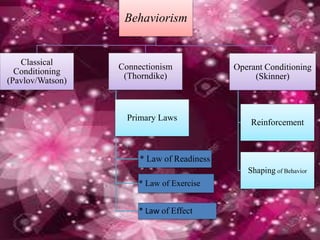
The document discusses the behaviorist perspective, which focuses on observable and measurable behaviors that are learned through conditioning and reinforcement. It describes classical conditioning experiments by Pavlov and operant conditioning by Skinner, which use positive and negative reinforcement to modify behaviors. Classical conditioning involves pairing a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a response, while operant conditioning modifies behaviors based on their consequences. [/SUMMARY]