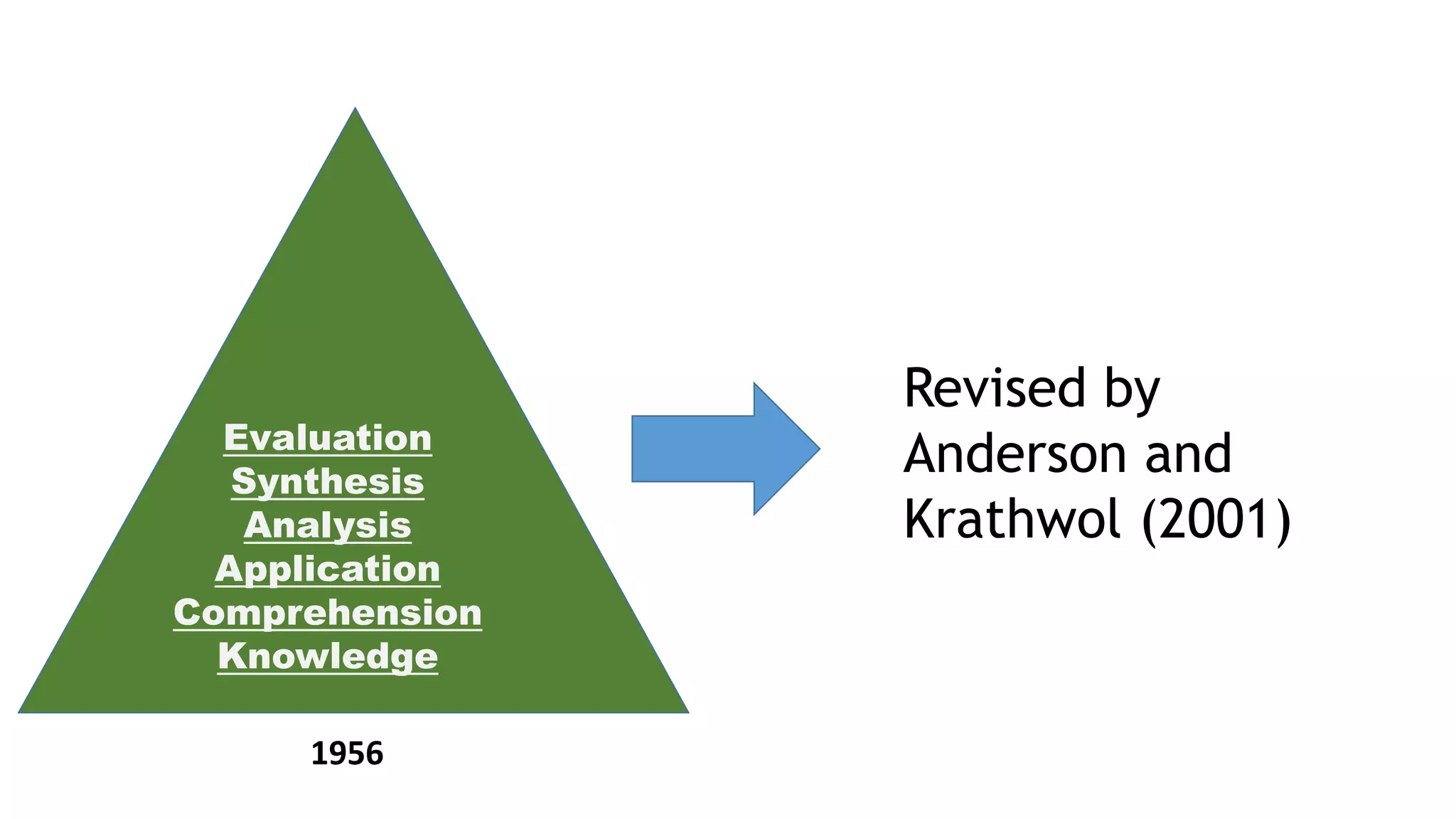
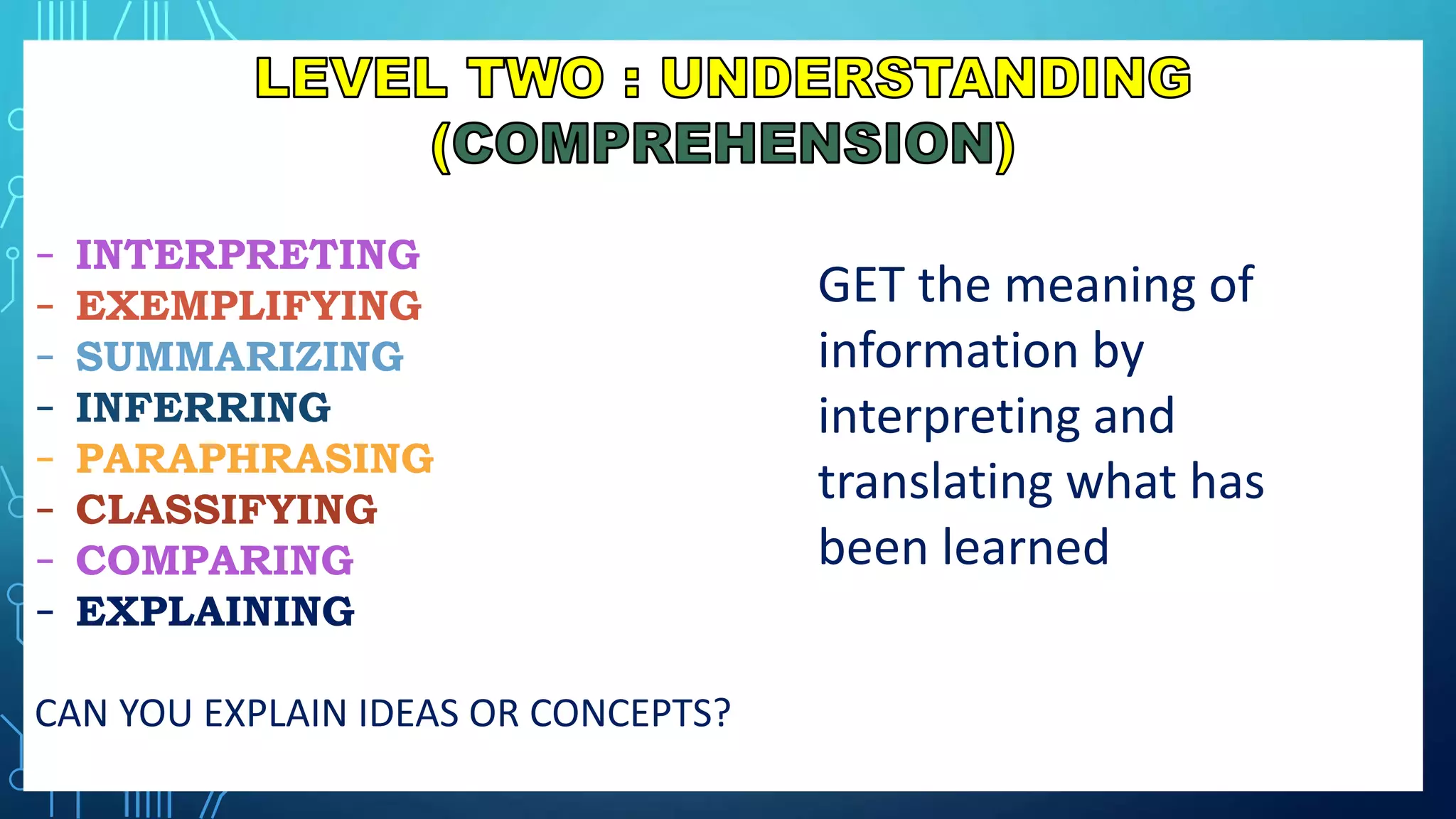
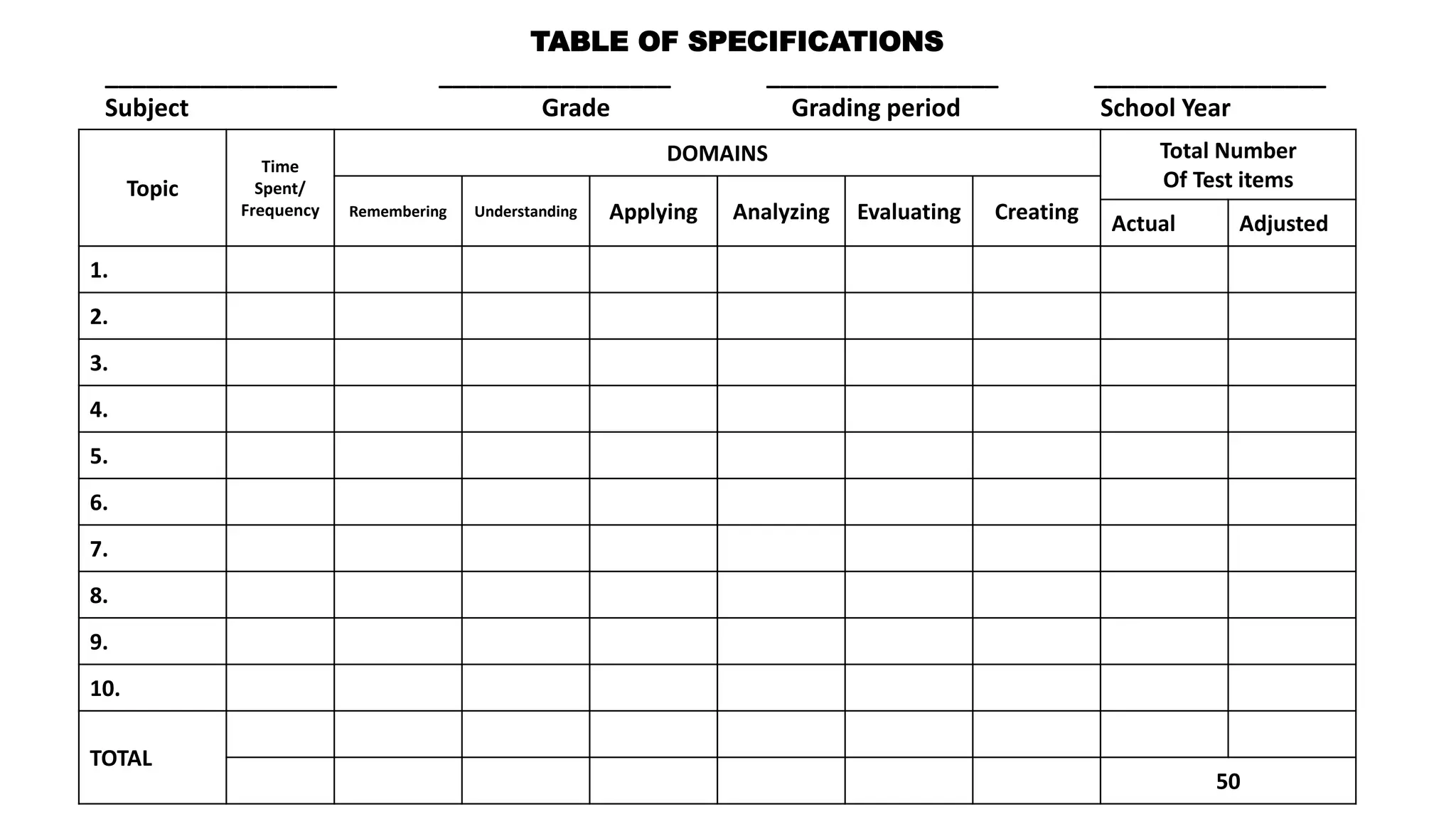
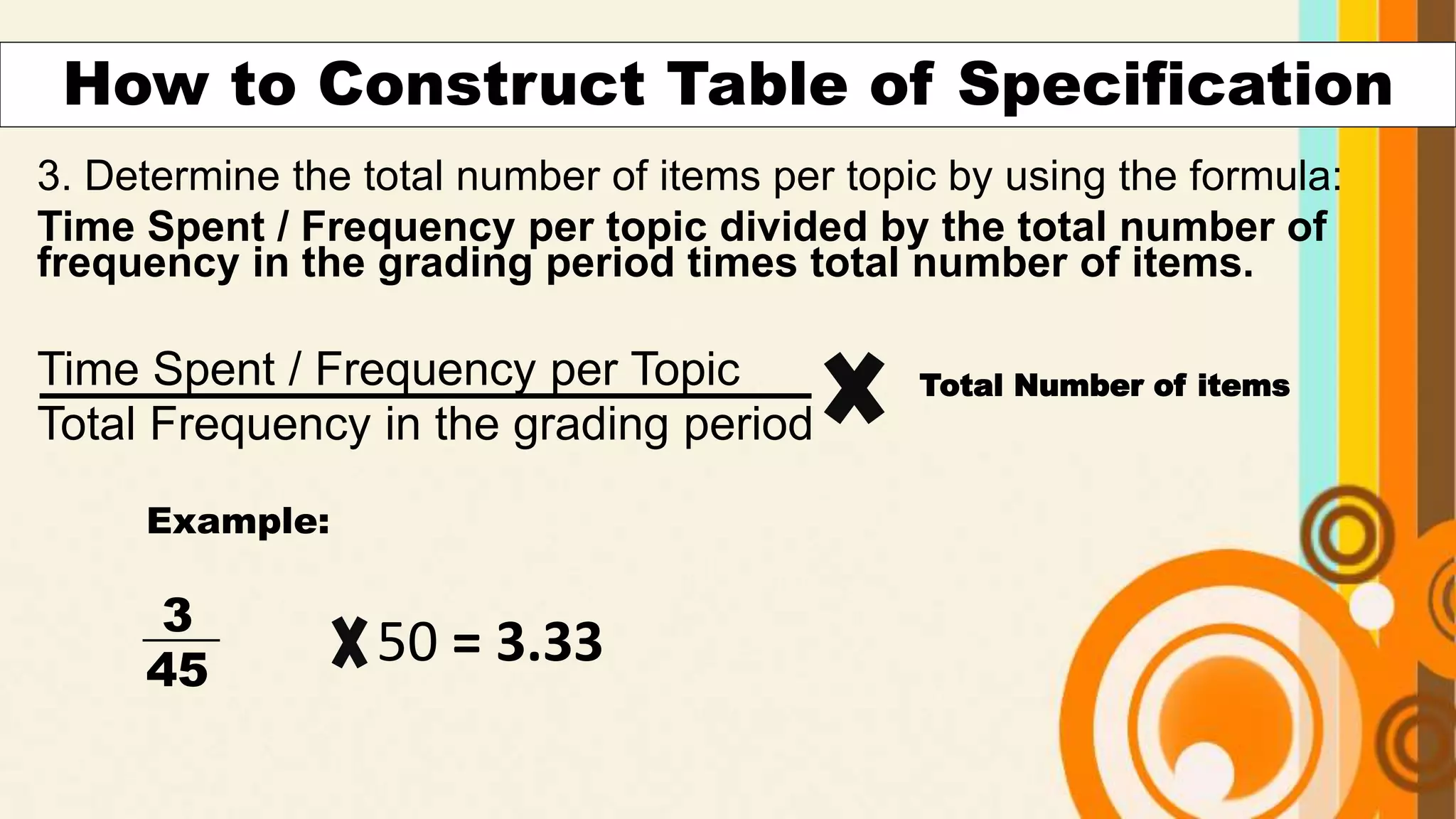
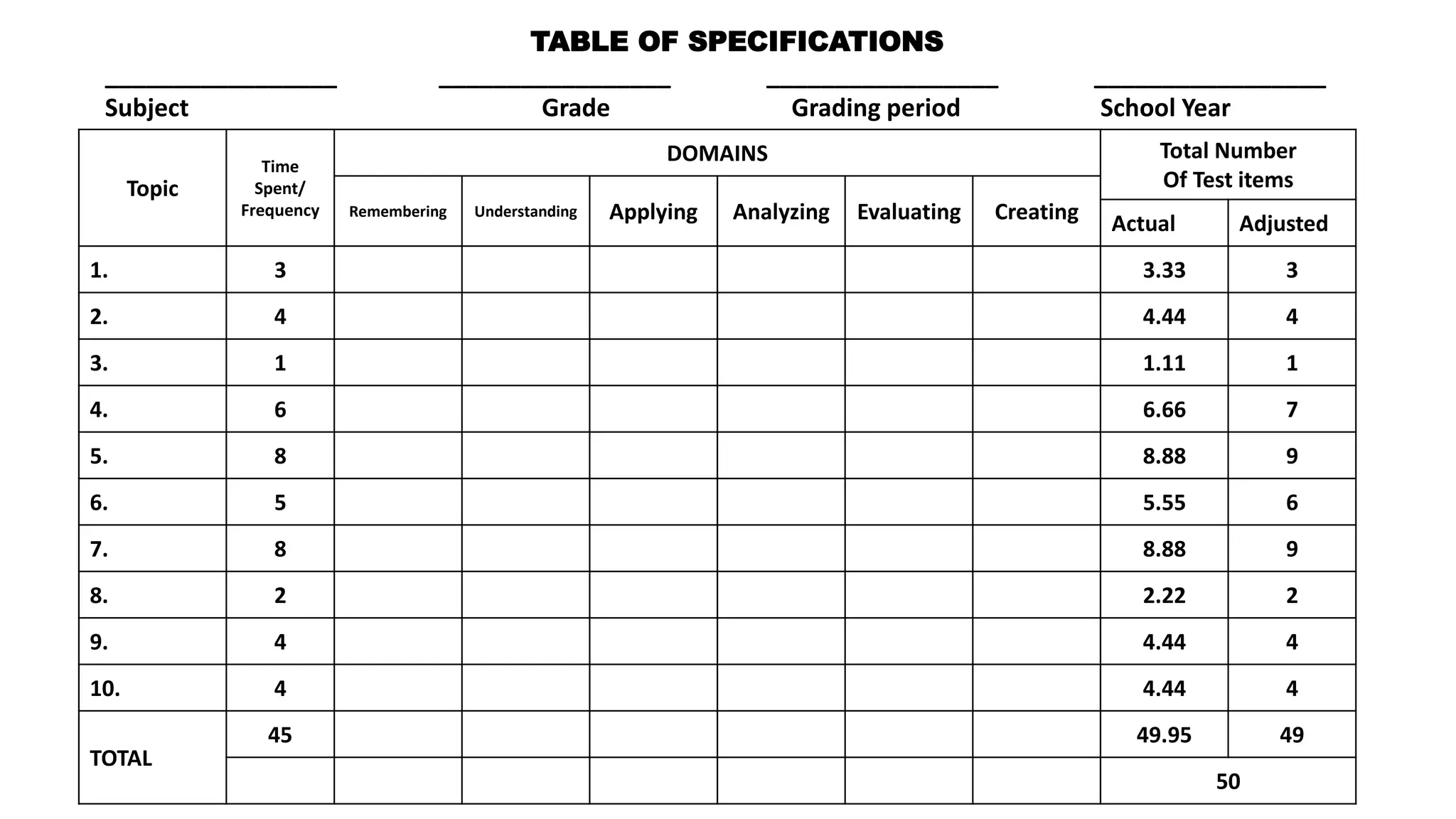
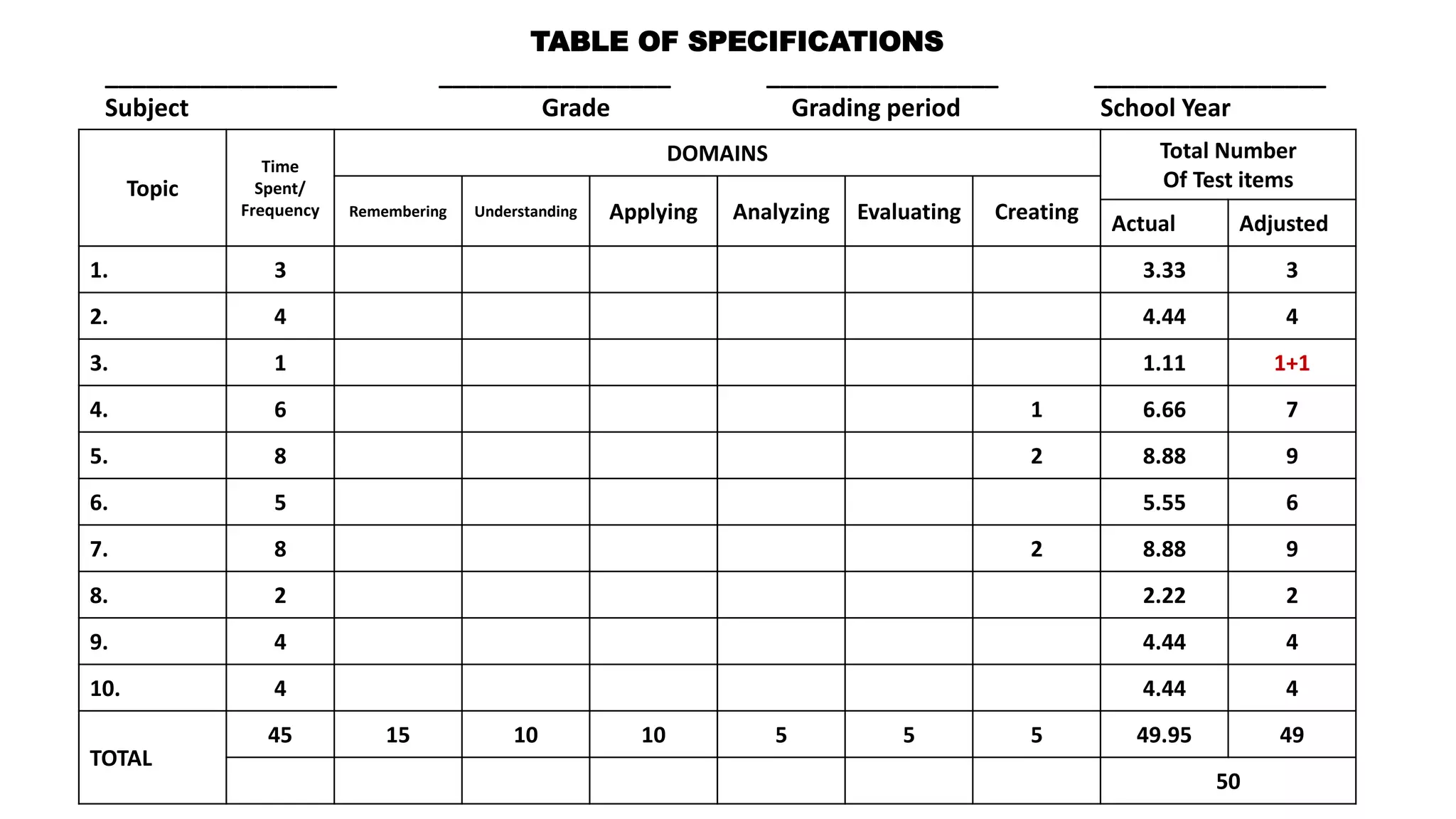
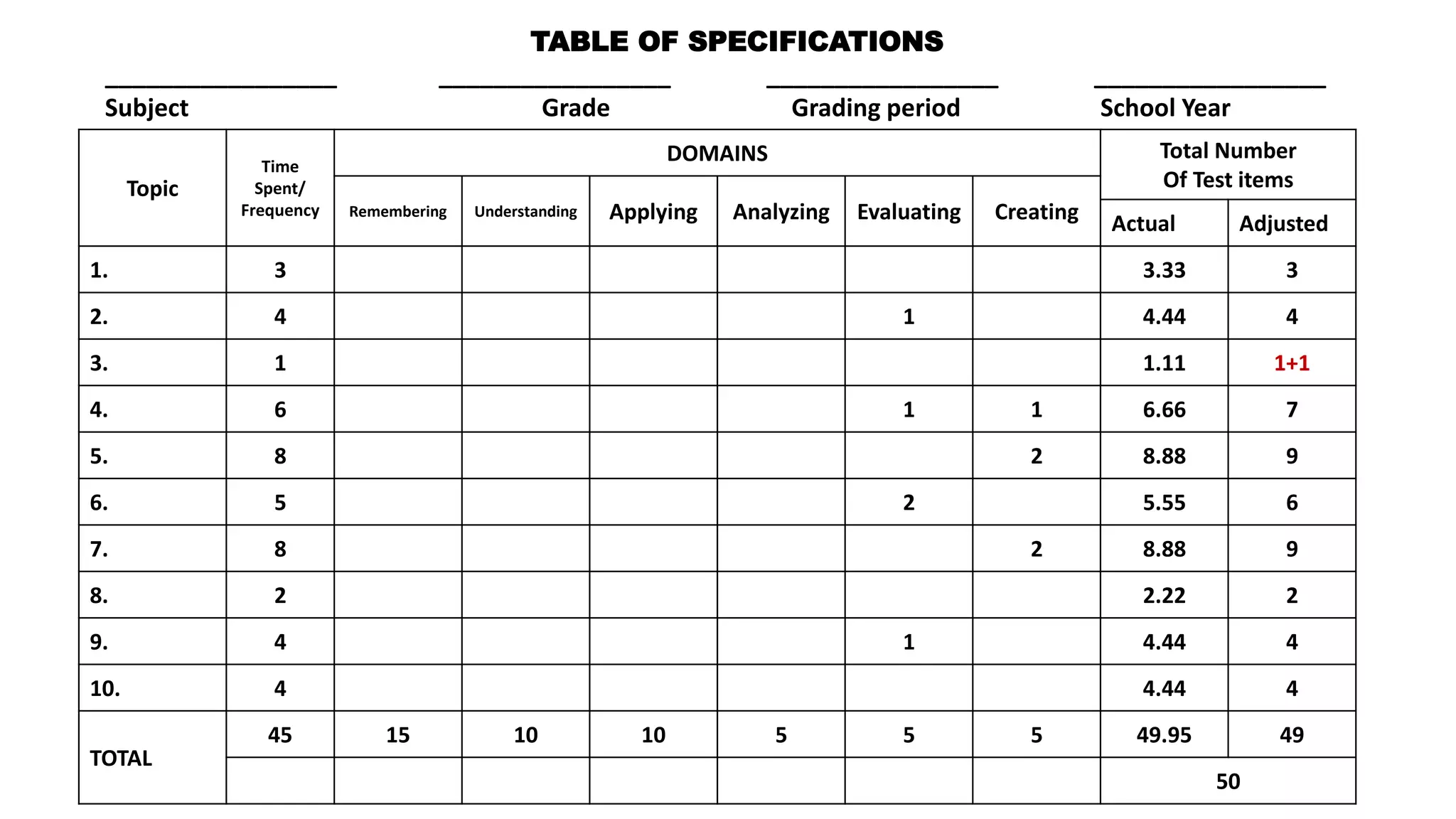
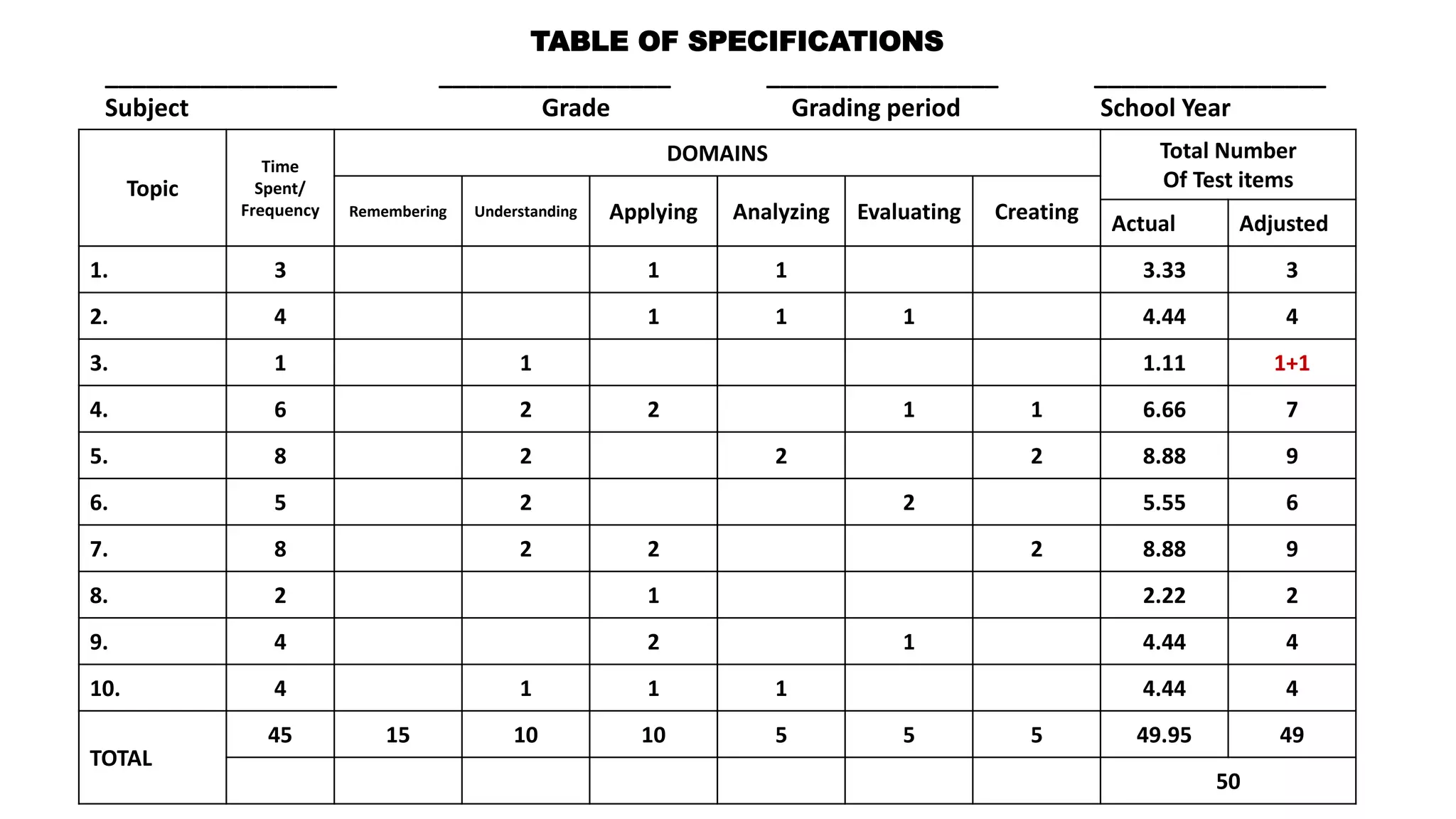
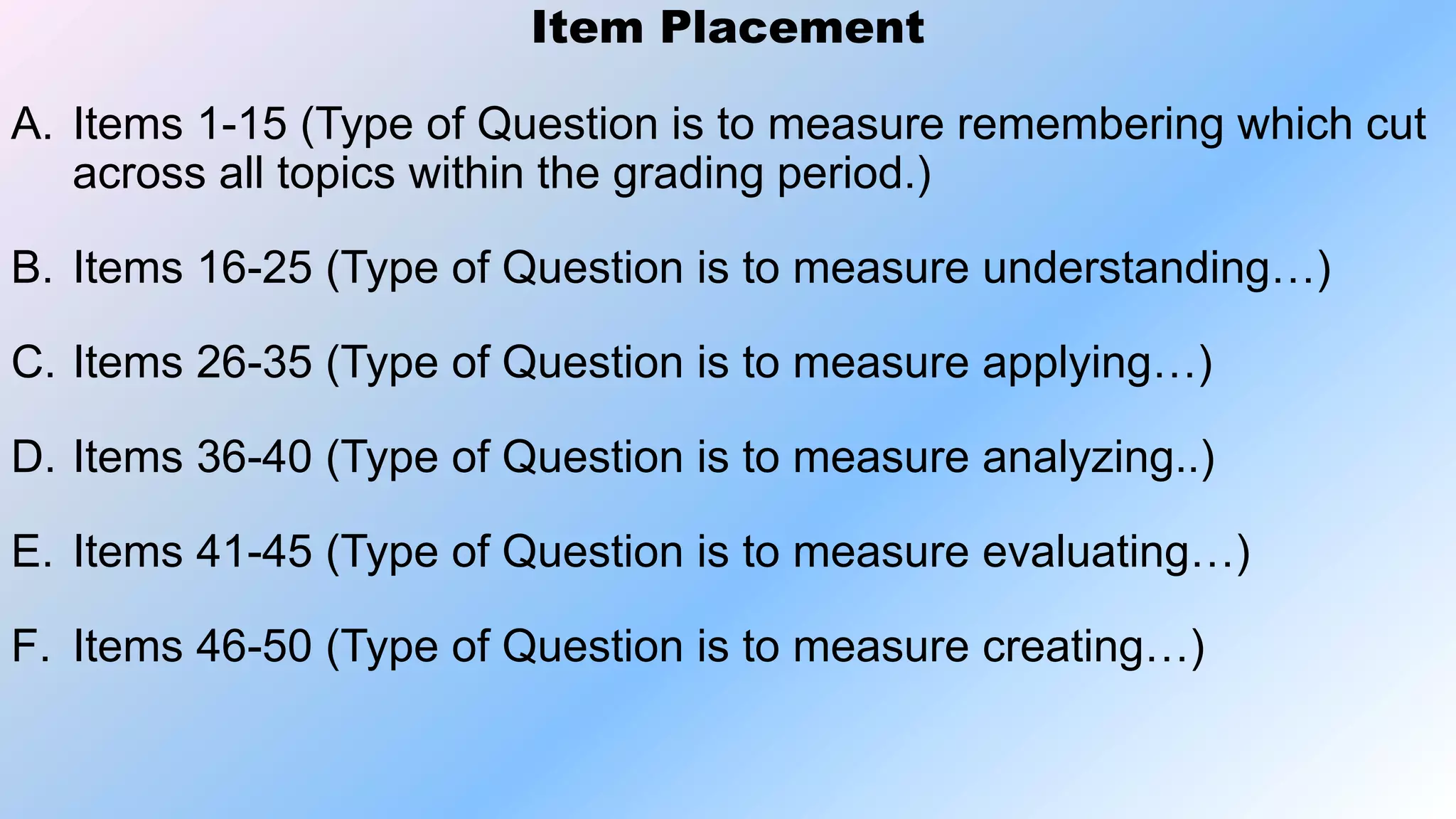
This document discusses how to construct a table of specifications for test questions. It provides a 7-step process: 1) Determine number of test items, 2) List topics and time spent, 3) Calculate number of items per topic, 4) Round numbers, 5) Adjust totals, 6) Scatter items by cognitive level, 7) Allocate items. The purpose is to ensure tests are valid and cover appropriate content in a balanced way based on Bloom's taxonomy. Constructing a table of specifications helps improve test validity and identify question types needed.