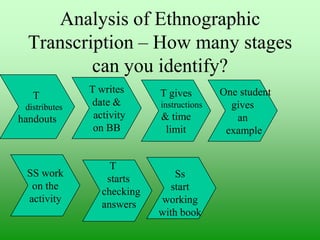
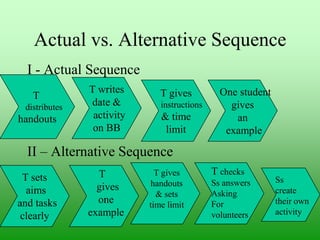
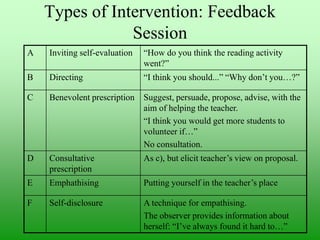
The document provides guidance on conducting classroom observations through an ethnographic lens. It emphasizes noticing small details without judgment, recording evidence descriptively, and focusing on what teachers and students say and do. The best tool for observation is ethnographic description, as it provides objective evidence to help teachers explore, discover, identify strengths and weaknesses, and create action plans. Teachers can analyze observation transcripts to identify stages of a lesson and create alternative sequences to improve instruction. Different observation tools like checklists, groupwork questions, and video can focus attention on various aspects of teaching. Feedback should describe rather than prescribe and invite self-evaluation from the teacher.