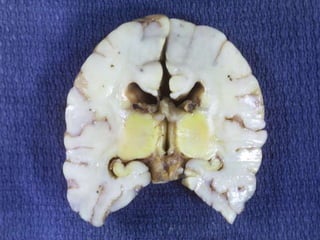
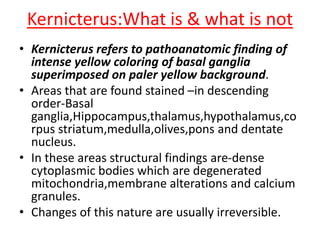
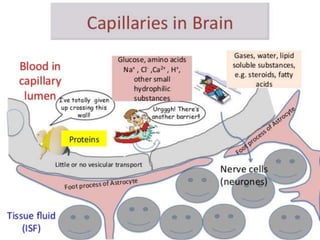
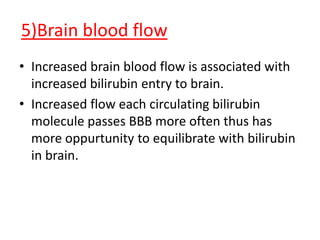
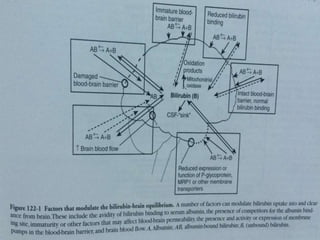
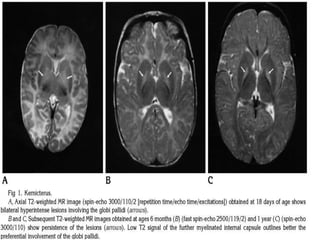
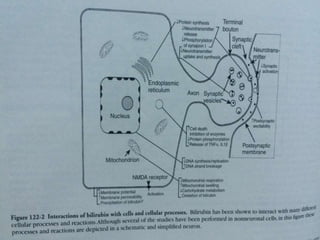
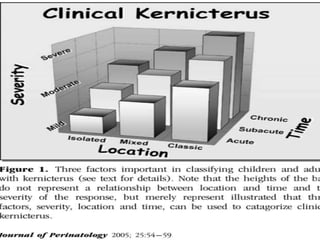
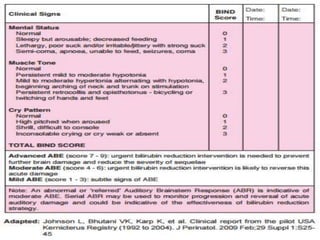
This document discusses the pathophysiology of bilirubin-induced neurological dysfunction (BIND), commonly known as kernicterus. It begins with a brief history of kernicterus and describes the areas of the brain that are most intensely stained by bilirubin, including the basal ganglia. It then explains bilirubin chemistry and solubility, how the blood-brain barrier influences bilirubin entry into the brain, and various cellular mechanisms by which high bilirubin levels can damage neurons. Specifically, bilirubin can uncouple oxidative phosphorylation, interact with and damage membranes, and alter neurotransmitter metabolism. The document concludes by outlining the clinical spectrum of BIND, from acute