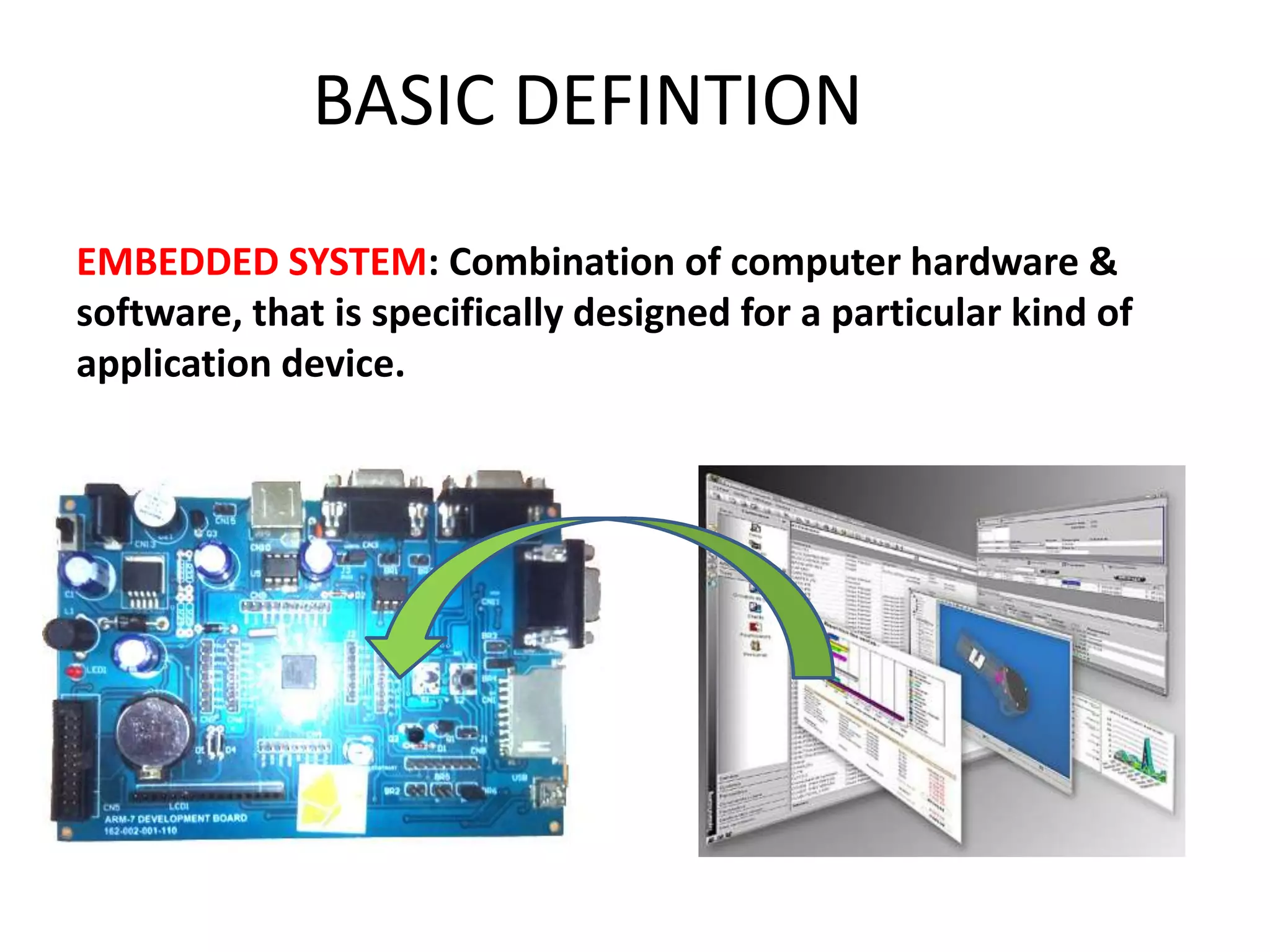
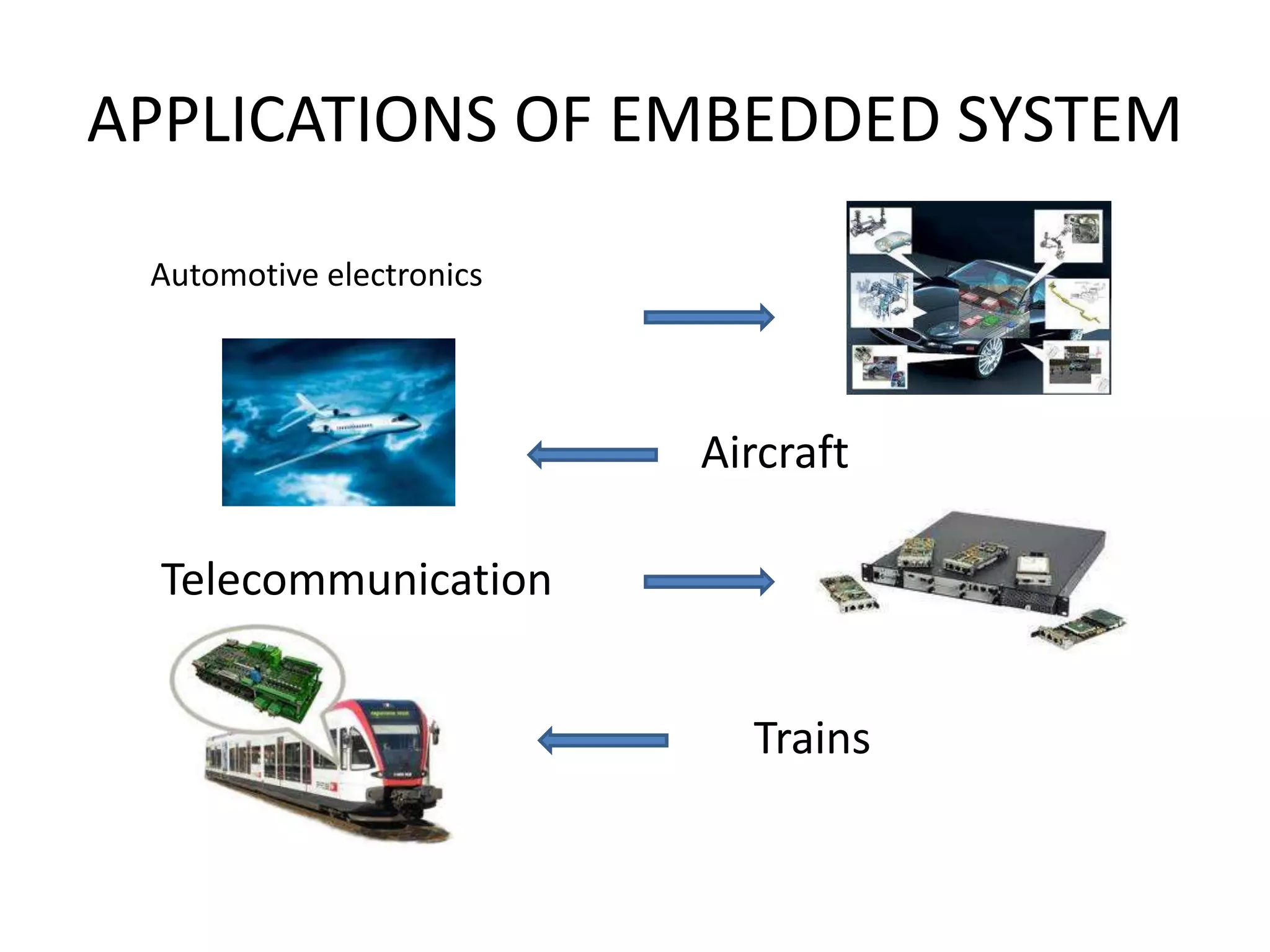
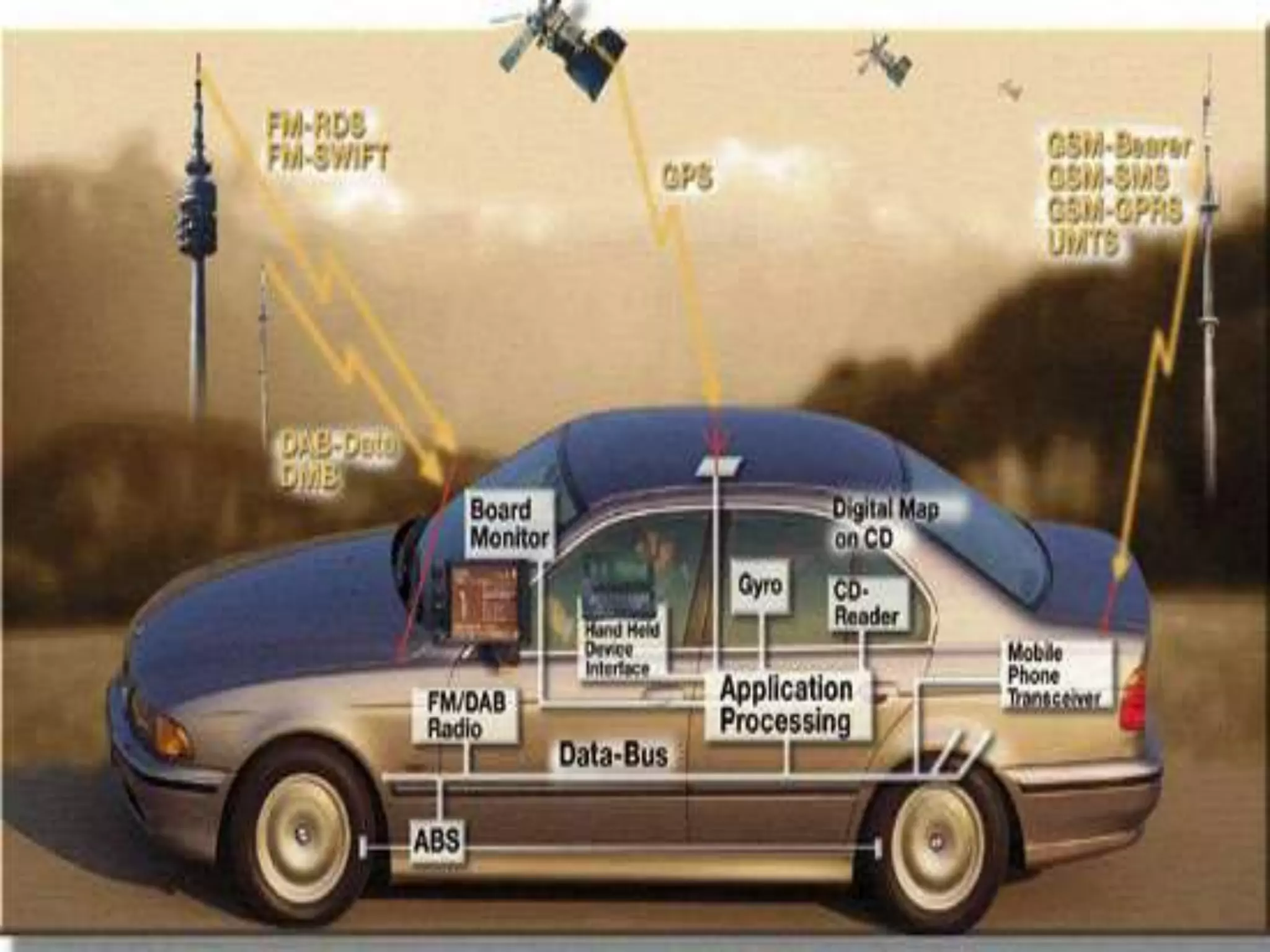
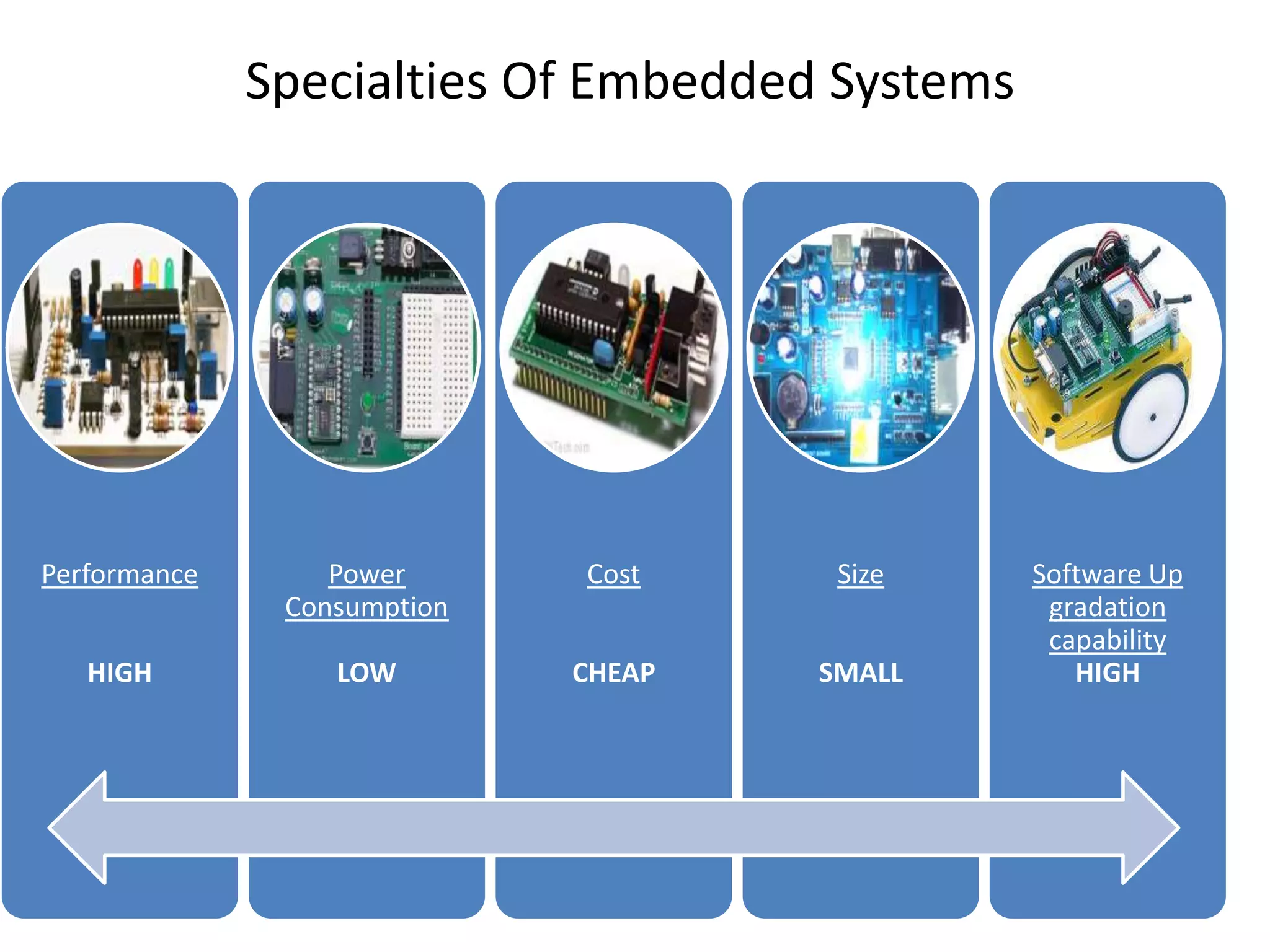
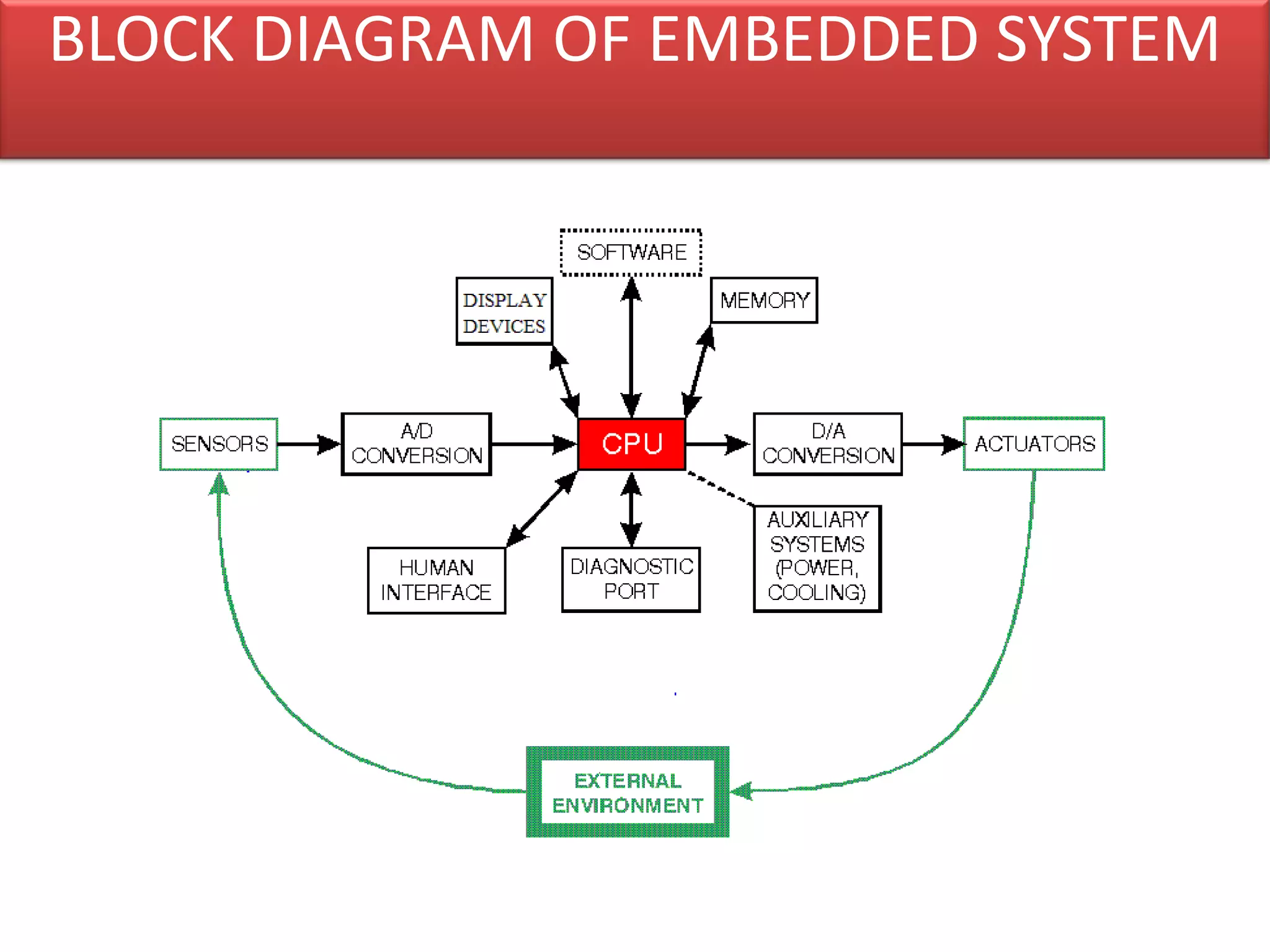
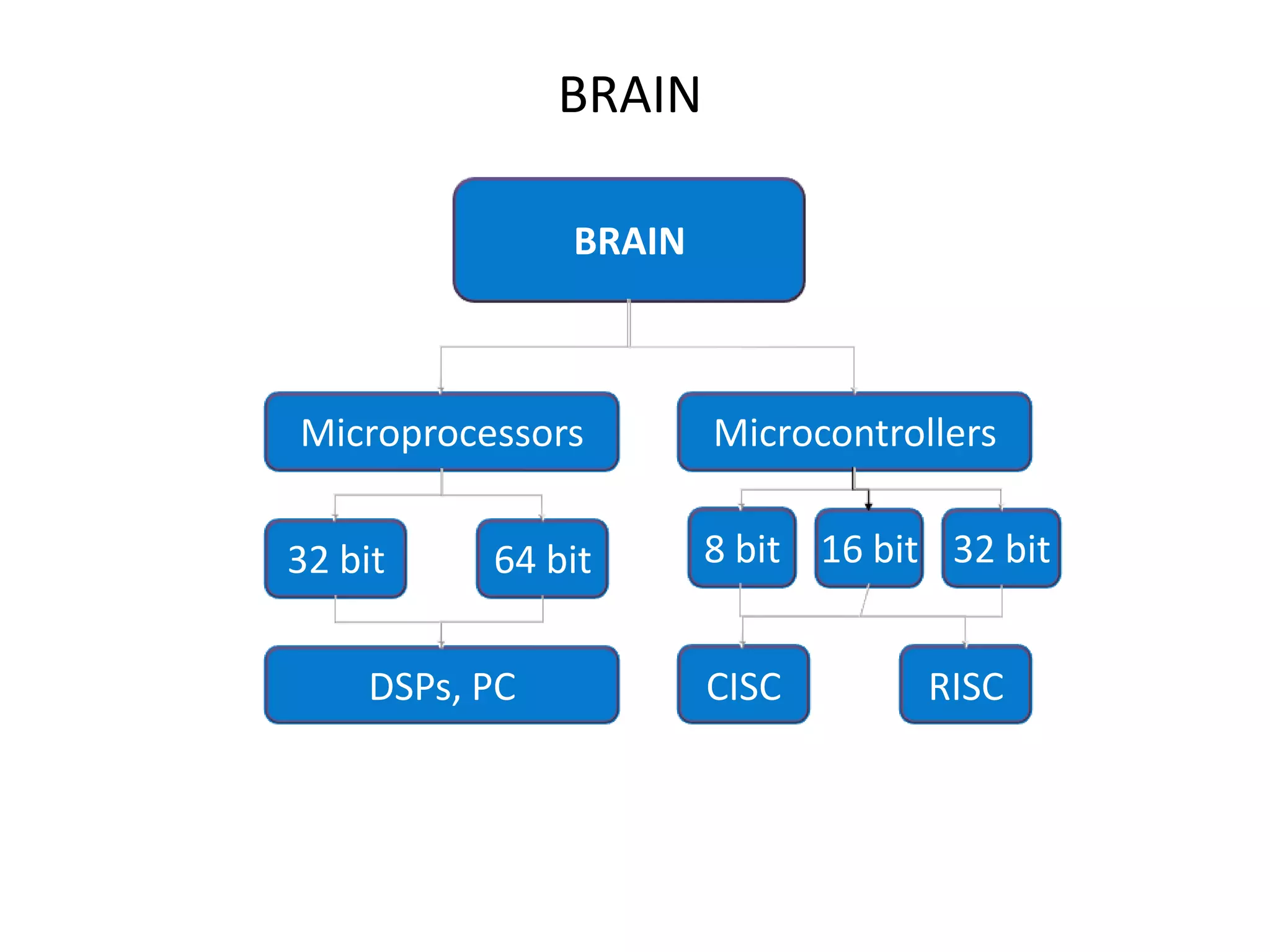
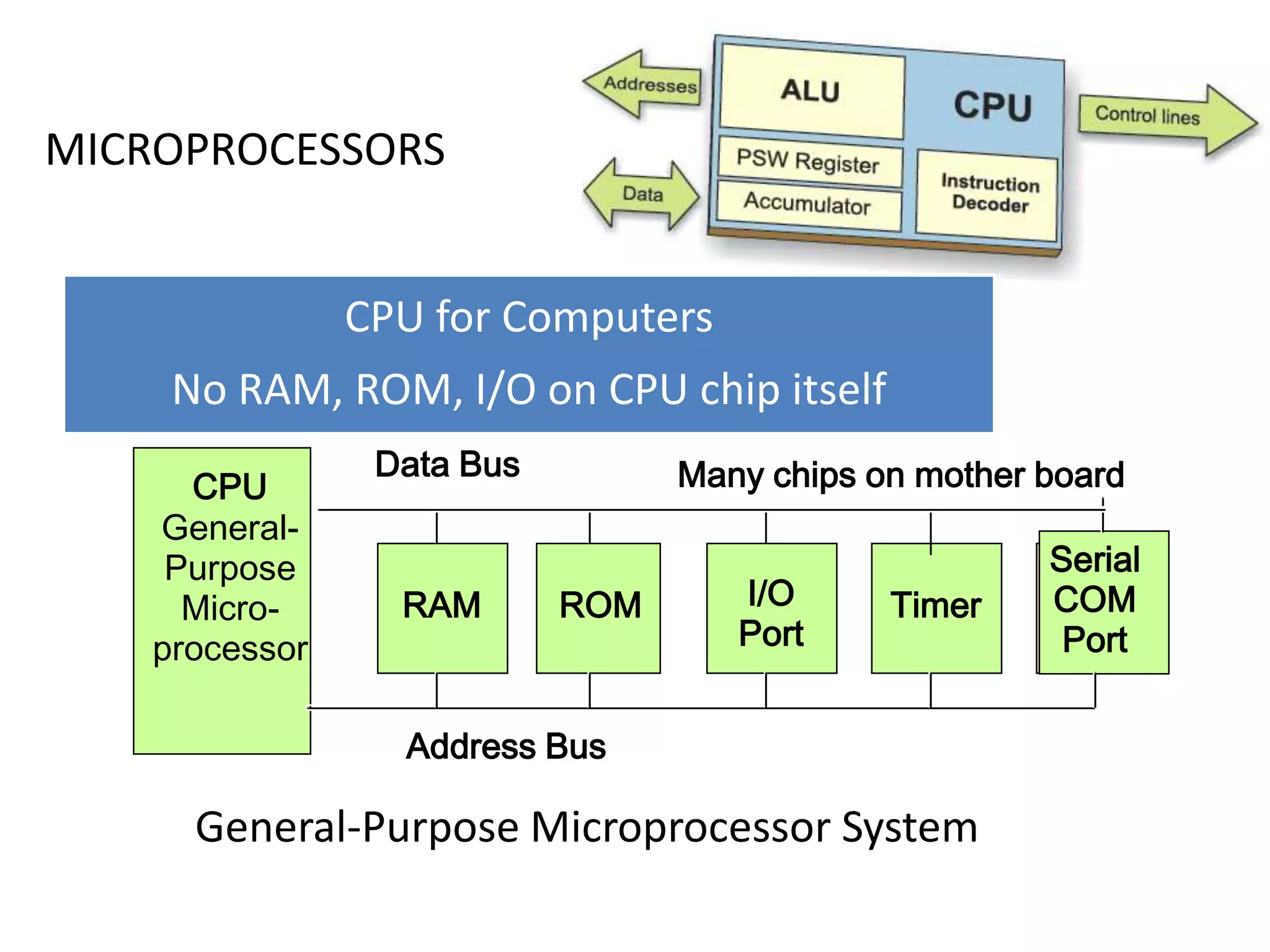
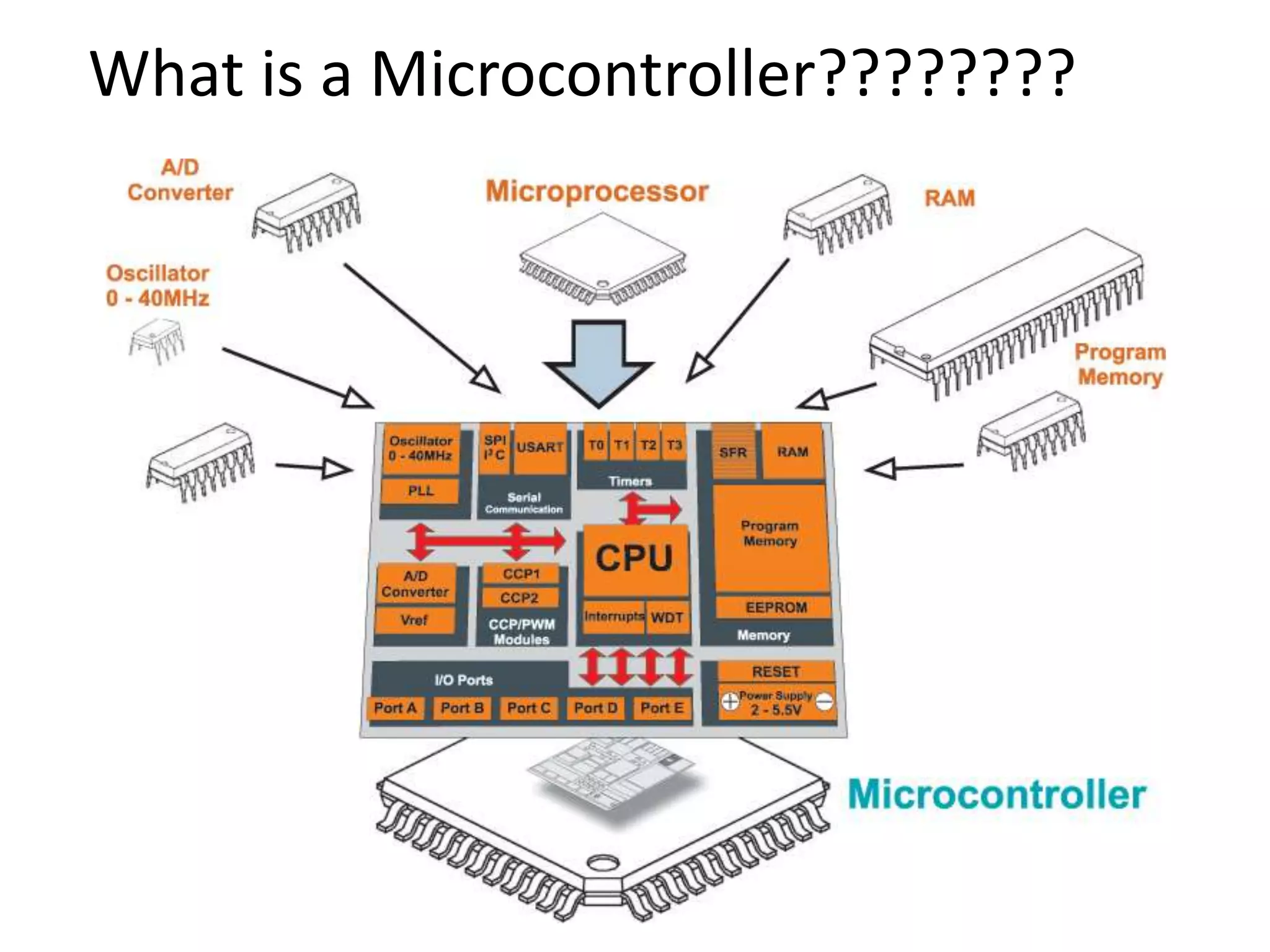
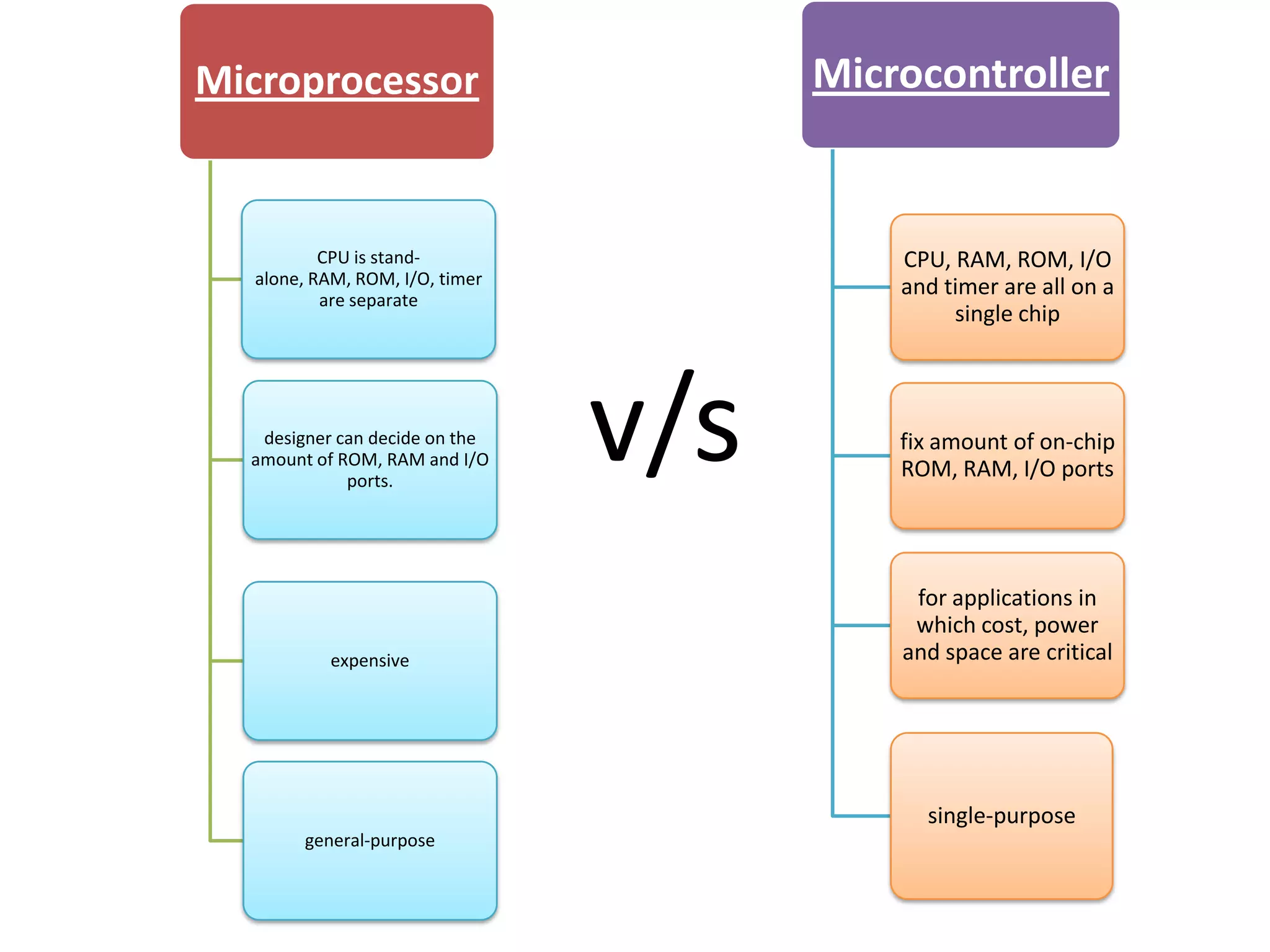
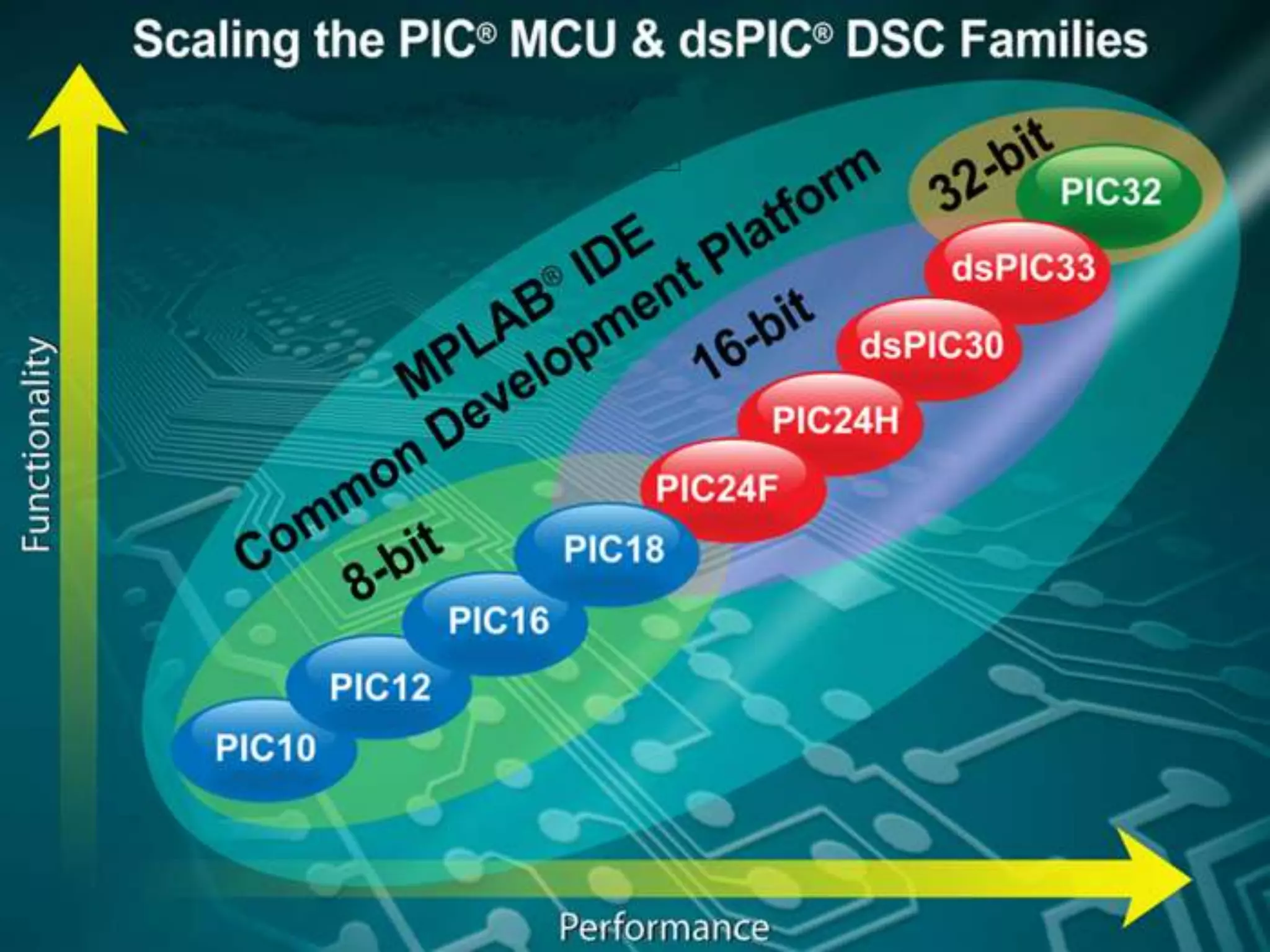
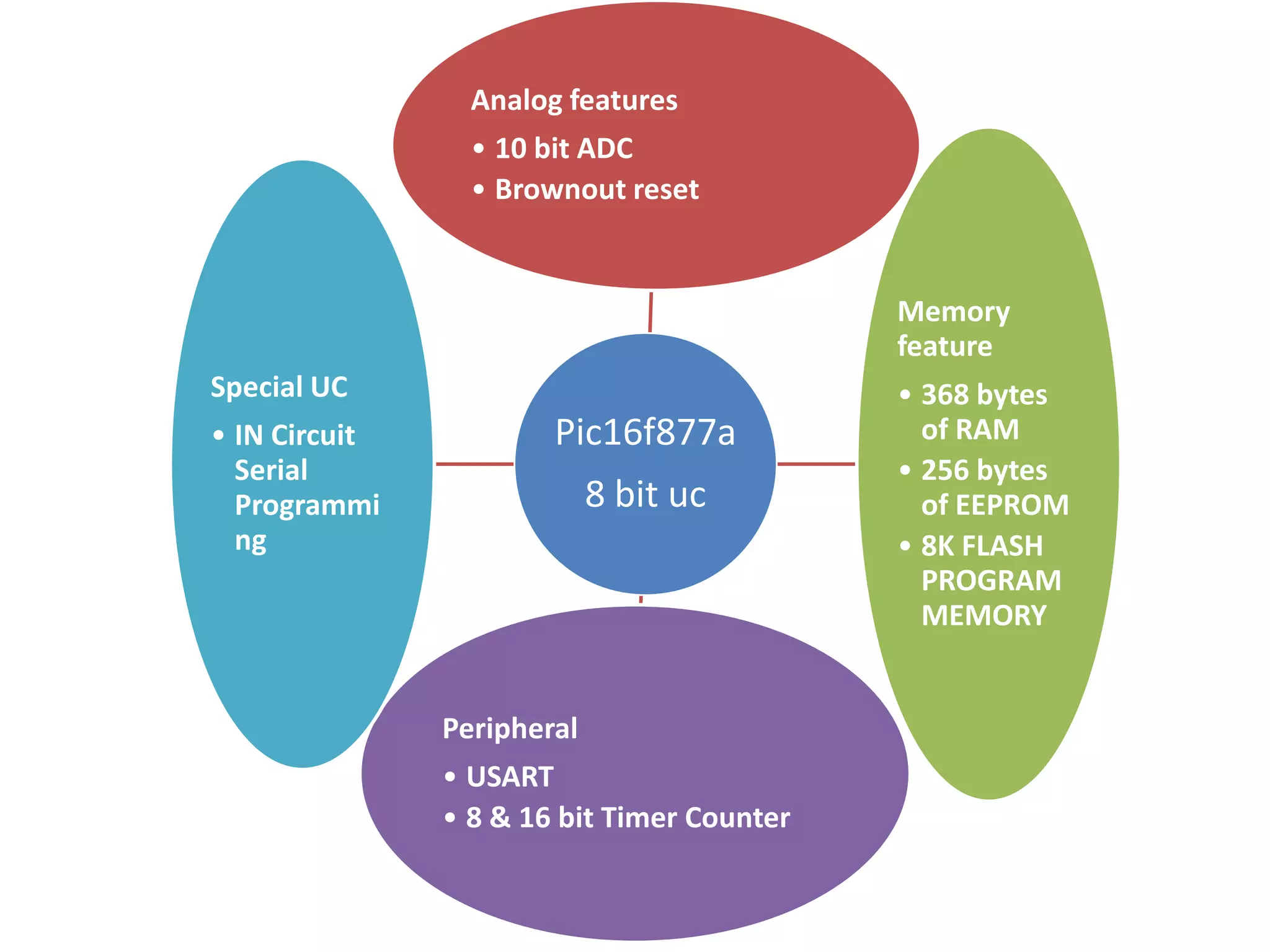
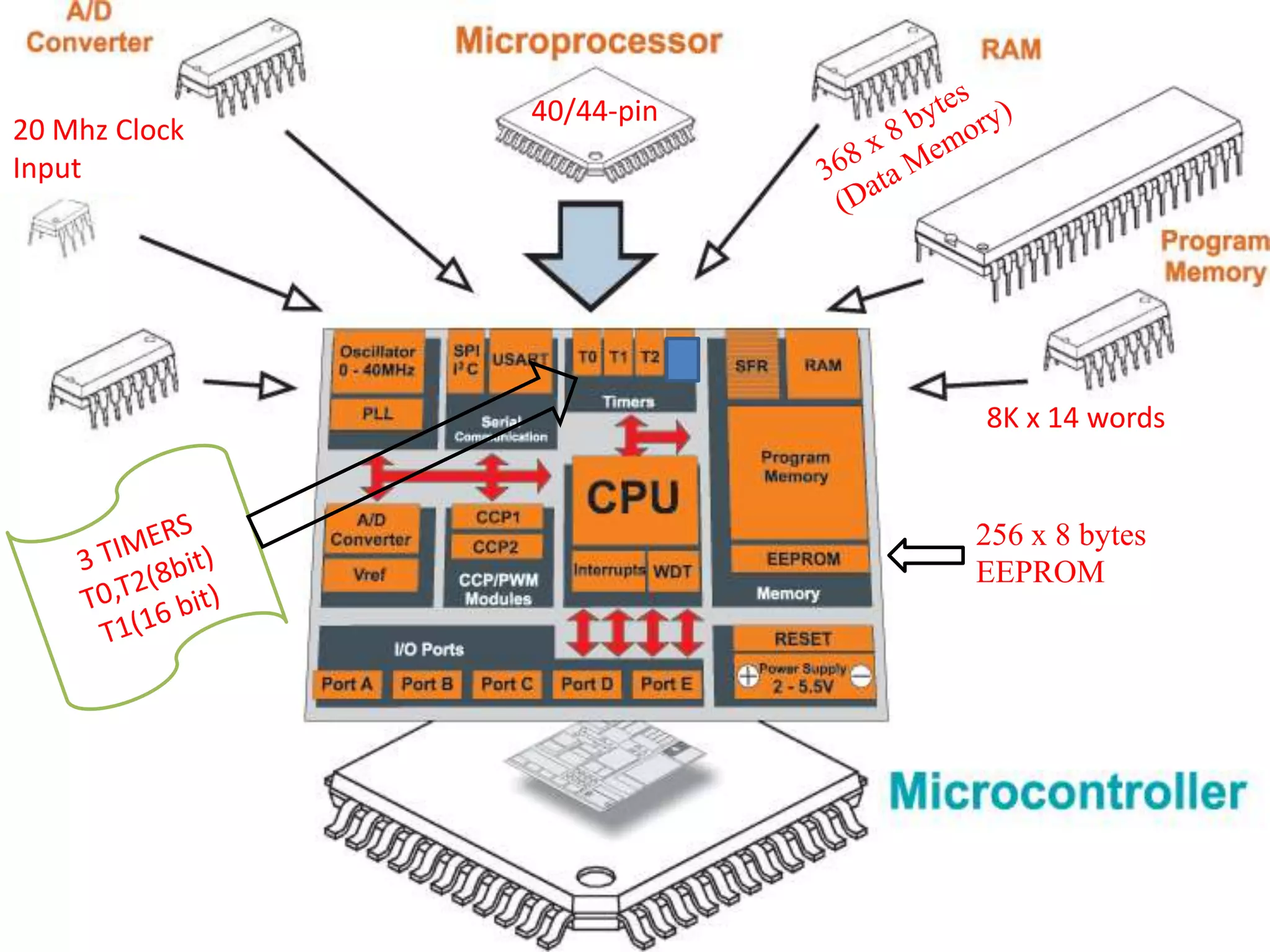
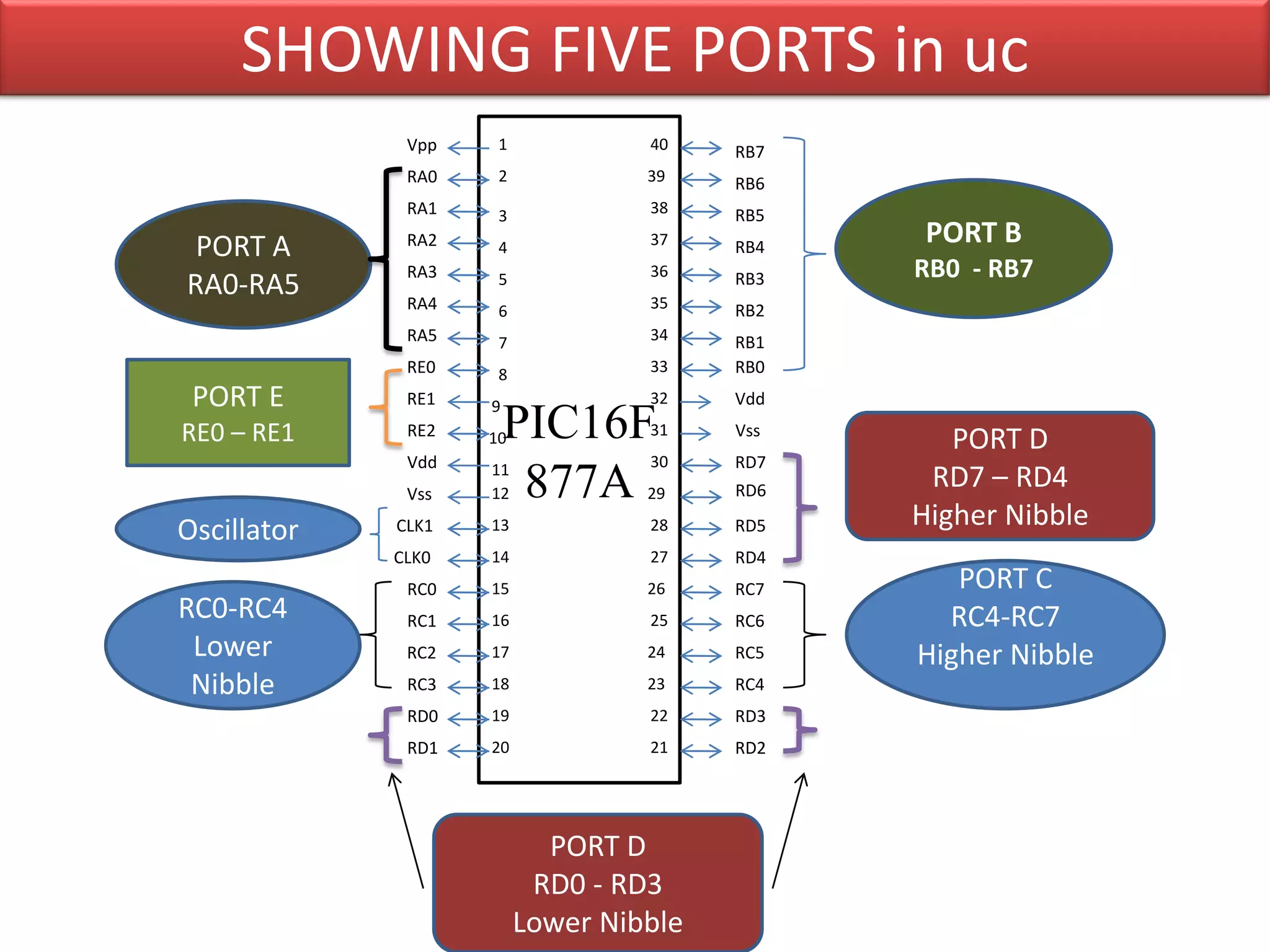
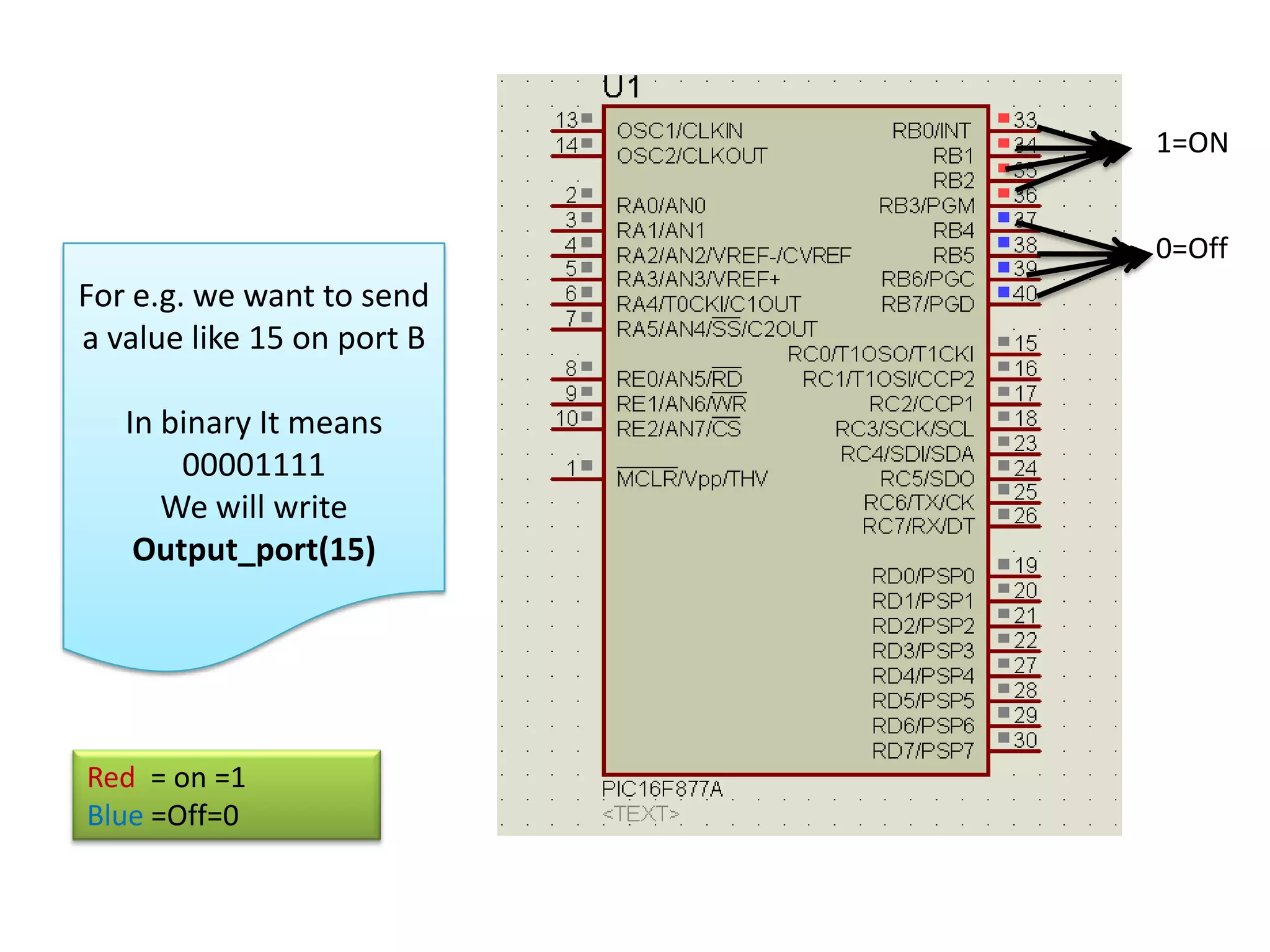
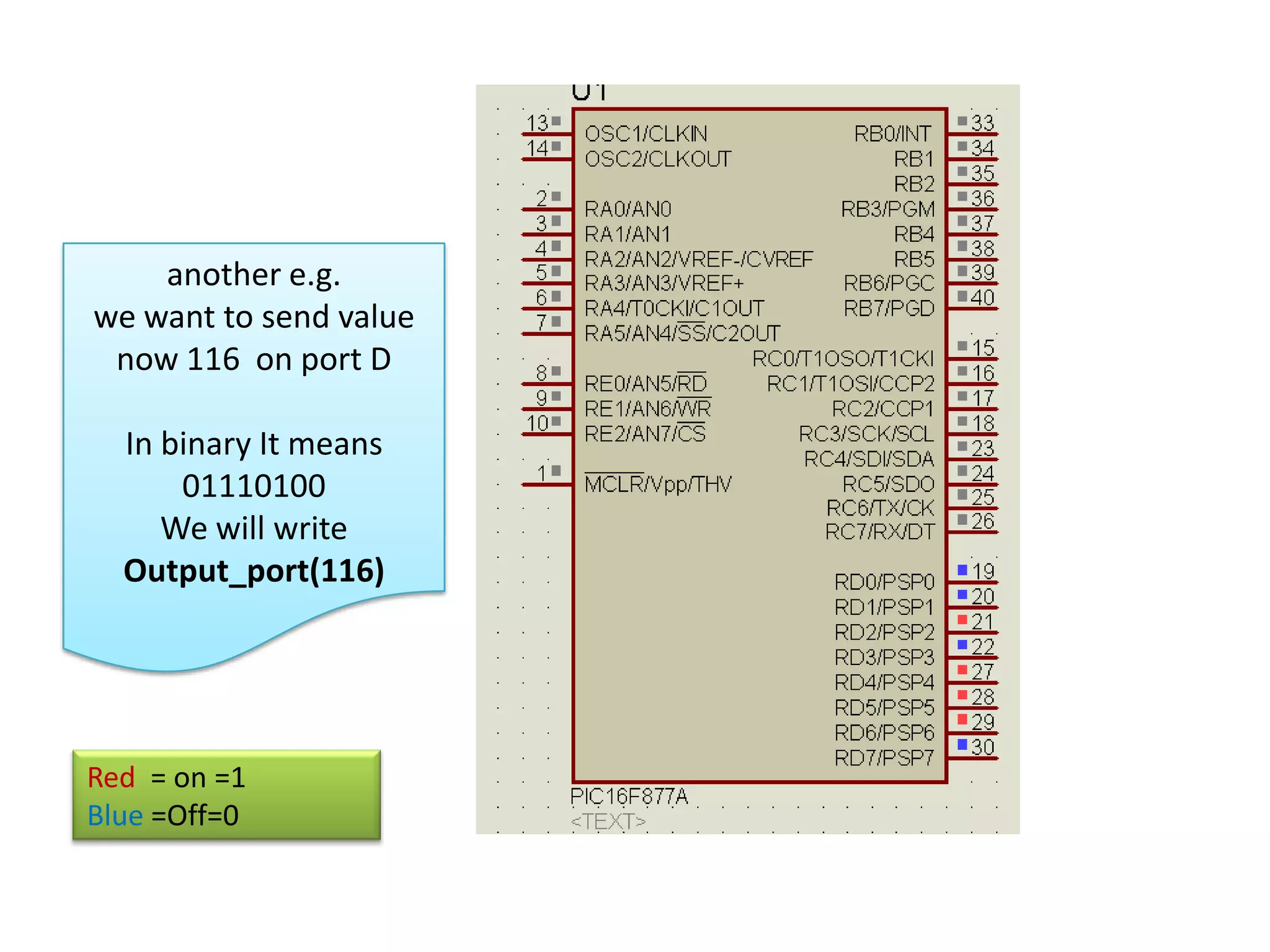
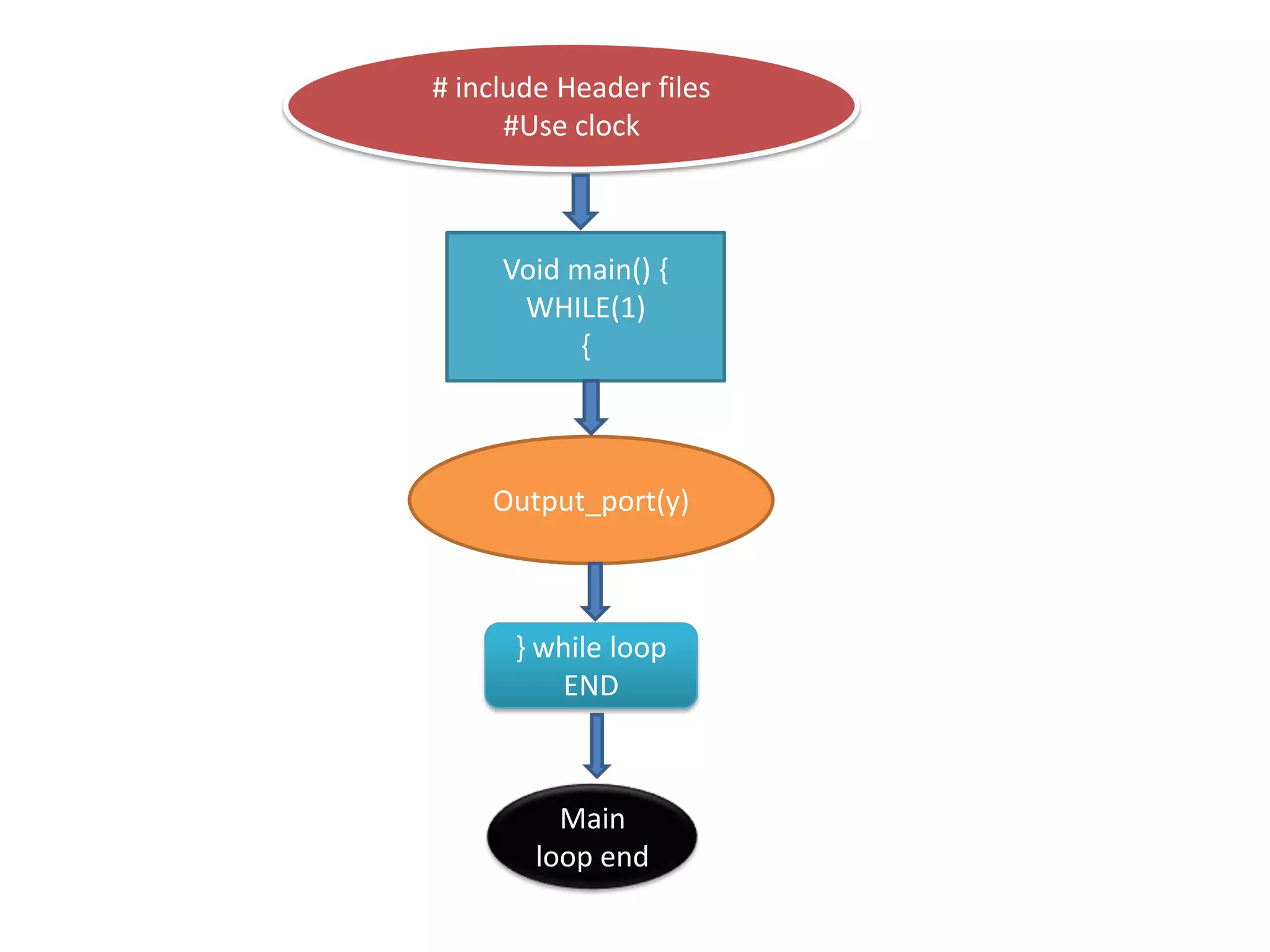
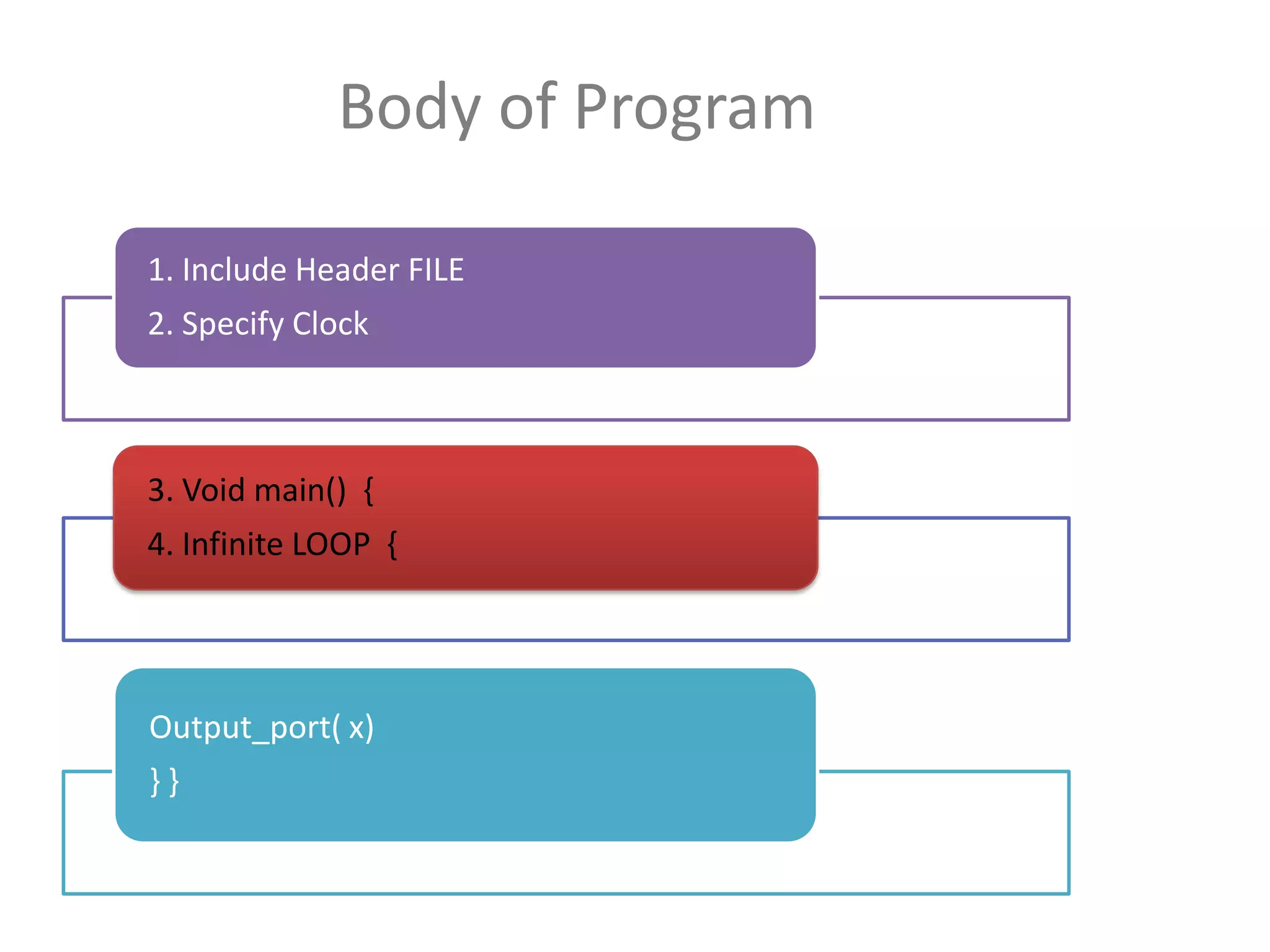
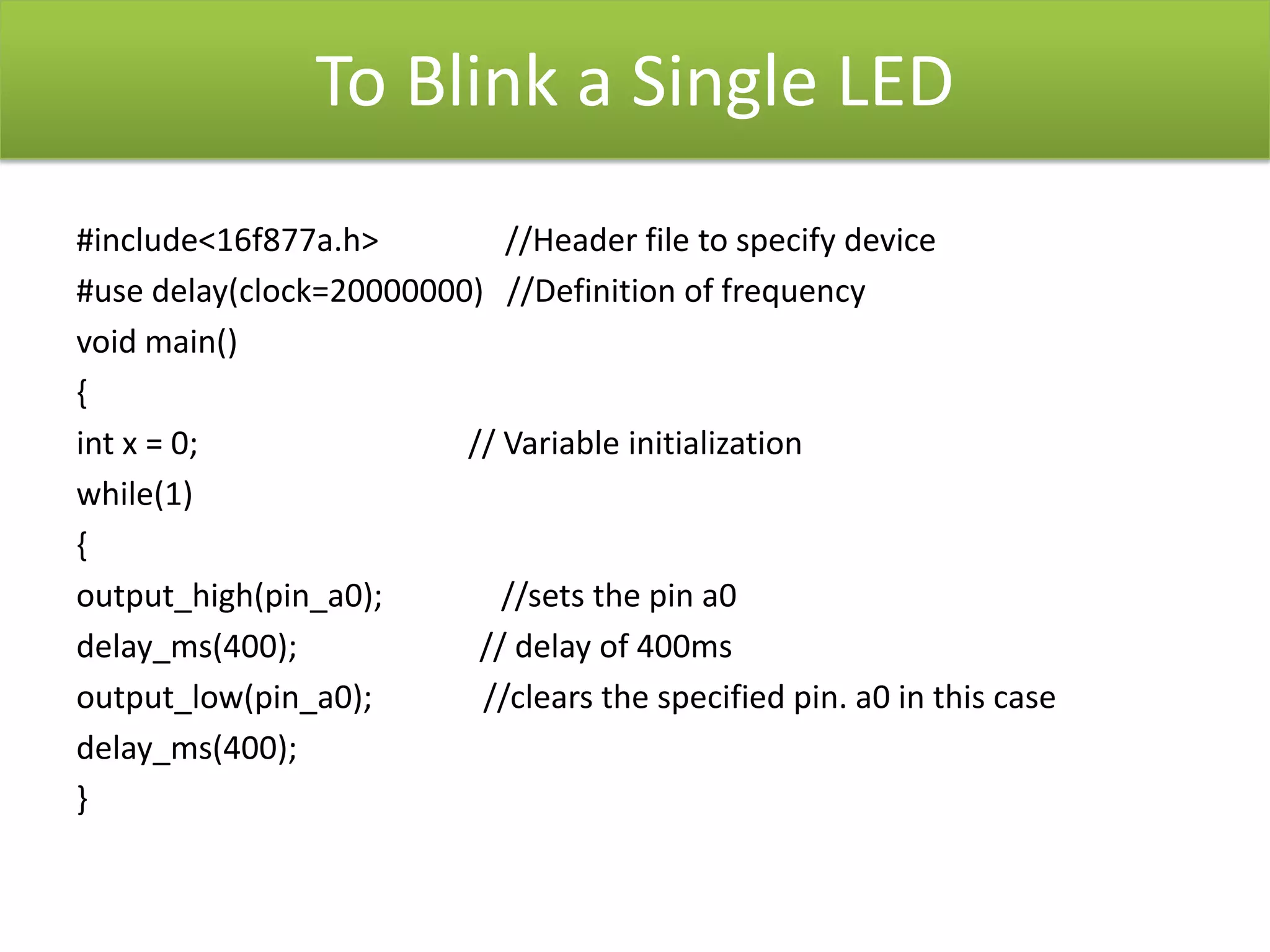
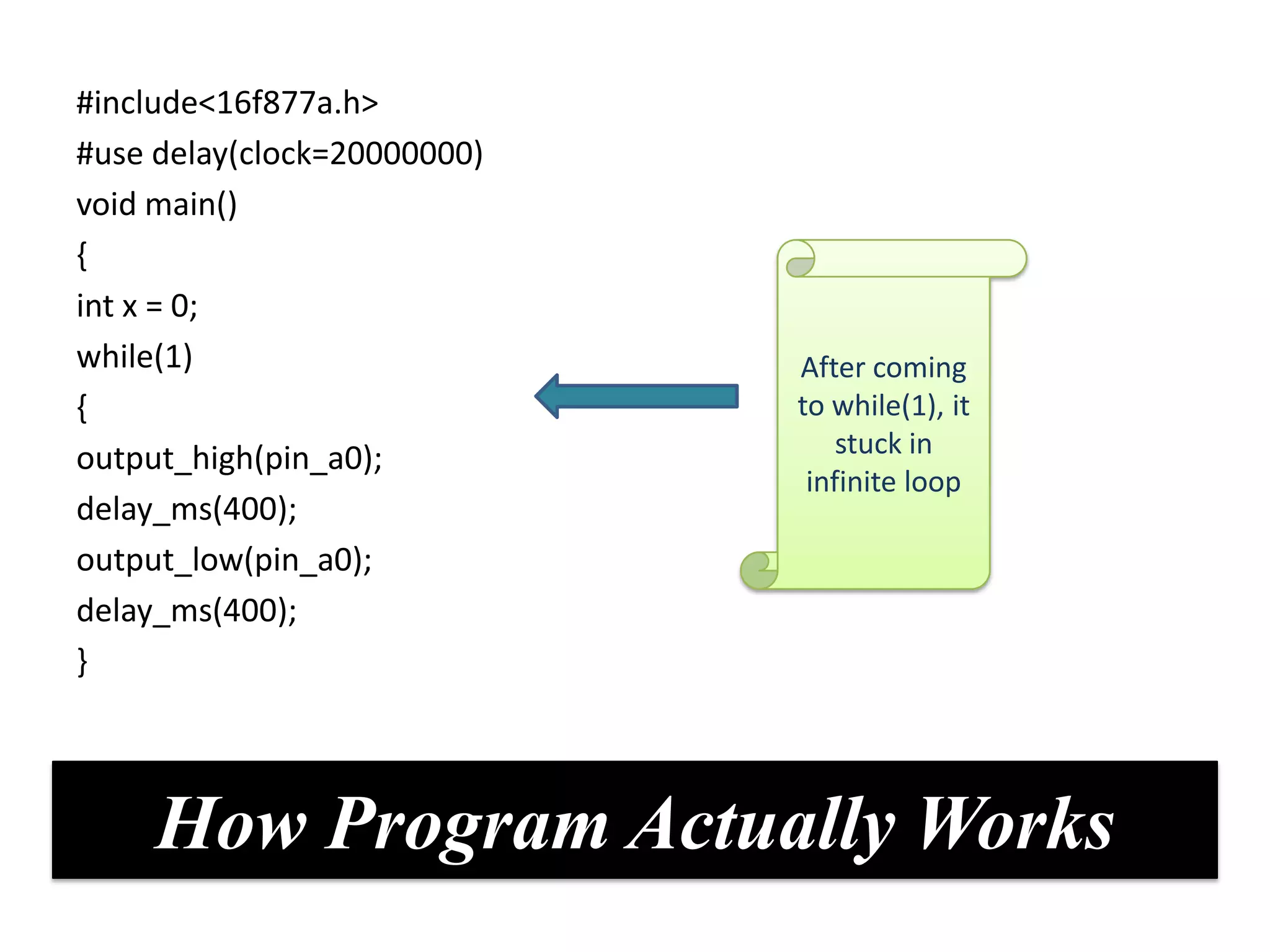
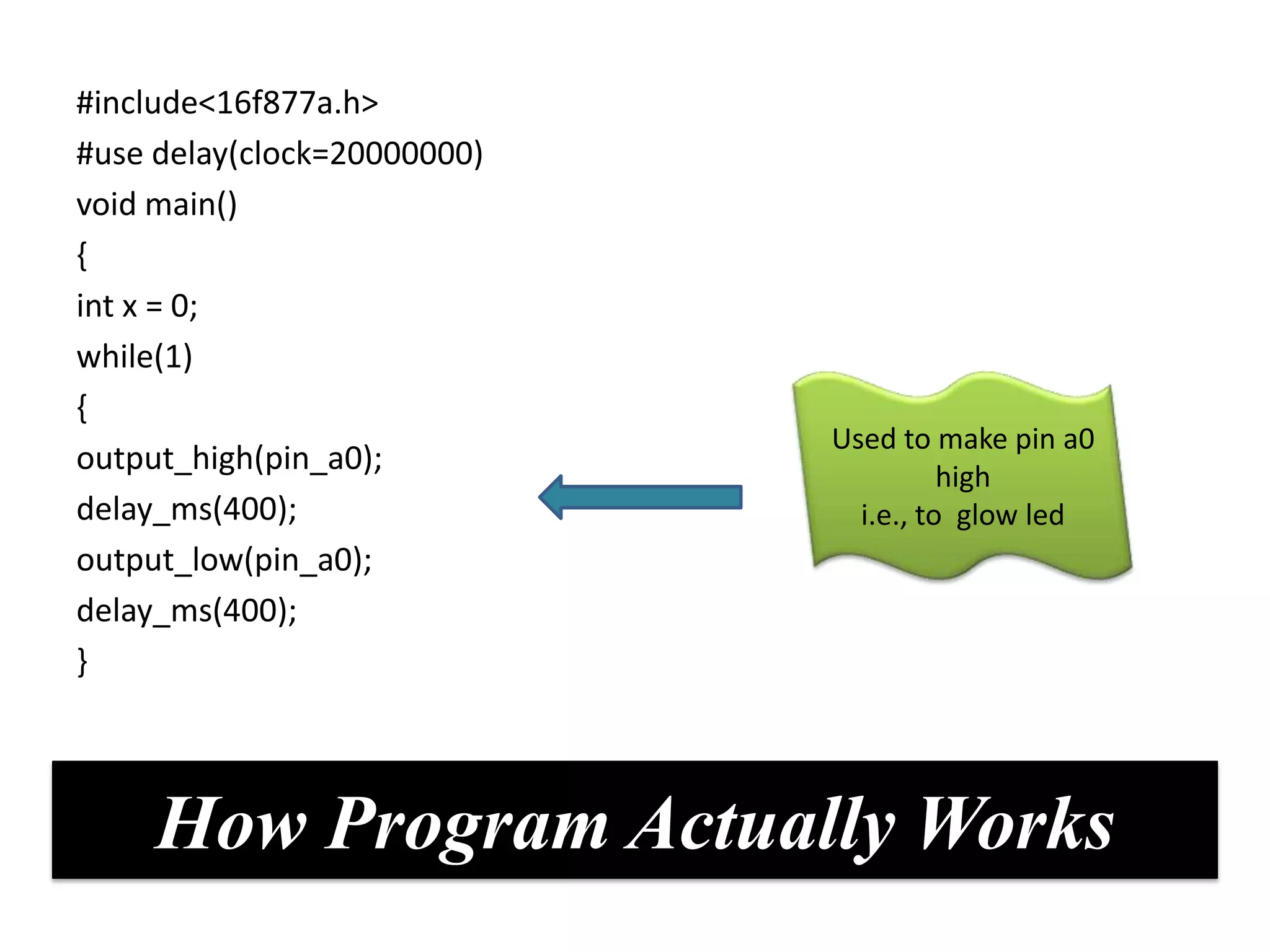
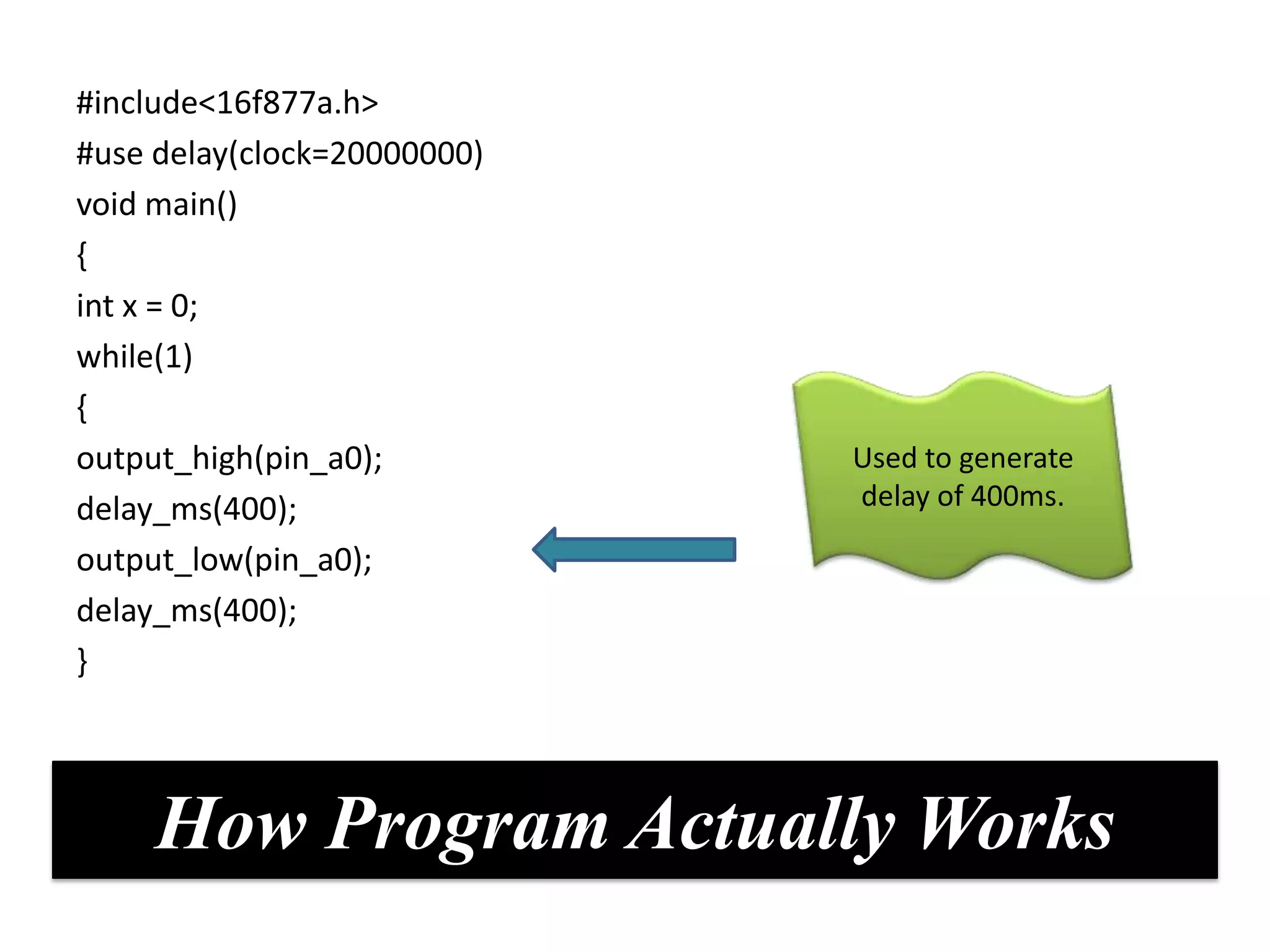
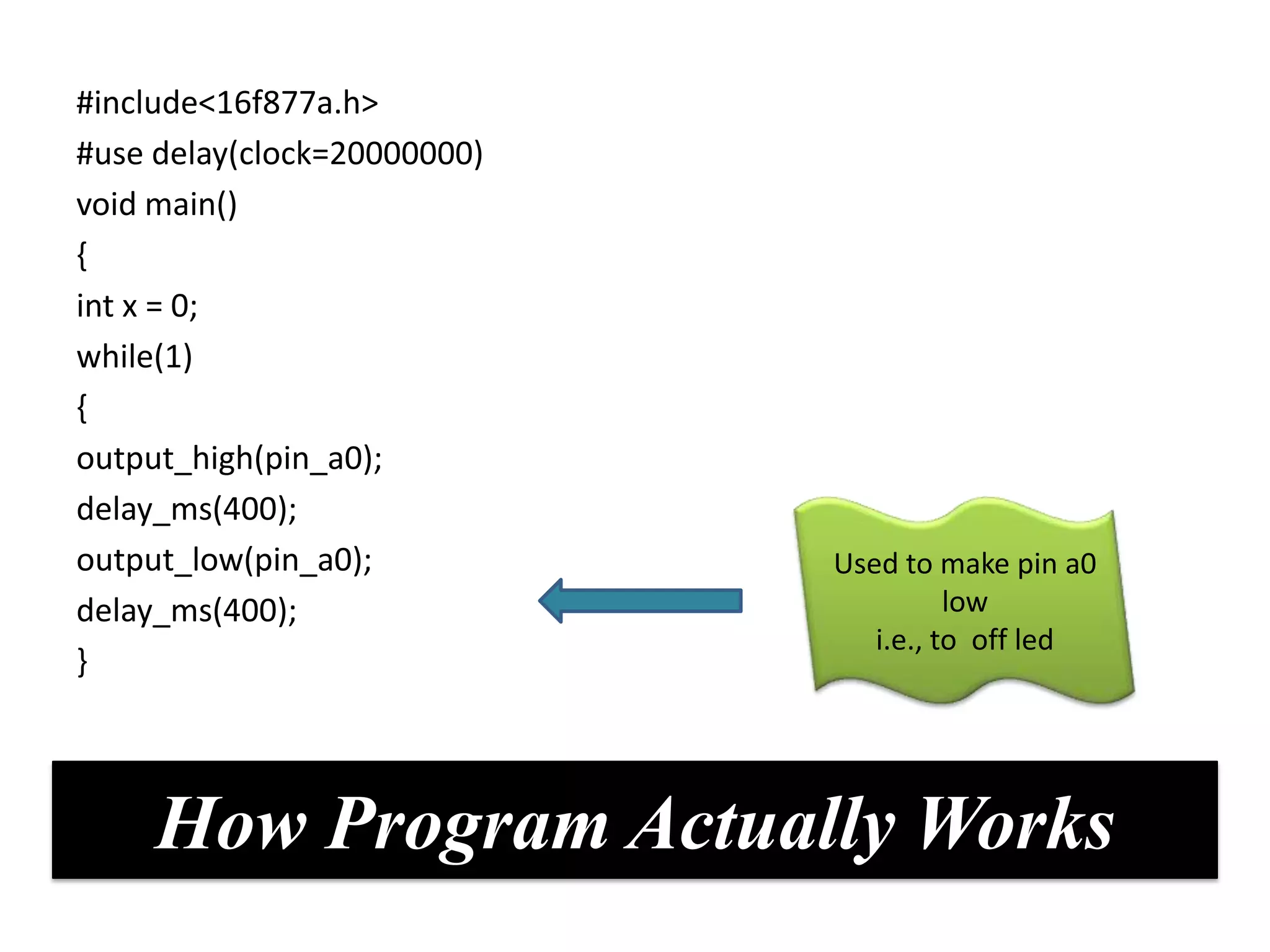
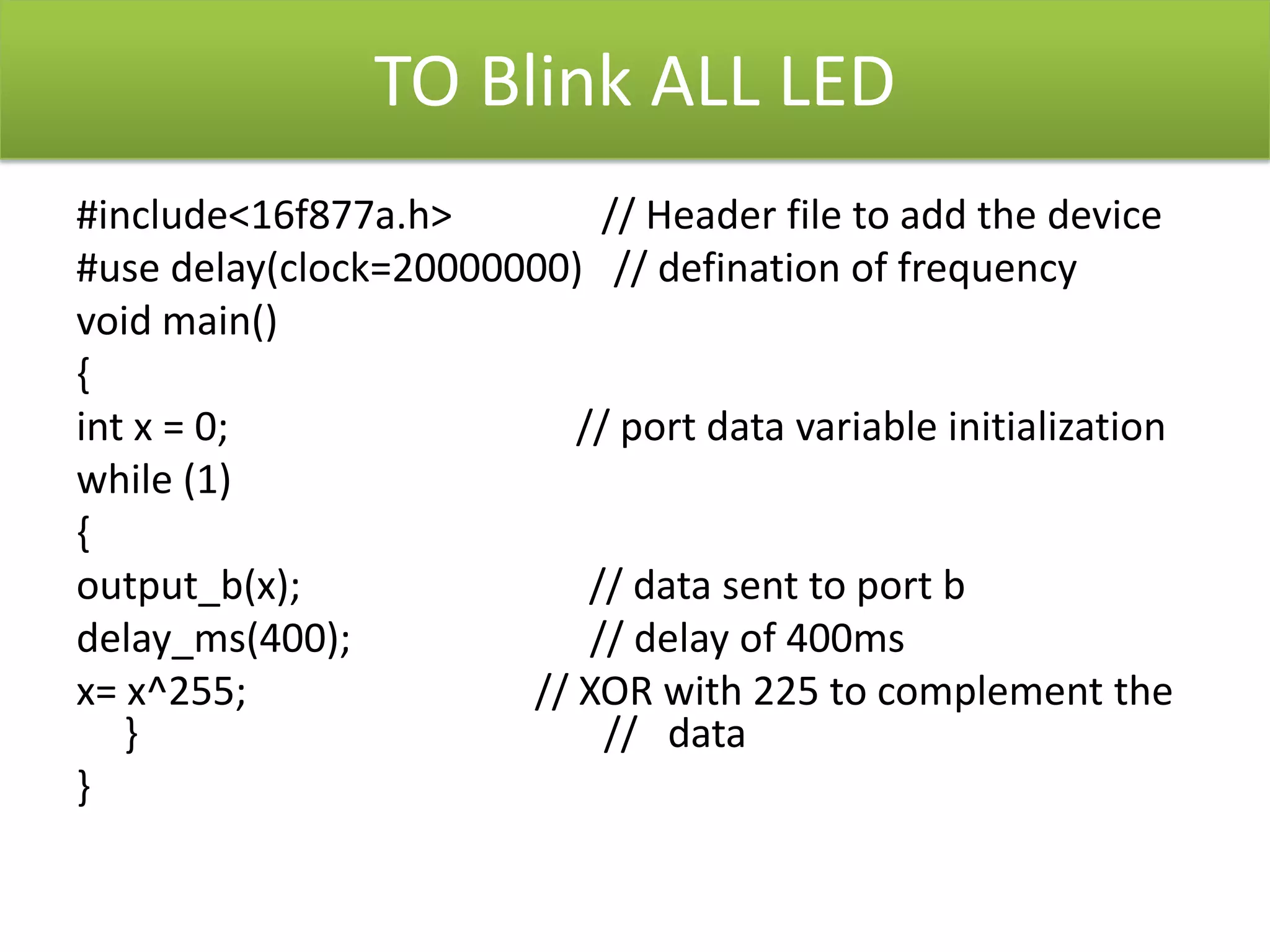
The document provides an overview of embedded systems and their components, particularly focusing on microcontrollers such as the PIC16F877A. It details the architecture, functionality, and programming of these systems, including examples of code to control outputs on various ports. Key features are highlighted, including microcontroller specifications, applications, and practical programming techniques for LED control.