1. Perinatal asphyxia refers to impaired gas exchange and oxygen deficiency in a fetus or newborn infant, occurring during labor, delivery, or immediately after birth.
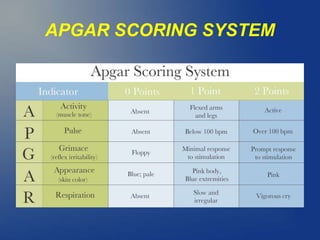
2. It can cause hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), a type of brain injury, in severe or prolonged cases. Clinical features of HIE include seizures, abnormal neurological exam, and multi-organ dysfunction.
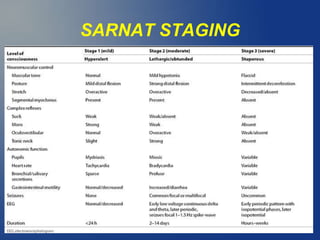
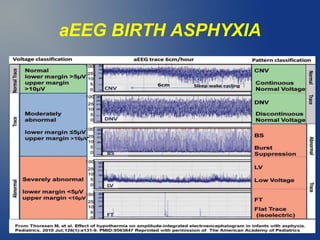
3. Diagnosis involves assessing risk factors, signs of asphyxia at birth, abnormal blood gas values, and neurological exam over time. Imaging and EEG can further evaluate brain injury. Prognosis depends on severity of encephalopathy and extent of brain injury.



![PERINATAL ASPHYXIA
1]First and second stage of labor
2]Impaired gas exchange:- fetal acidosis,
hypoxemia, and hypercarbia.
3]Fetal acidosis:-umbilical arterial blood pH
<7.0,
4]The likelihood of brain injury is
relatively low with this degree of acidosis in
cord blood at birth](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-4-320.jpg)
![A]Perinatal hypoxia, ischaemia,
and asphyxia
B]Perinatal/Neonatal depression
C]Neonatal encephalopathy
D]Hypoxic encephalopathy
E]Hypoxic ischaemic brain injury](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-5-320.jpg)
![Perinatal hypoxia, ichaemia, and
asphyxia
1]Decreased oxygen
2]decreased blood flow
3]Decreased gas exchange
PRENATAL, PERINATAL, POSTNATAL DATA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-6-320.jpg)
![Perinatal/Neonatal depression
Physical examination:First hour after birth.
1]Depressed mental status
2]Muscle hypotonia, and/or
3]Disturbances in spontaneous respiration and
cardiovascular function.
After the first hour or so of life: neonatal
encephalopathy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-7-320.jpg)
![Neonatal encephalopathy
Clinical and not an etiologic:abnormal neurobehavioral
state
1]Altered consciousness (including hyperalert state)
2]Brainstem and/or motor dysfunction.
3]No specific etiology
irreversible OR reversible conditions as maternal
medications or hypoglycemia in baby.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-8-320.jpg)
![Hypoxic ischaemic
encephalopathy
1]Clinical evidence of encephalopathy
2]Objective data: Hypoxic-ischemic (HI) mechanism as the
underlying cause](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-9-320.jpg)
![Hypoxic ischaemic brain injury
1]Neuropathology attributable to hypoxia and/or
ischemia
2]neuroimaging HUS, MRI, CT] or pathologic
(postmortem)
3]Biochemical markers of brain injury such as
CK-BB and neuron specific enolase (NSE) are not
used routinely in clinical practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-10-320.jpg)




![Placental factors:
1]Abnormal placentation
2]Abruption
3]Infarction
4]Fibrosis
5]Hydrops](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-15-320.jpg)
![Umbilical cord accidents:
1] Prolapse
2] Entanglement
3] True knot
4] Compression](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-16-320.jpg)
![Fetal factors:-
1] anemia (e.g., from fetal-maternal hemorrhage)
2]infection
3]cardiomyopathy
4]hydrops
5]severe cardiac/circulatory insufficiency](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-17-320.jpg)
![Neonatal factors:
1] cyanotic congenital heart disease
2]PPHN
3]cardiomyopathy
4]neonatal cardiogenic and/or septic shock
5]meconium aspiration syndrome
6]neonatal pneumonia
7]pneumothorax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-18-320.jpg)





![Immediate neuronal death (necrosis):
- Intracellular osmotic overload of Na+ and Ca2+
- Ion pump failure as above or
- Excitatory neurotransmitters acting on in
otropic receptors (such as the N-methyl-Daspartate
[NMDA] receptor).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-24-320.jpg)









![Neurological signs
1]encephalopathy
2]brainstem and cranial nerve signs
3]motor signs
4]seizures
5]increased ICP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-35-320.jpg)




![Multiorgan dysfunction
1]Kidney injury
2]Cardiac
3]Pulmonary
4]Liver
5]Gastrointestinal
6]Hematologic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perinatalasphyxia1-200325071028/85/Perinatal-asphyxia-41-320.jpg)