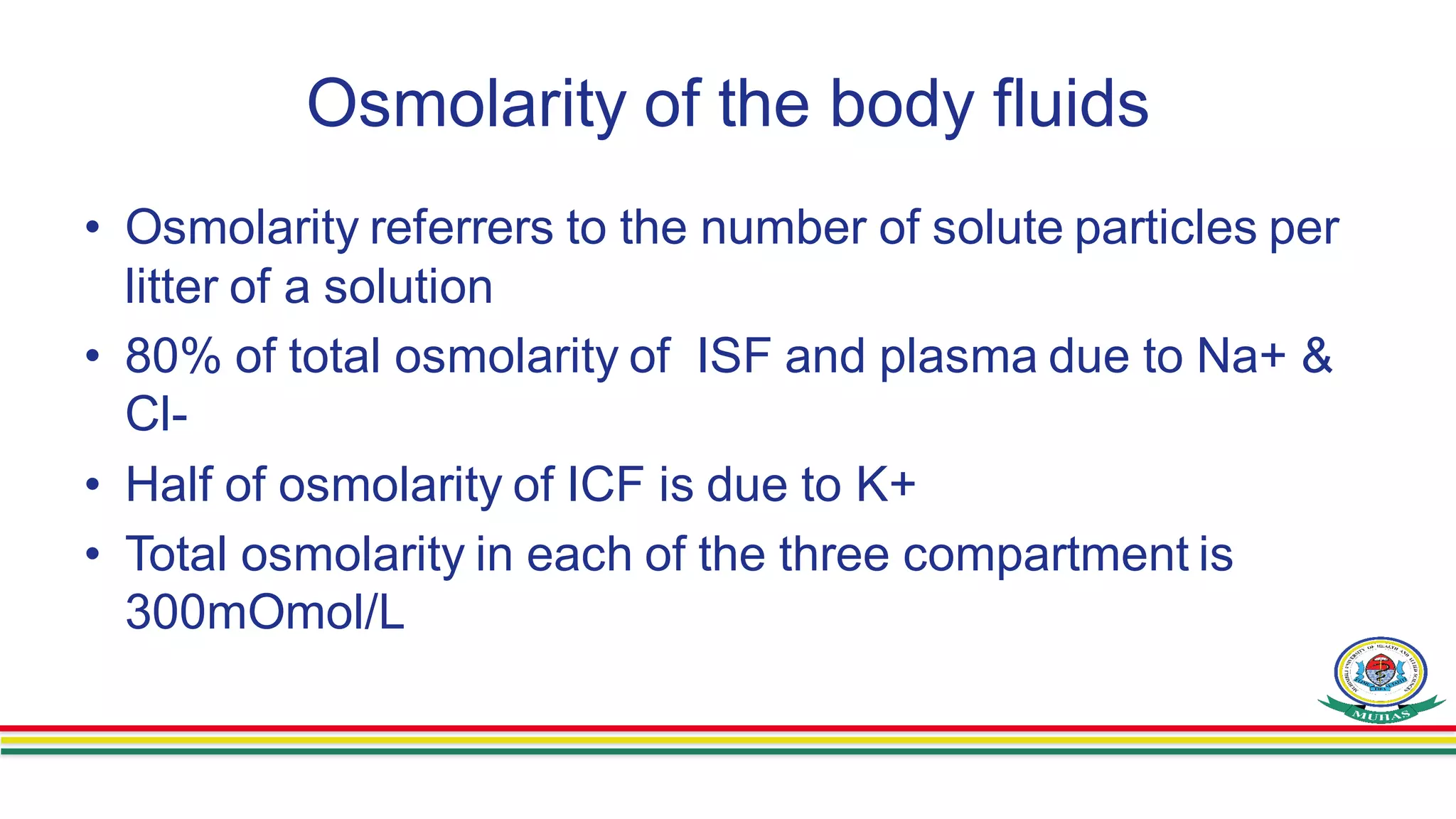
This document discusses body fluids and their composition and movement within the body. It covers the following key points:
- The body maintains fluid balance through intake of water and electrolytes and output through urine, sweat, and feces. Total daily water intake is around 2,500ml while output is also around 2,500ml.
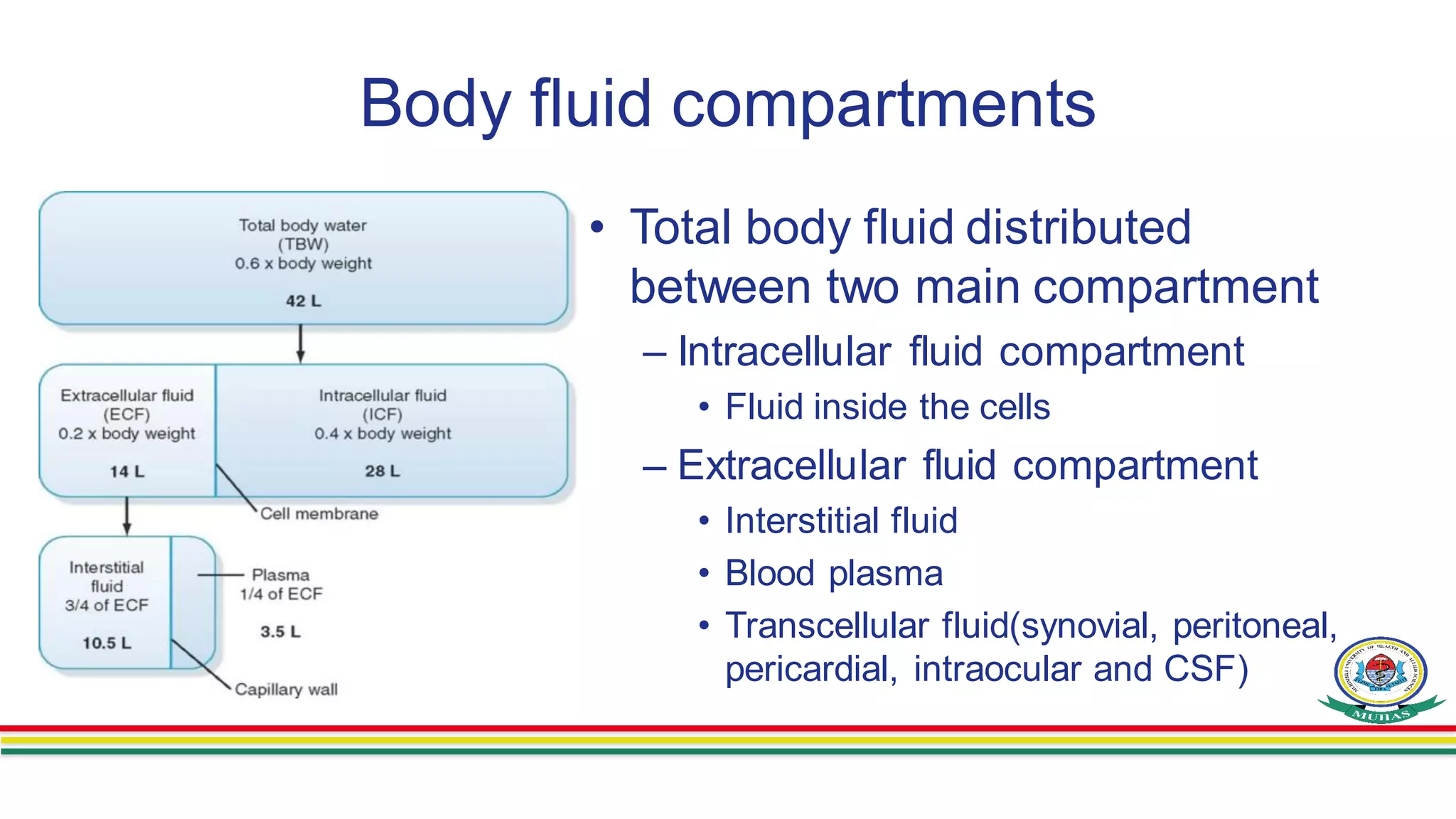
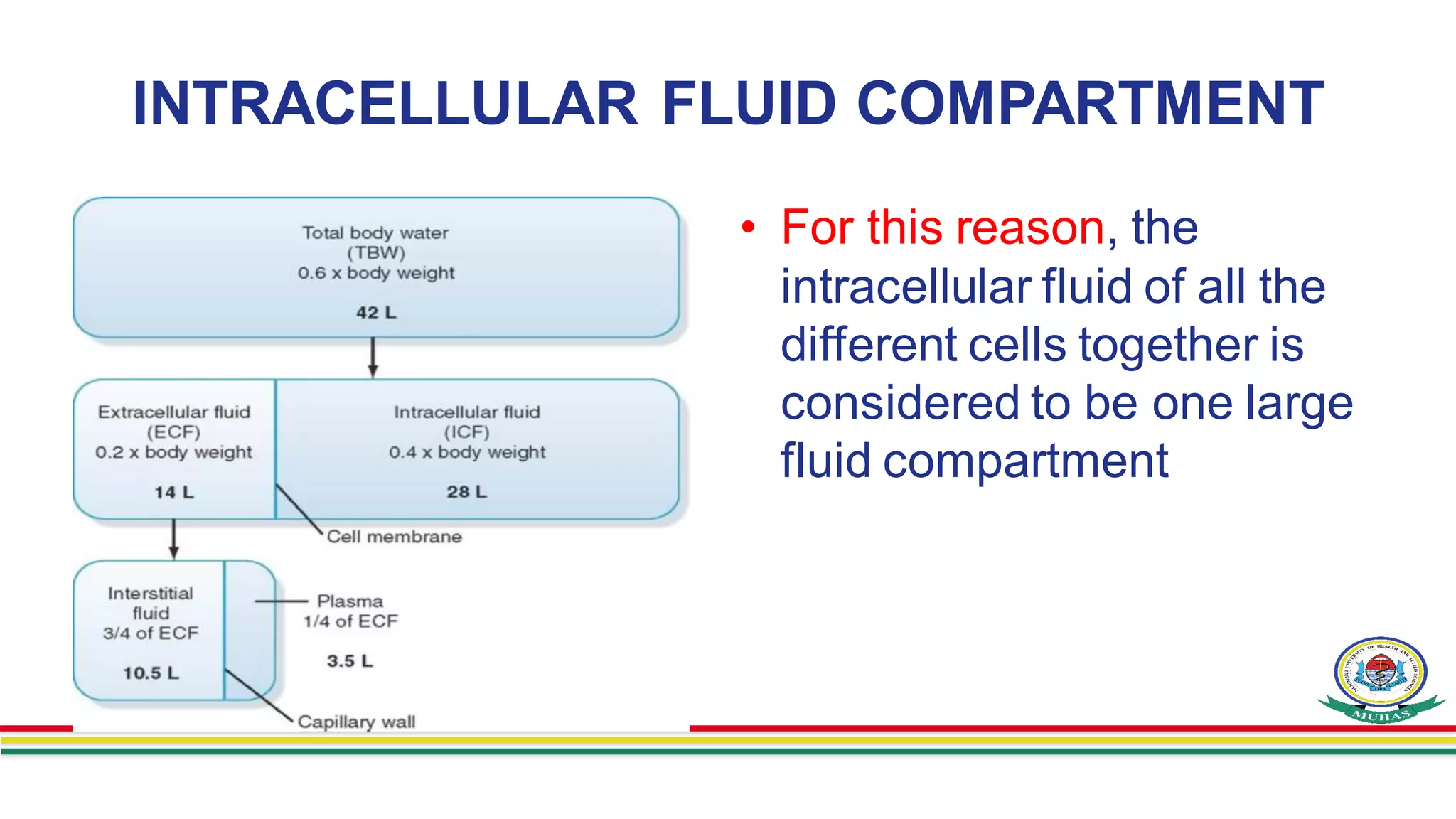
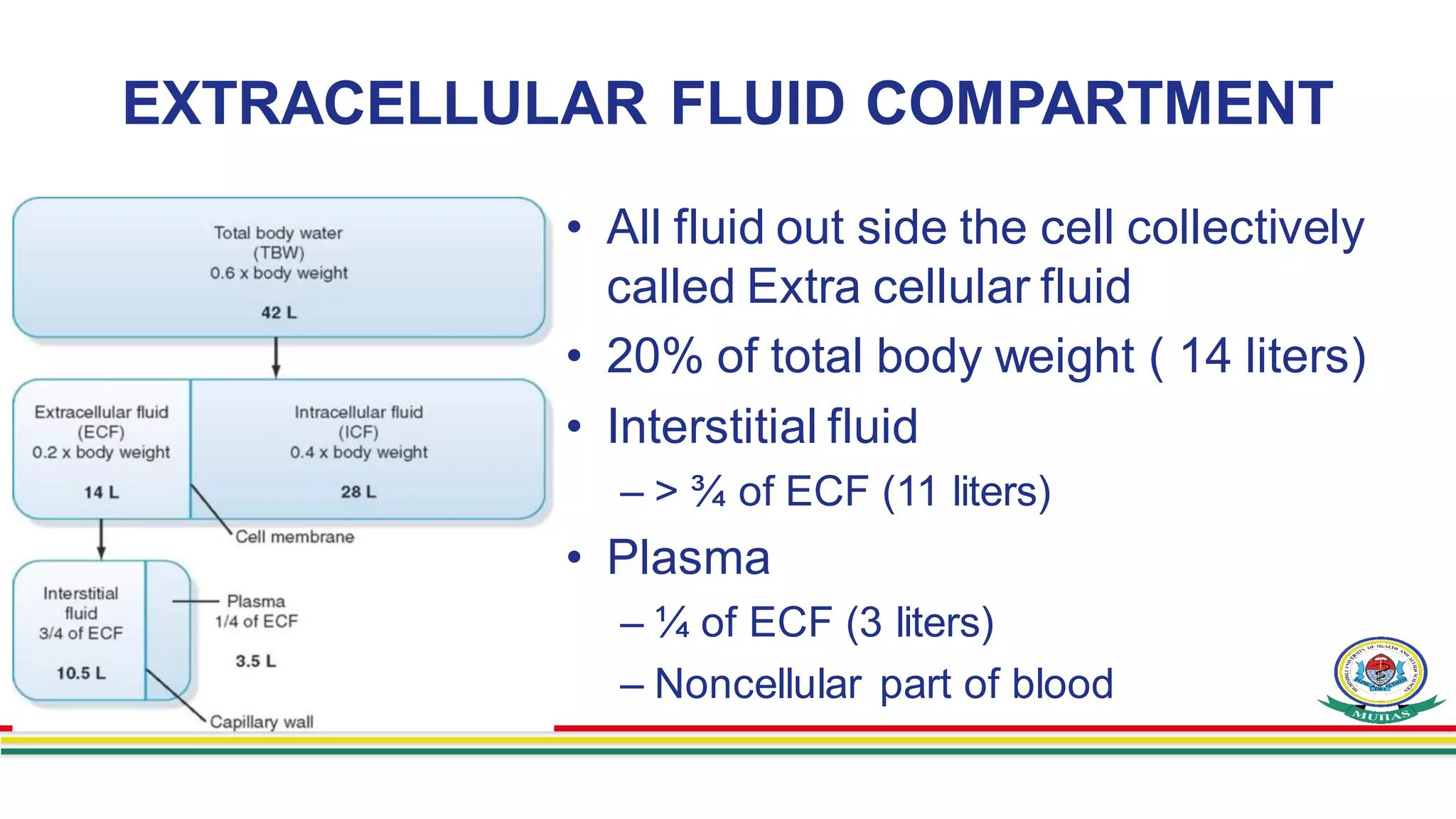
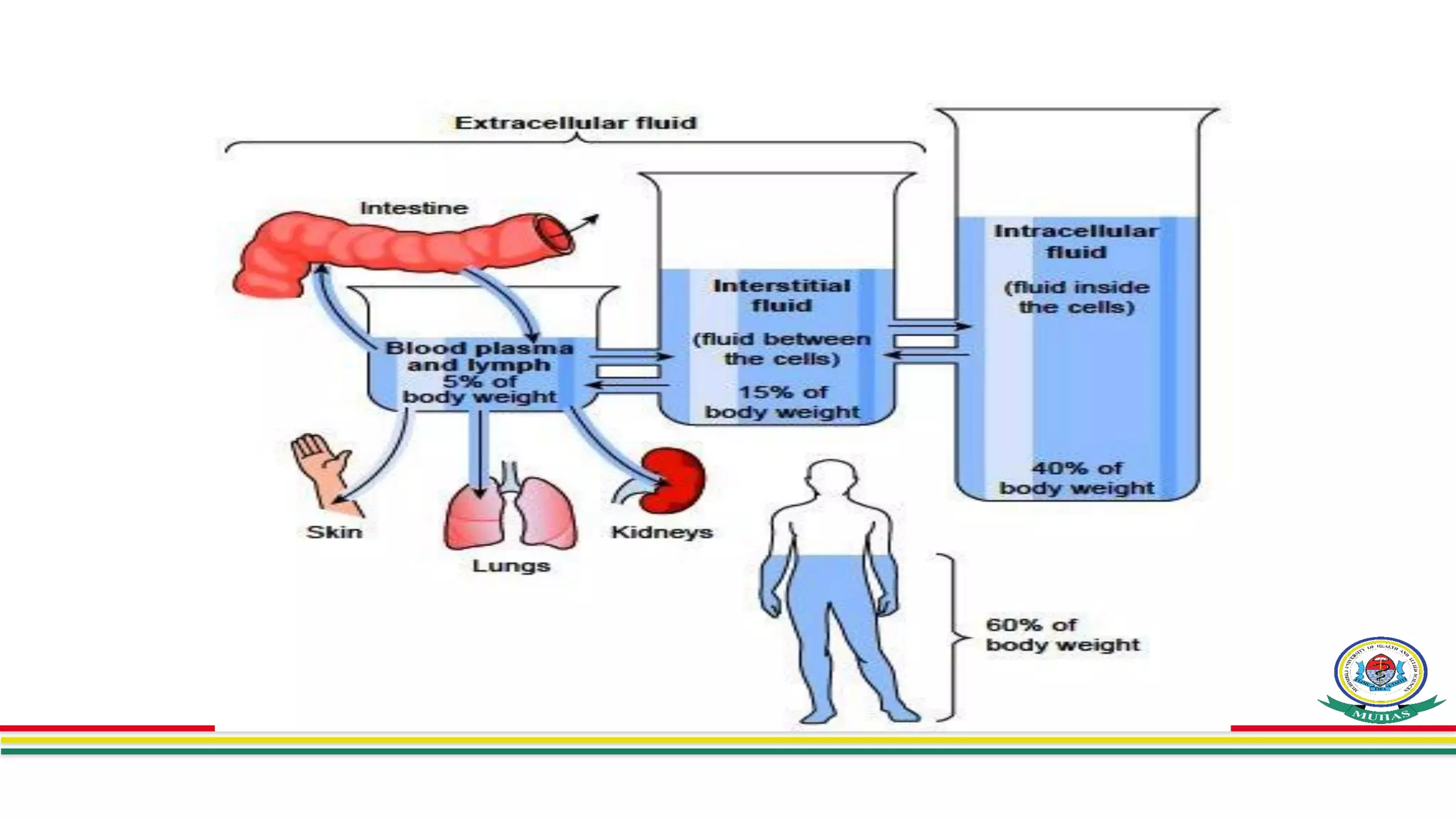
- Body fluids are contained within two main compartments - intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF). ICF makes up around 28 liters and ECF makes up around 14 liters. ECF is further divided into interstitial fluid and plasma.
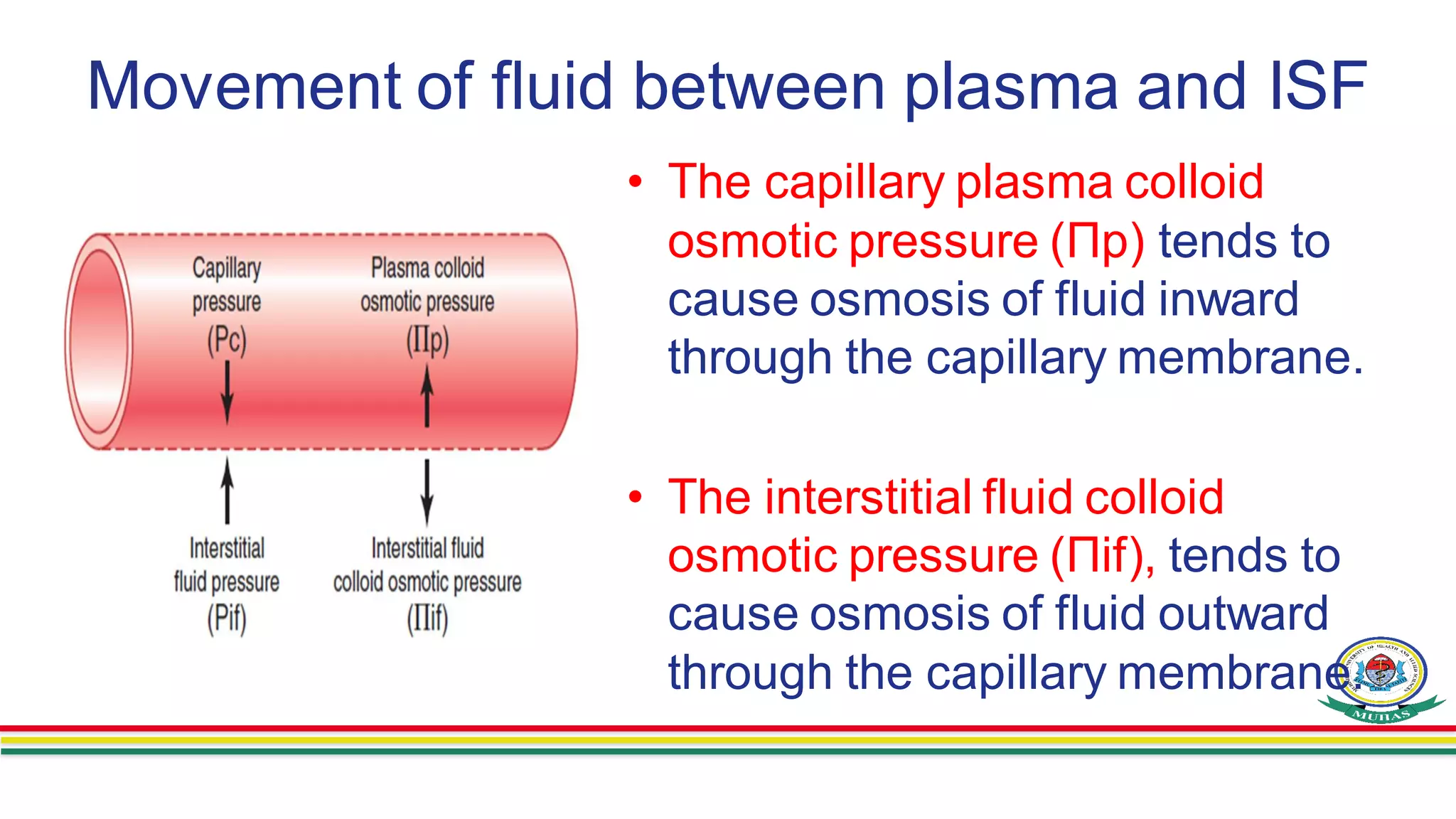
- Movement of fluid between compartments is determined by osmotic forces and hydrostatic pressures across semiper






































![Osmosis and Osmotic pressure
• If sodium chloride is added to the
extracellular fluid
– water rapidly diffuses from the cells
through the cell membranes into the
extracellular fluid until the water
concentration on both sides of the
membrane becomes equal
– Cause Cells to shrink
ICF
ECF
capillary
Selectivelypermeable
cell membrane
[NaCl]
H2O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bodyfluids-230203031157-61374920/75/Body-fluids-pdf-44-2048.jpg)
![Osmosis and Osmotic pressure
• if sodium chloride is removed from
the extracellular fluid
– water diffuses from the extracellular
fluid through the cell membranes and
into the cells.
– Cause Cells to swelling
ICF
ECF
Selectivelypermeable
cell membrane
[NaCl]
H2O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bodyfluids-230203031157-61374920/75/Body-fluids-pdf-45-2048.jpg)