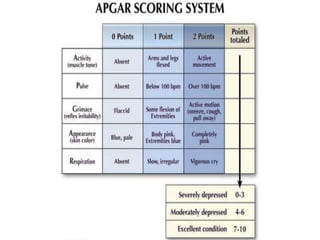
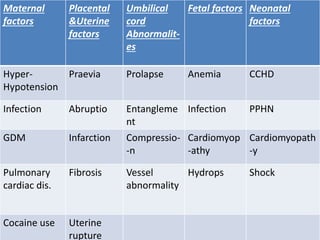
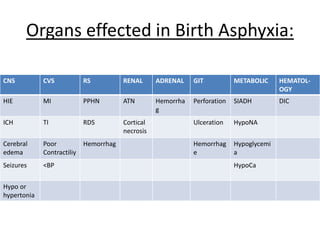
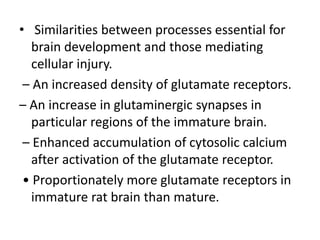
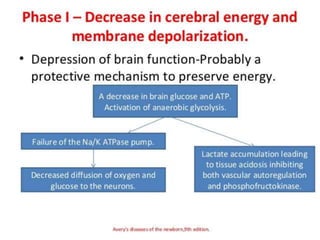
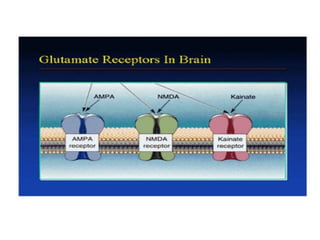
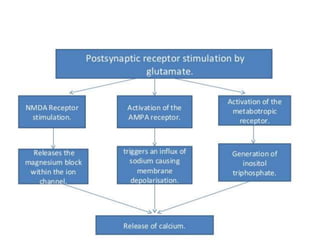
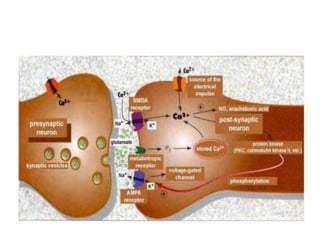
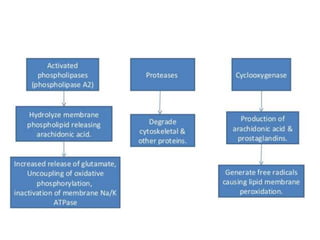
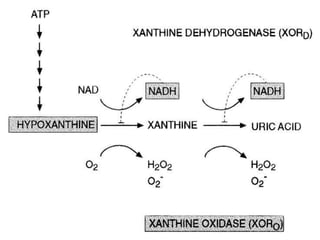
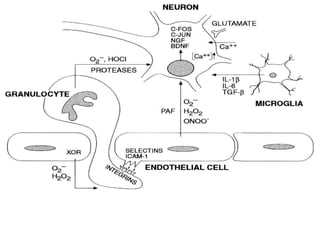
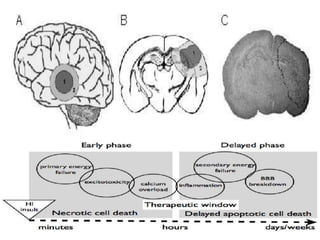
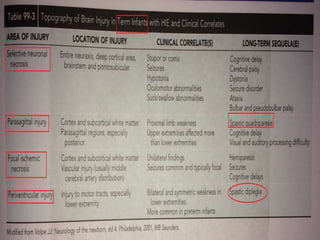
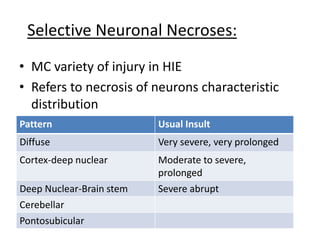
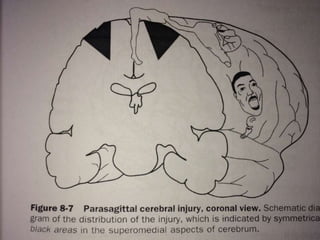
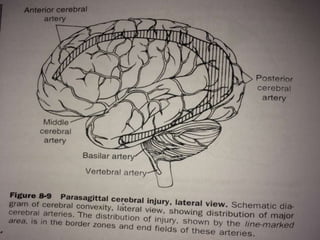
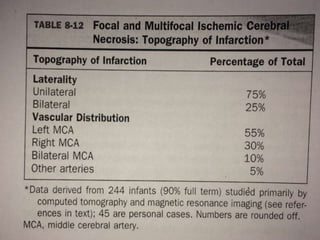
Perinatal asphyxia, also known as birth asphyxia, is a common cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity worldwide. It occurs due to impaired gas exchange leading to hypoxemia and hypercarbia during labor or delivery. In India, 250,000-350,000 infants die each year due to birth asphyxia within the first three days of life. It can result in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), a type of neonatal brain injury. The pathogenesis of HIE involves energy failure, excitotoxicity from glutamate, oxidative stress, and cell death mechanisms like necrosis and apoptosis. Specific patterns of brain injury seen in HIE include selective neuronal necrosis, parasagittal cerebral