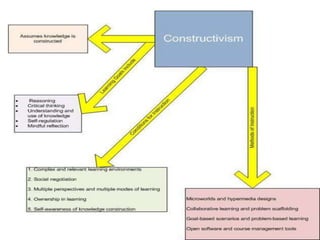
This document discusses constructivism as it relates to knowledge construction and concept learning. It outlines key aspects of constructivism including influential figures like Piaget, Bruner, Vygotsky, and Dewey. It describes individual and social constructivism and characteristics like learners constructing understanding based on prior knowledge and learning being facilitated by social interaction. The document also discusses organizing knowledge through concepts defined by features, prototypes, and exemplars. It provides tips for effective concept learning including defining concepts, using examples, and relating concepts to each other. Finally, it discusses applying constructivism by making learning hands-on and relating topics to real life.