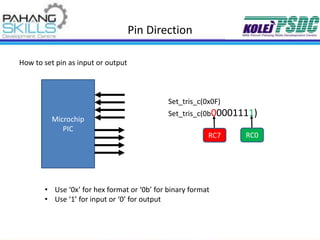
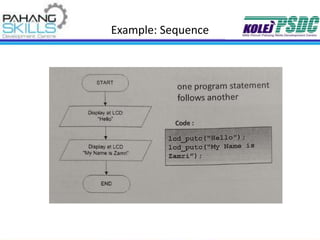
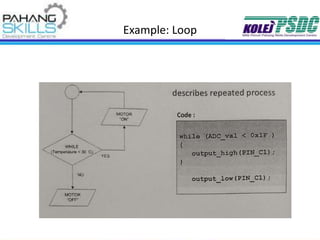
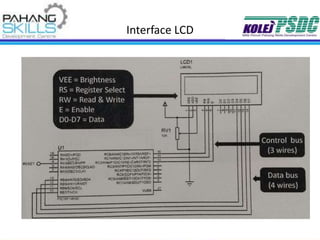
This document provides information about the PIC16F877A microcontroller. It discusses:
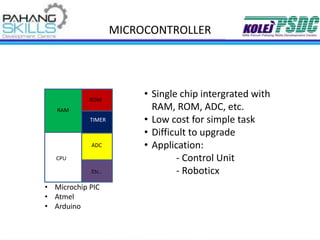
- The PIC16F877A is a popular 8-bit microcontroller with features like RAM, ROM, timers, ADC and I/O pins.
- It provides a block diagram showing the architecture and memory mapping of the chip.
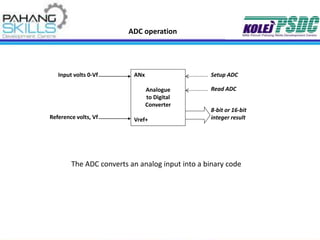
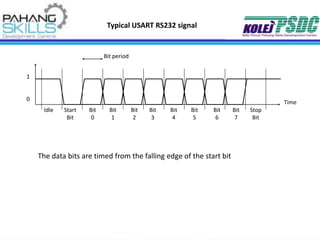
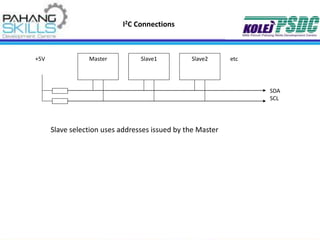
- Programming and interfacing aspects like I/O pin operation, ADC, interrupts and communication protocols are described.