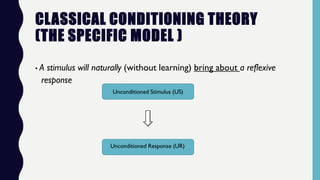
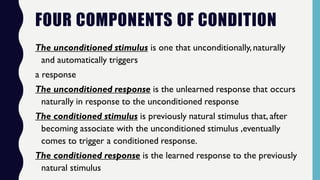
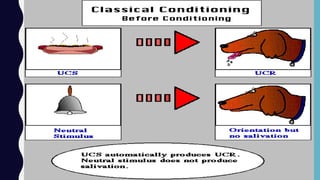
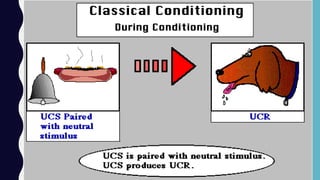
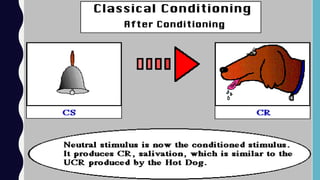
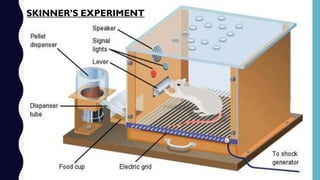
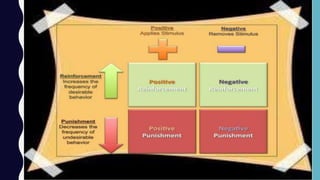
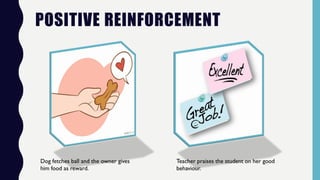
This document provides an overview of classical and operant conditioning. It discusses how classical conditioning involves forming associations between stimuli through repeated pairing, as discovered by Ivan Pavlov, and identifies the key components of classical conditioning. It also defines operant conditioning as modifying behavior through reinforcement and punishment based on consequences, as outlined by B.F. Skinner's experiments with rats pressing levers. The document further explains the concepts of reinforcement, both positive and negative, as well as punishment, both positive and negative, in operant conditioning.