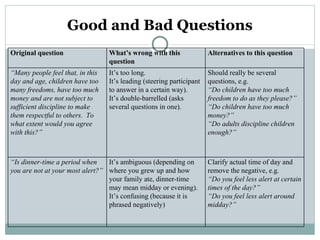
The document provides an outline for a presentation on questioning. It discusses defining questioning, types of questions including open, closed, specific, probing, hypothetical, and reflective questions. The importance of questioning in teaching and learning is explained as a way to encourage discussion, arouse interest, maintain learning, summarize major points, reinforce learning, stimulate students' questioning skills, review and re-teach, and assess teaching and learning. Effective questioning techniques include encouraging student questions, considering all questions, using "APPLE" which stands for Ask, Pause, Pounce, Listen, and Echo, and keeping questions clear, thought-provoking, and properly directed. The document also differentiates between good questions that are clearly stated using common