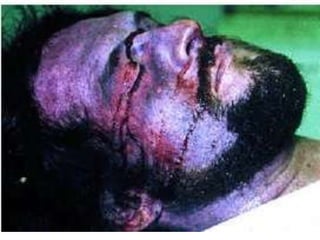
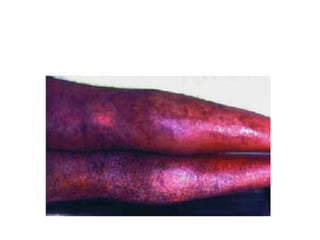
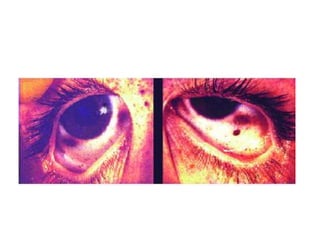
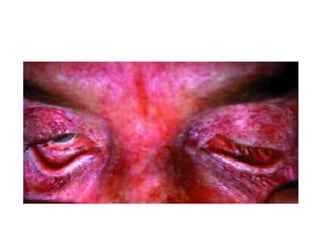
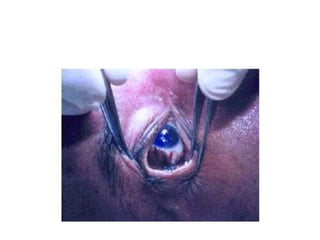
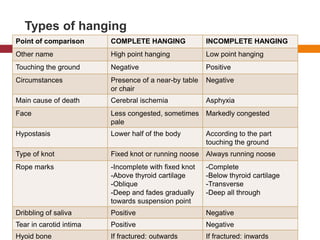
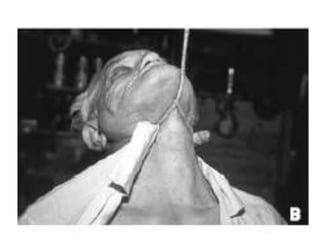
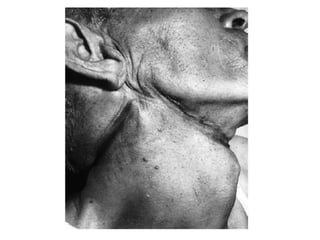
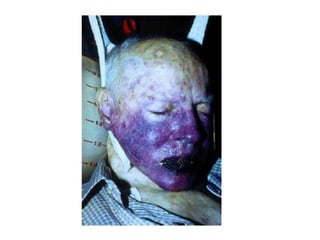
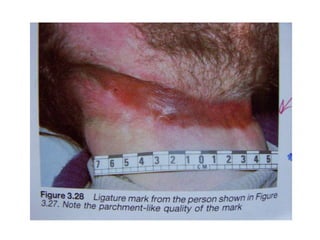
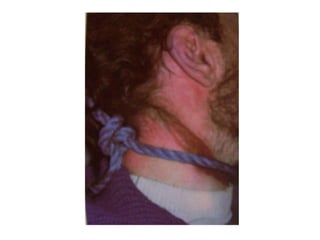
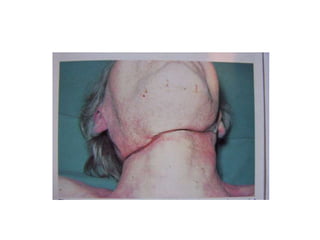
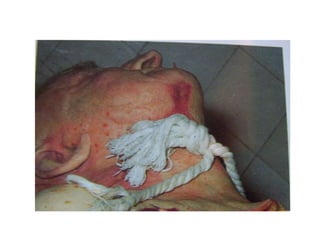
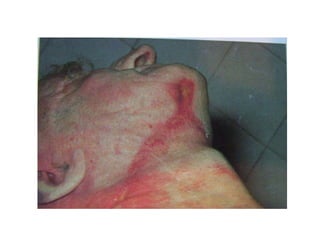
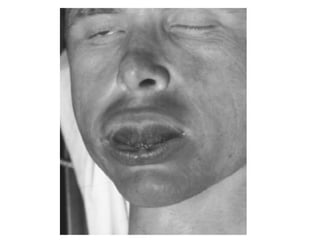
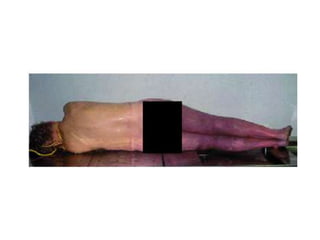
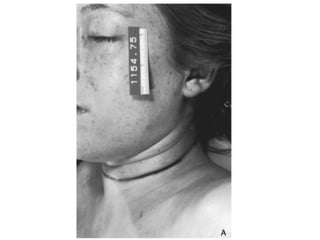
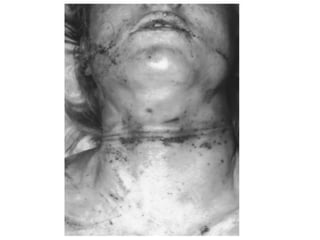
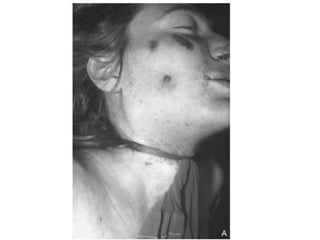
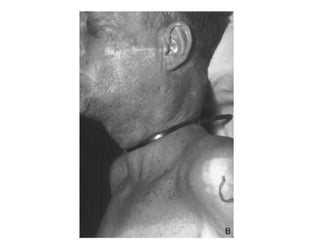
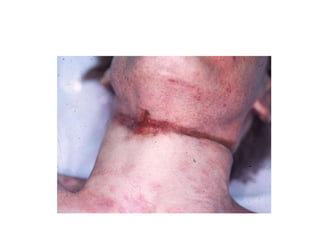
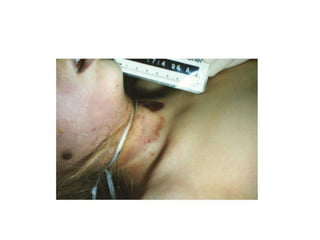
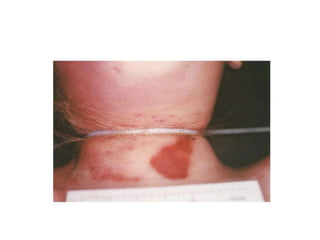
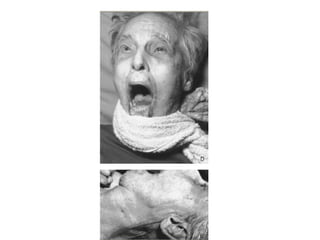
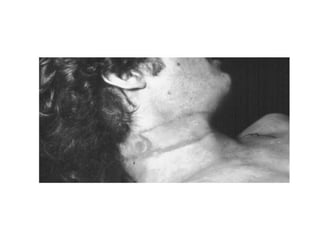
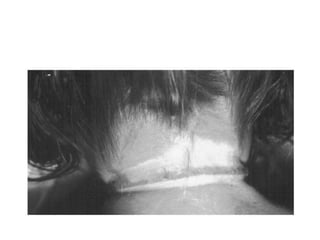
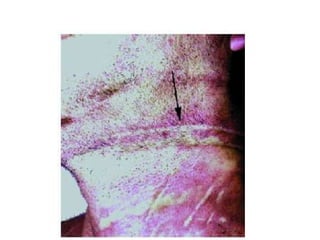
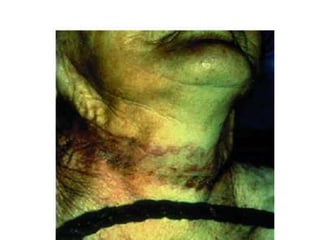
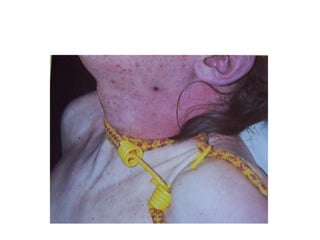
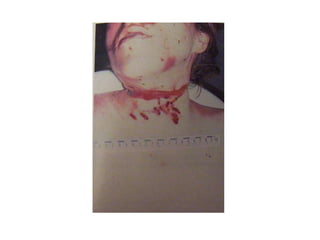
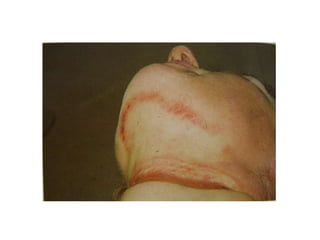
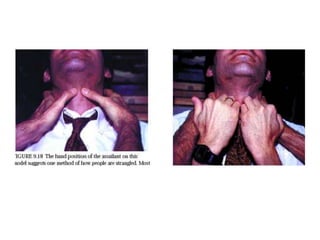
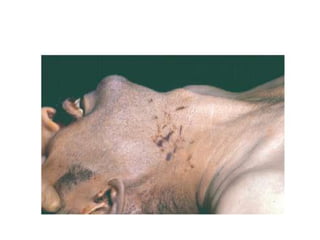
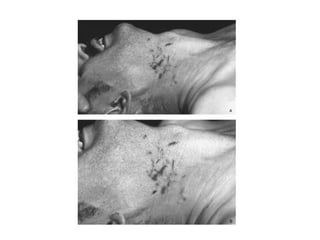
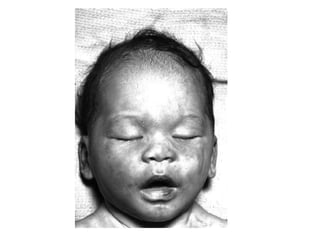
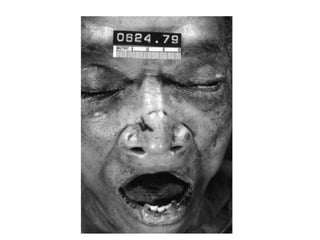
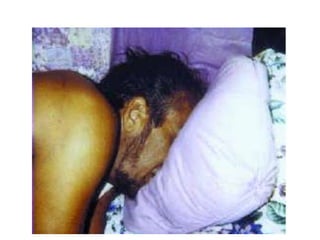
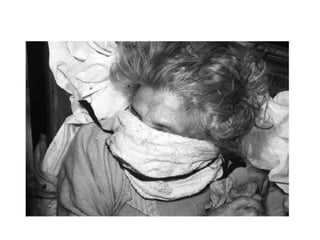
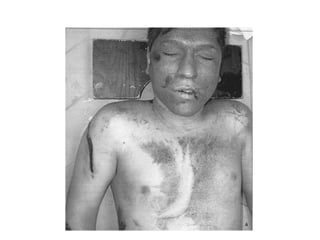
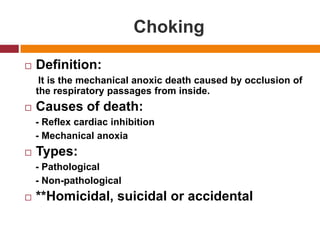
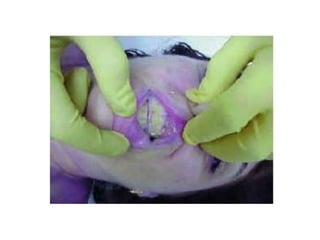
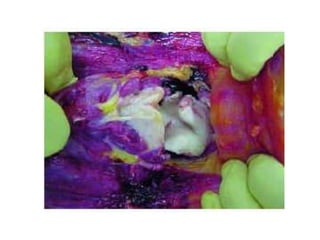
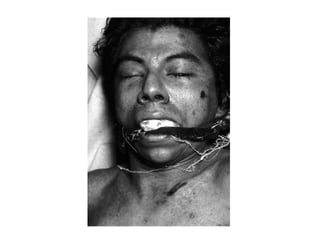
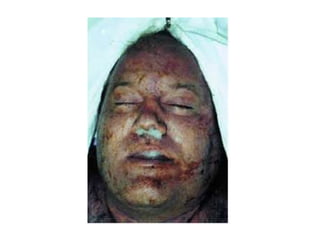
This document defines and describes various types of asphyxia including mechanical asphyxia, anoxic anoxia, anemic anoxia, stagnant anoxia, histotoxic anoxia, hanging, strangulation, throttling, smothering, traumatic asphyxia from overlaying, choking, and drowning. It discusses the causes of death, post-mortem findings, and whether the asphyxia could be homicidal, suicidal, or accidental for each type.