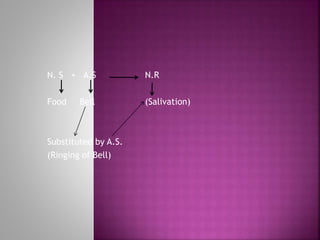
This document summarizes two important theories of learning: classical conditioning and operant conditioning. Classical conditioning, proposed by Ivan Pavlov, involves associating an unconditioned stimulus that naturally elicits a response with a conditioned stimulus, until the conditioned stimulus comes to elicit the response on its own. Operant conditioning, proposed by B.F. Skinner, is based on the idea that learning is a function of changes in behavior due to consequences. Reinforcement and punishment are used to modify occurrences of behaviors.