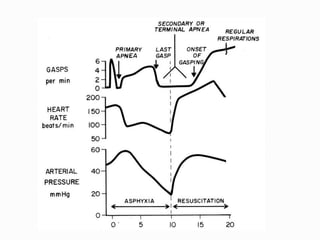
This document provides guidance on managing birth asphyxia through proper newborn resuscitation. Key points discussed include:
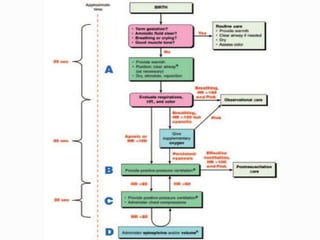
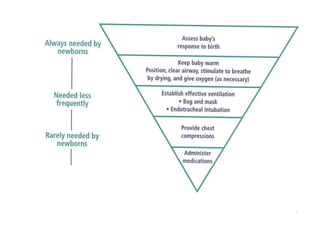
1. Preparation for delivery is critical as each birth is an emergency, ensuring proper equipment and staff readiness.
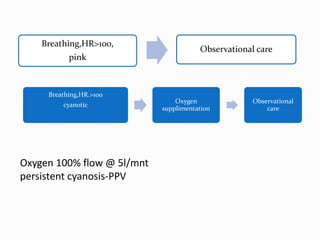
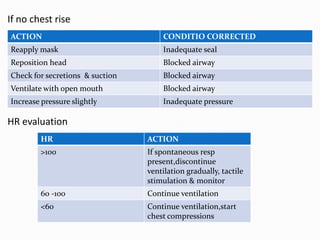
2. Initial resuscitation steps are providing warmth, clearing the airway, drying and stimulating the newborn. Positive pressure ventilation may be needed if breathing does not improve.
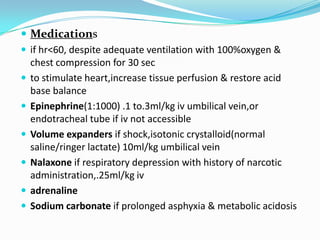
3. If the heart rate remains low despite adequate ventilation, chest compressions and medications like epinephrine may be administered to support circulation. Intubation should only be considered in specific situations.
4. Post resuscitation care focuses on monitoring vital signs and providing support until stabilization is achieved.