Embed presentation
Download to read offline



![Integral
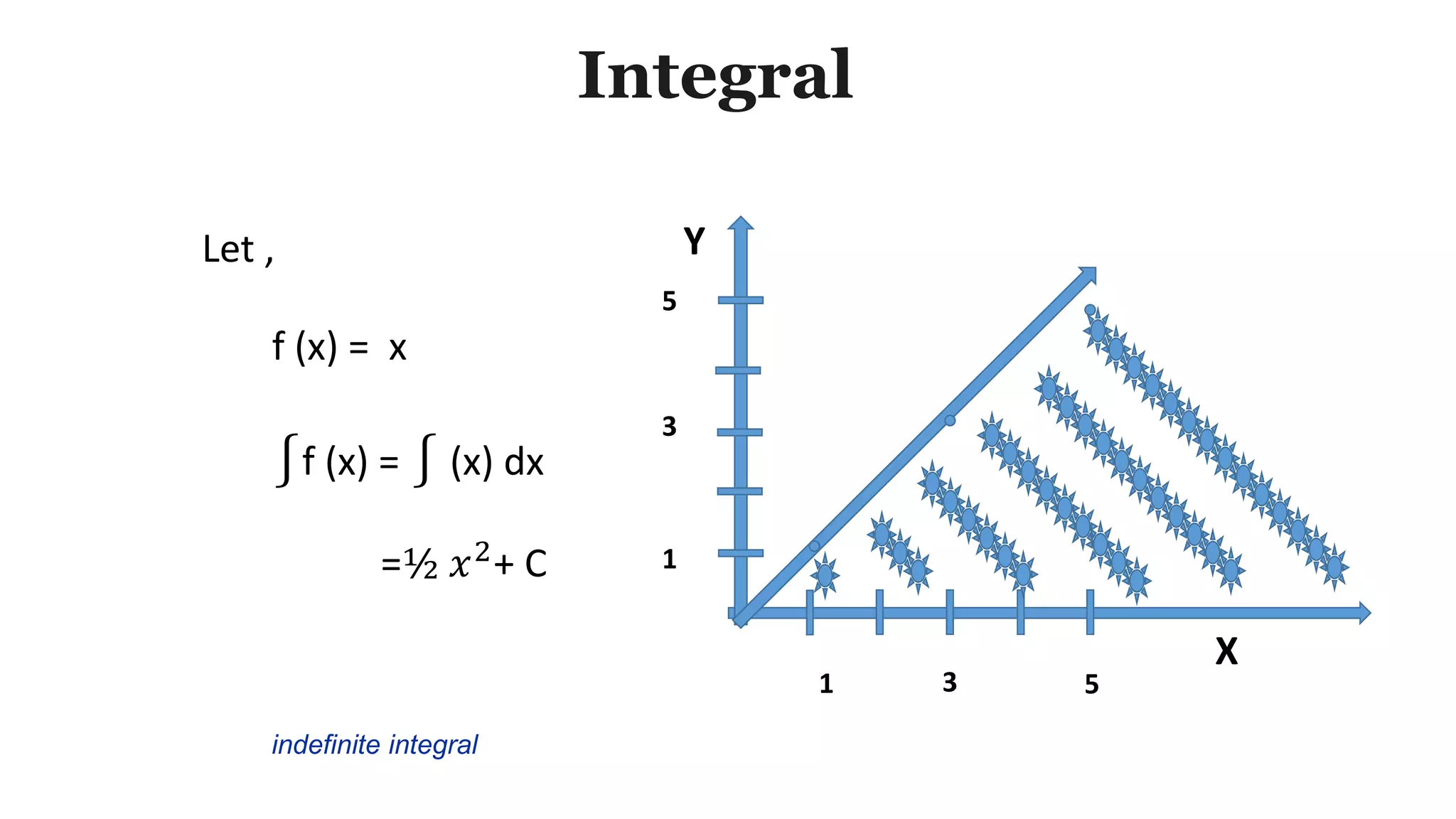
Let , Y
X
1 3 5
1
3
5
f (x) = x
0
= 0
3
𝑥 𝑑𝑥
=[½ 𝑥2
]0
3
=1/2 (9-0)
=4.5
1
2
∗ 𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 ∗ 𝐻𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡
=0.5 *3 *3
=4.5
finite integral](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/habib152-15-6040-170222173340/75/Basic-Integral-5-2048.jpg)

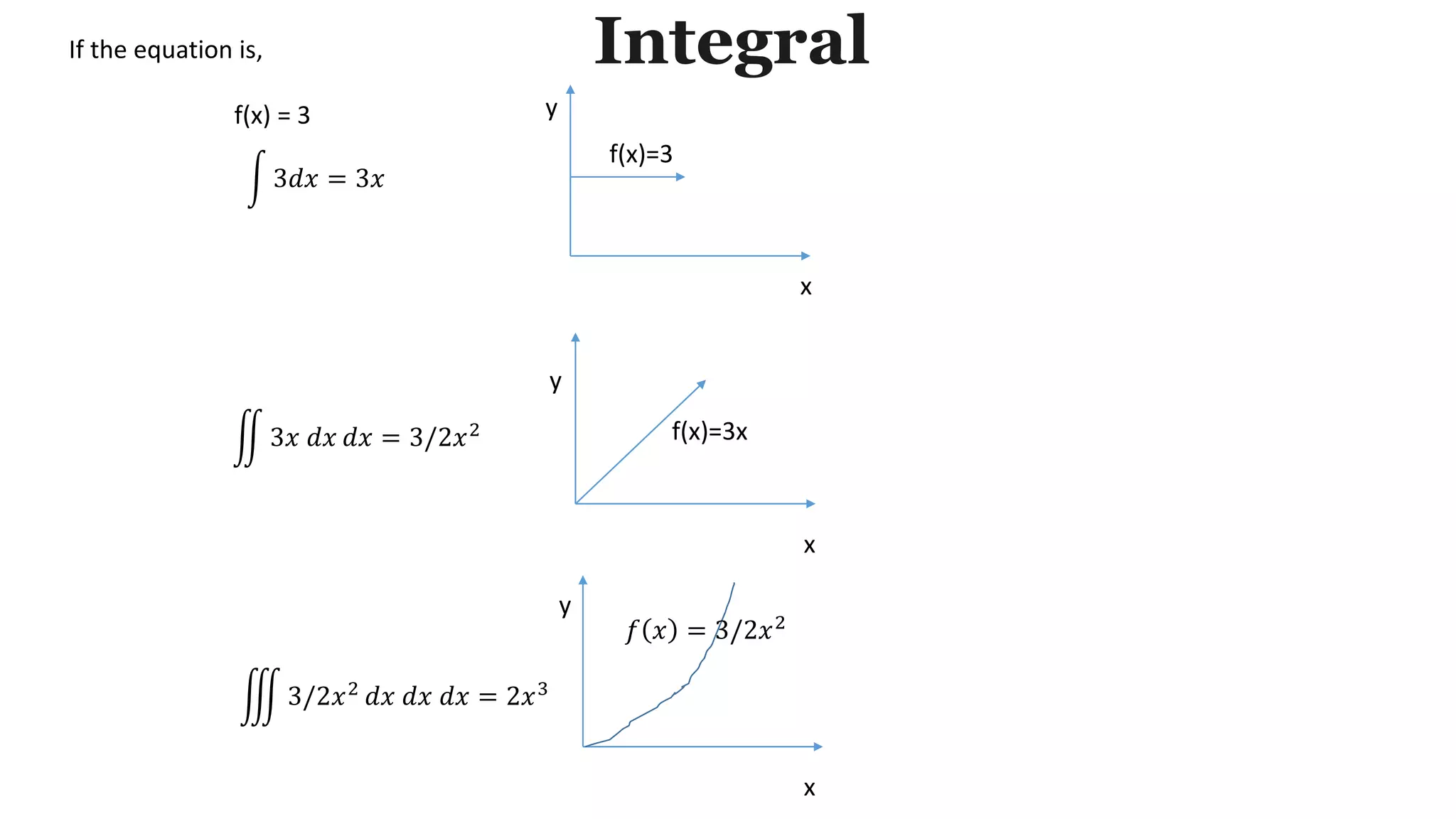


The document discusses integrals and their use in calculating areas and volumes. It defines an integral as combining infinitesimal data to determine displacement, area, volume, and other concepts. The document provides an example of calculating the indefinite integral of the function f(x)=x as 1/2x^2 + C and the definite integral from 0 to 3 of f(x)=x as 4.5 by using the integral formula and verification with the area of a rectangle formula.




![Integral
Let , Y
X
1 3 5
1
3
5
f (x) = x
0
= 0
3
𝑥 𝑑𝑥
=[½ 𝑥2
]0
3
=1/2 (9-0)
=4.5
1
2
∗ 𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 ∗ 𝐻𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡
=0.5 *3 *3
=4.5
finite integral](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/habib152-15-6040-170222173340/75/Basic-Integral-5-2048.jpg)


