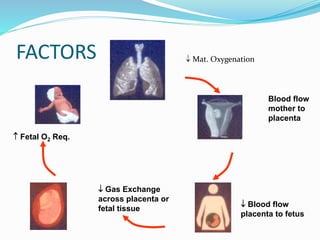
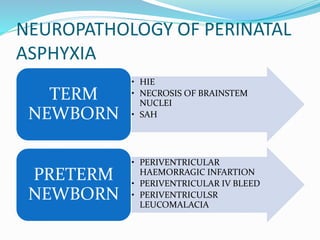
Perinatal asphyxia refers to lack of oxygen and poor perfusion experienced by the fetus or newborn during delivery or birth. This can lead to hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy and multi-organ system dysfunction in the newborn. Key criteria for diagnosing perinatal asphyxia include an umbilical cord pH less than 7.0, low Apgar scores for more than 5 minutes, and neurological or multi-organ abnormalities in the newborn period. The pathophysiology involves hypoxia, ischemia and reperfusion injury damaging cells and organs. Management focuses on supporting oxygenation, circulation, temperature and metabolism to prevent further brain injury.