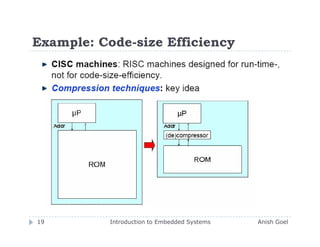
The document provides an introduction to embedded systems. It defines embedded systems as systems that use a microprocessor or microcontroller to perform a dedicated function. Embedded systems are found in everyday devices like cell phones, washing machines, and traffic signals. The document discusses the characteristics of embedded systems and provides examples. It also compares embedded systems to general purpose computers and describes typical embedded system architectures.