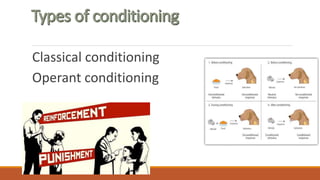
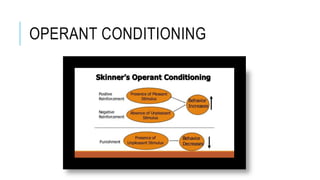
Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behavior, encompassing various sub-fields like human development and clinical psychology. The document discusses key theories in psychology, particularly behaviorism and its founders such as John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner, emphasizing the roles of classical and operant conditioning in understanding behavior. Behaviorism focuses on observable behavior and posits that behavior is influenced by environmental conditions and reinforcement, while acknowledging its strengths and limitations.