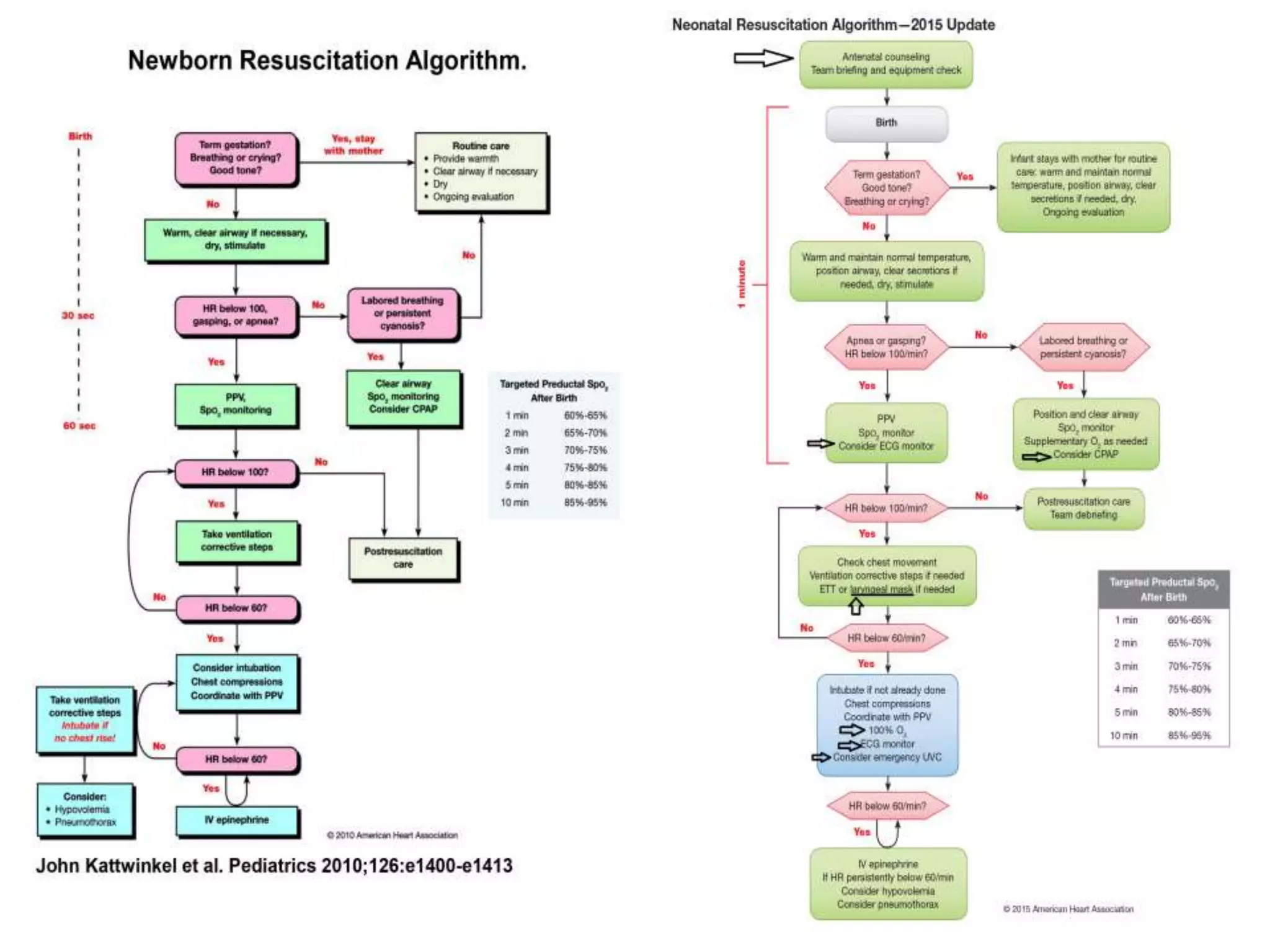
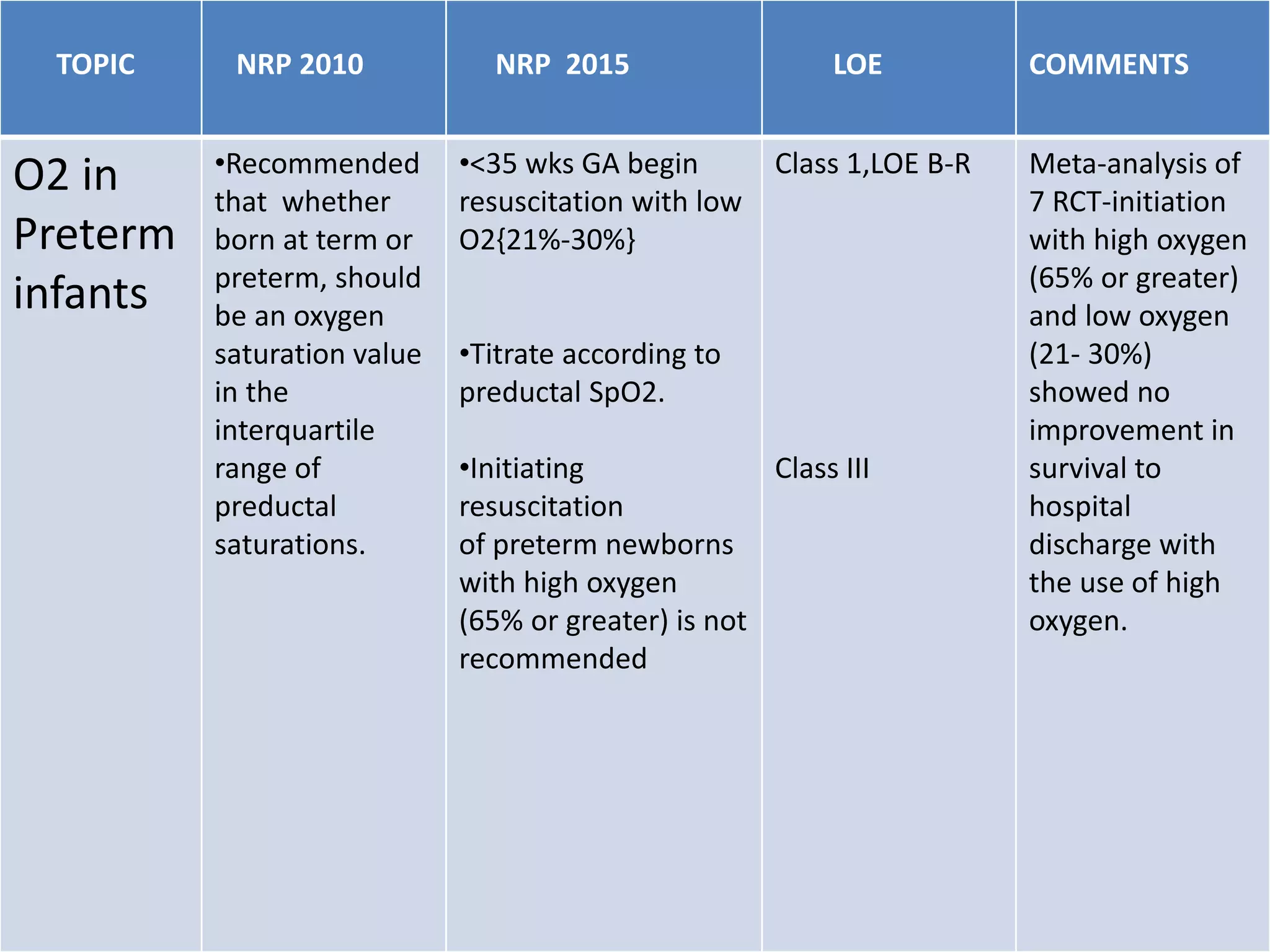
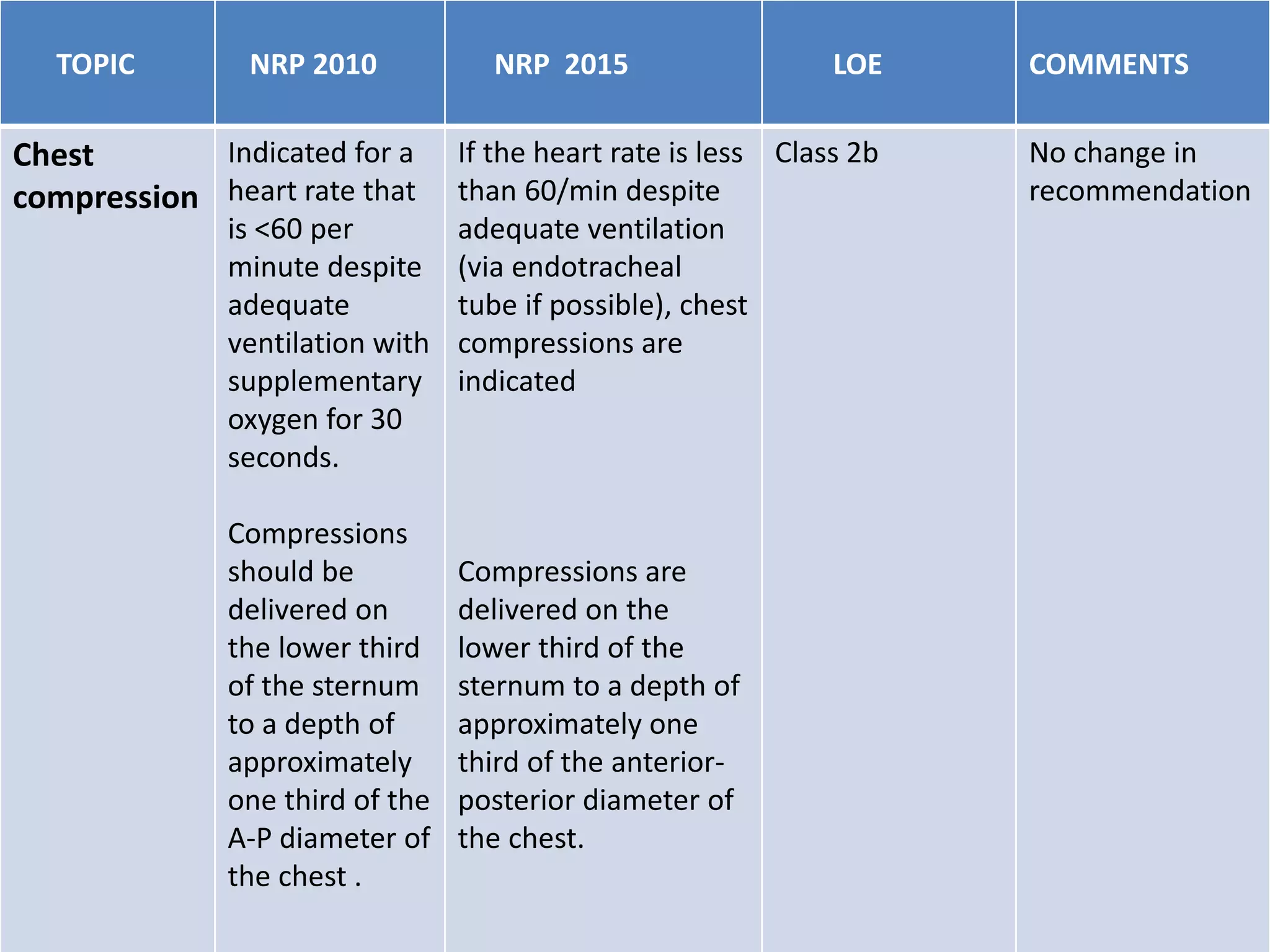
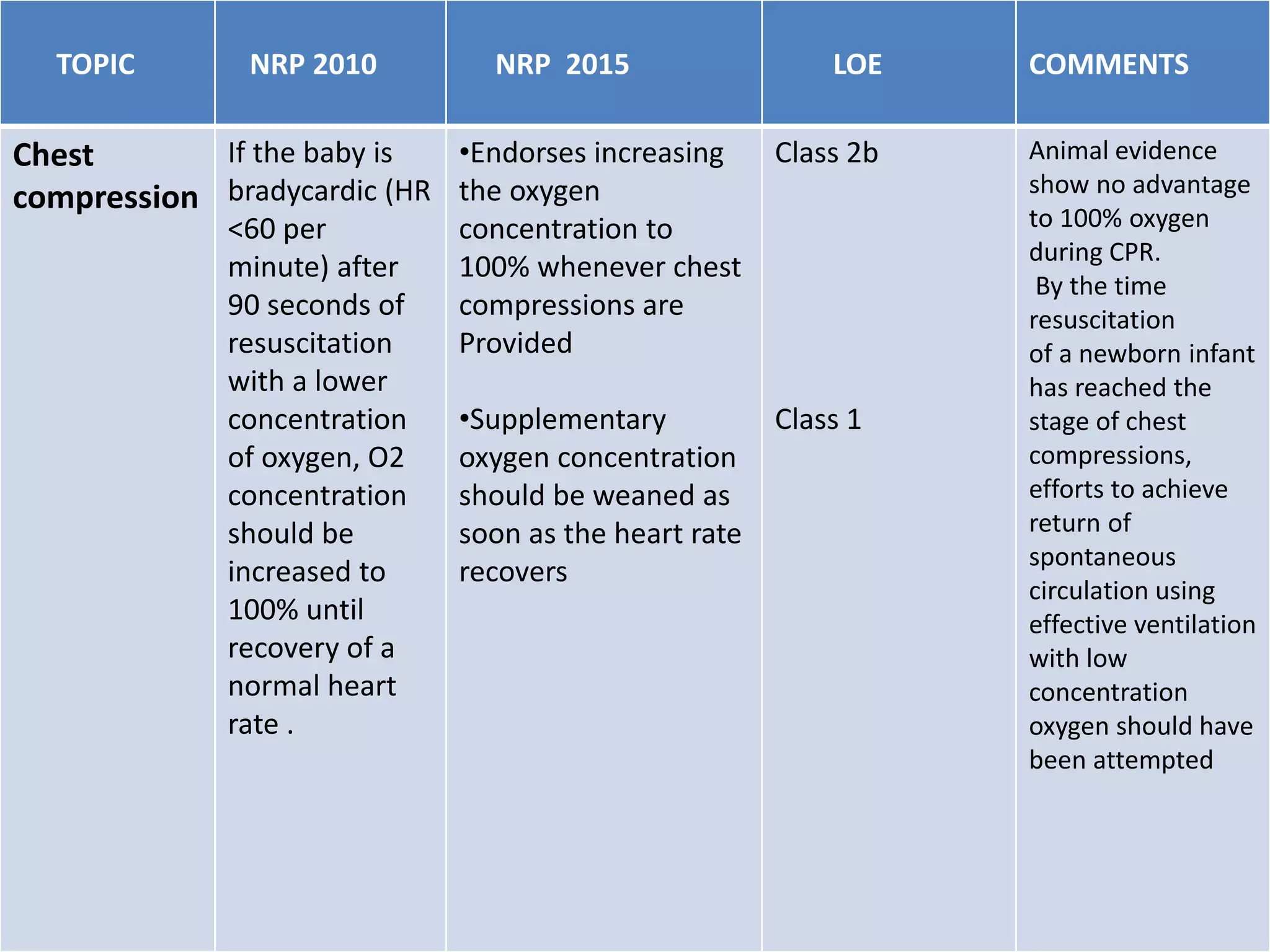
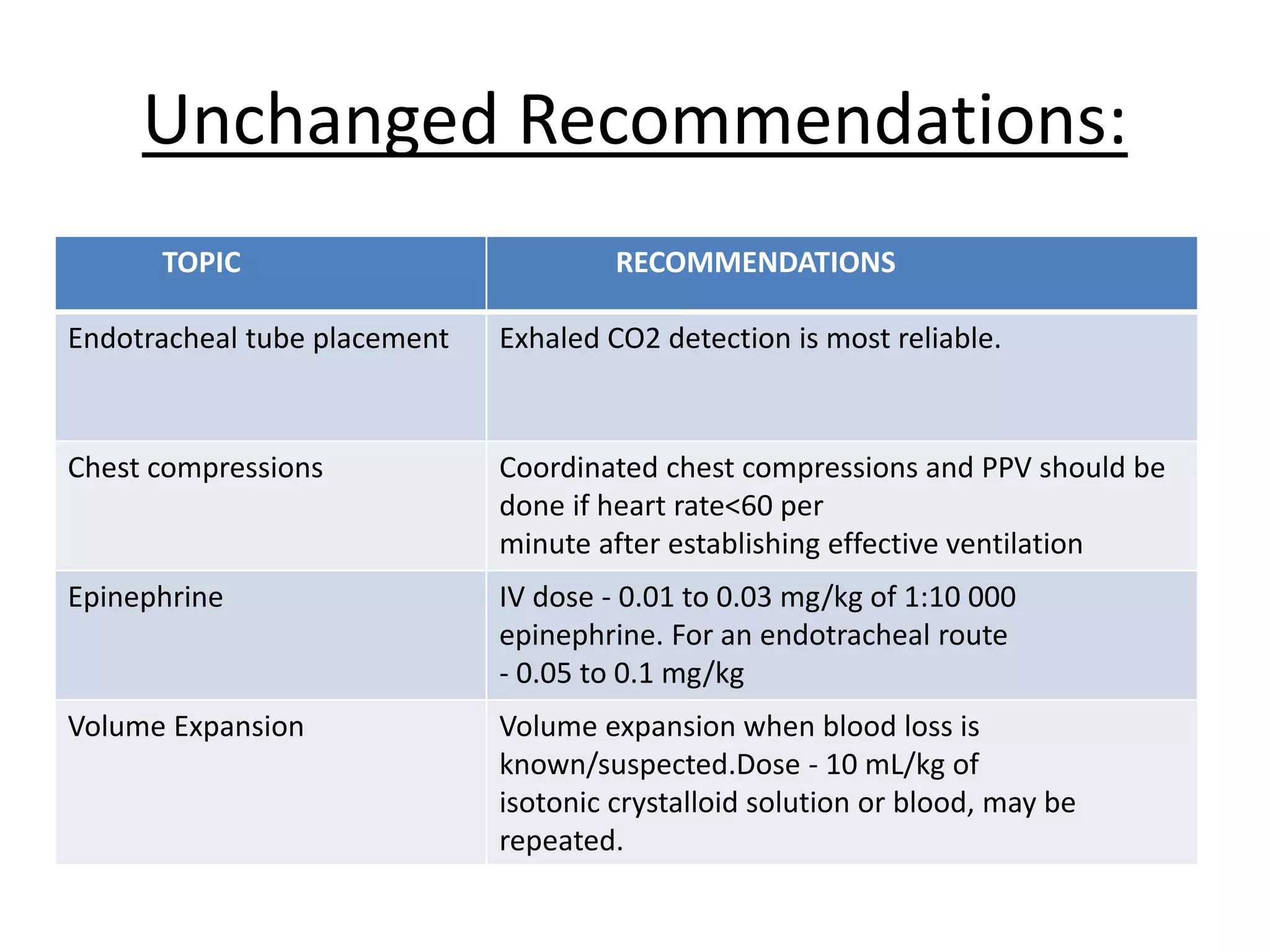
The 2015 AHA Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines update provides recommendations for several changes:
1. Positive pressure ventilation for preterm infants should include PEEP of 5cmH2O. Laryngeal masks are recommended when intubation is not feasible for infants >34 weeks.
2. Initiation of resuscitation for preterm infants should use low oxygen (21-30%) titrated to target saturation rather than high oxygen. Term infants should be initiated with room air.
3. Chest compressions are indicated if the heart rate is <60/minute despite ventilation. The 2-thumb technique is preferred for compressions.
4. Assessment of heart rate response is the best measure