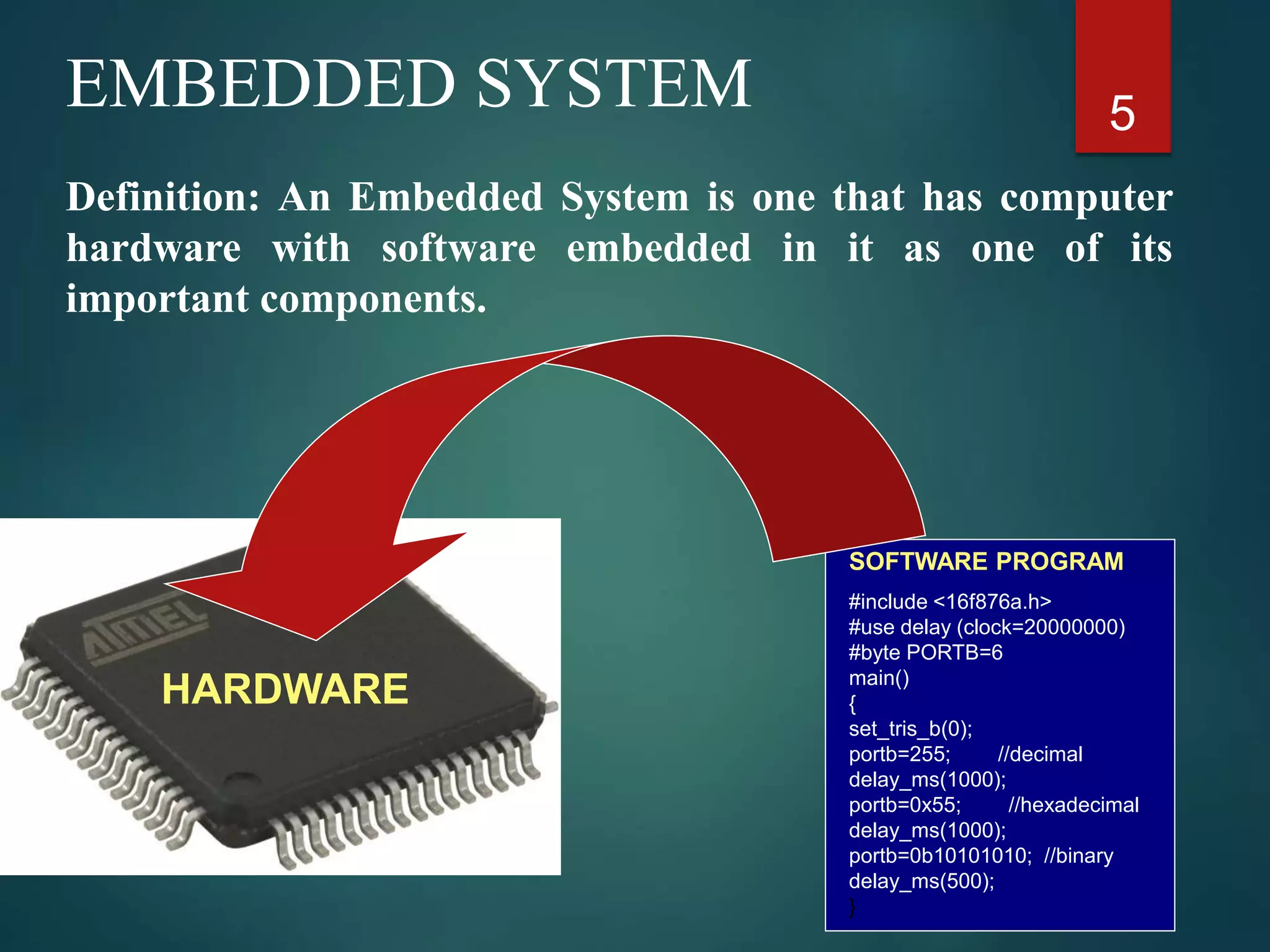
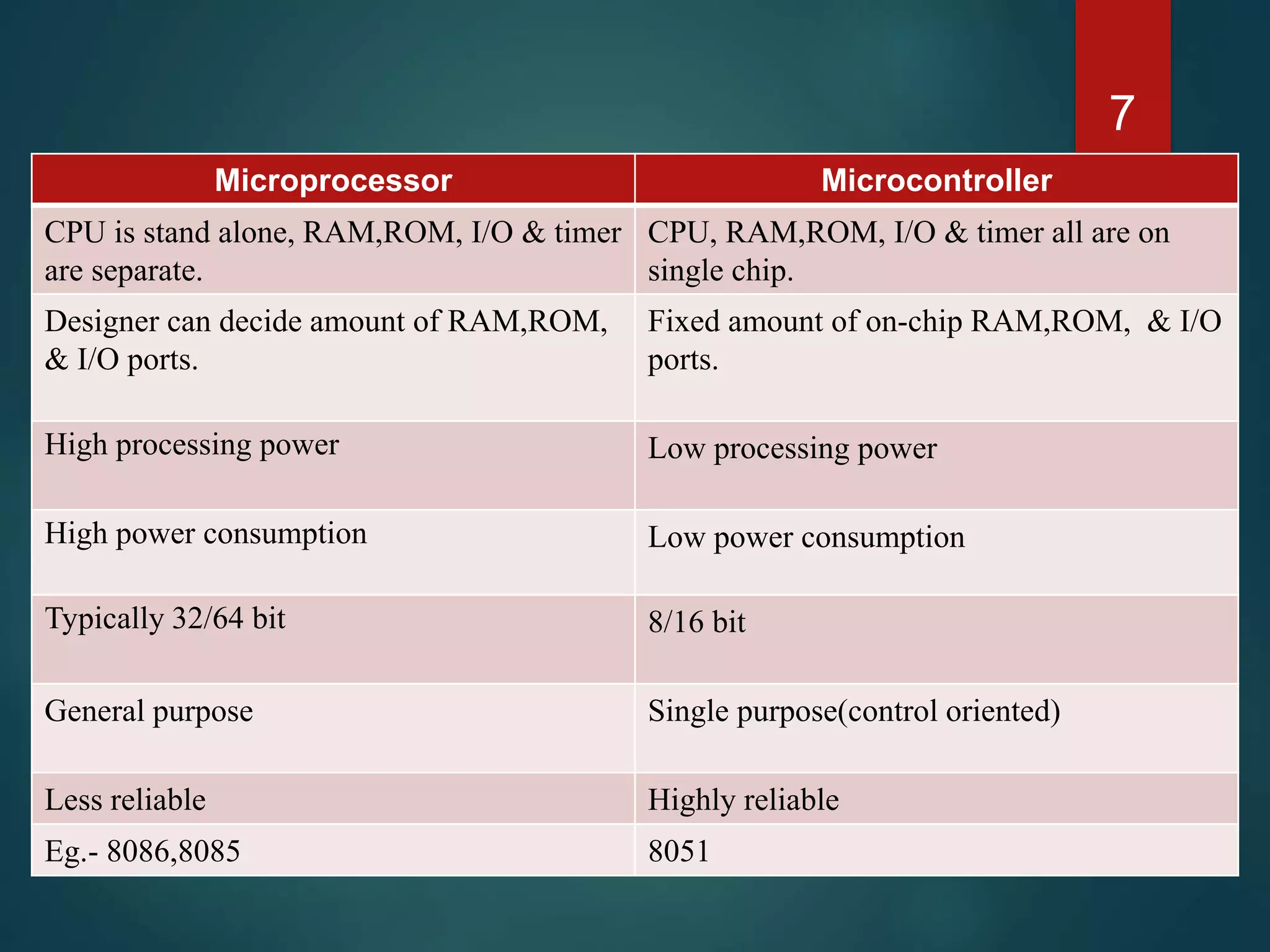
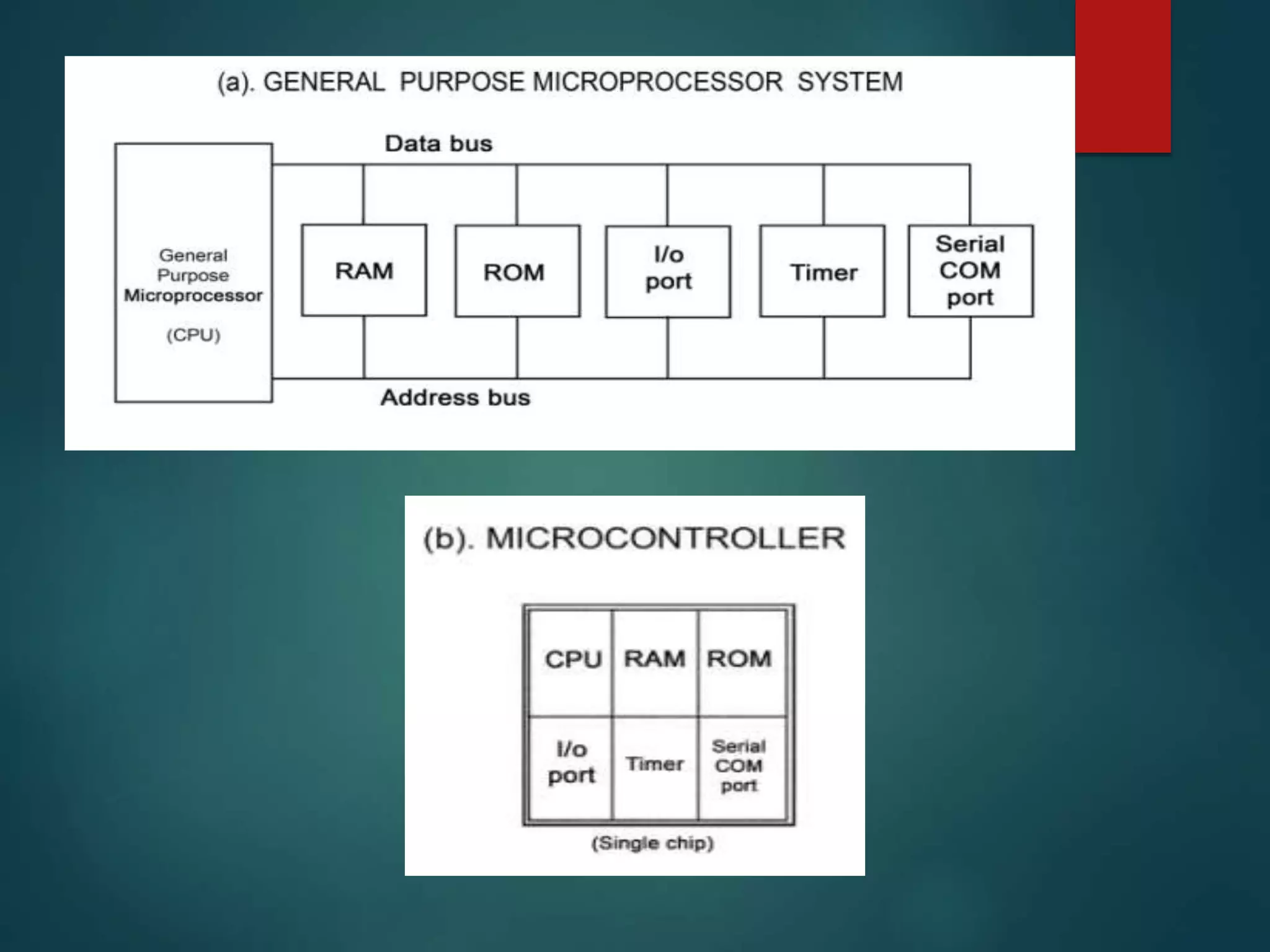
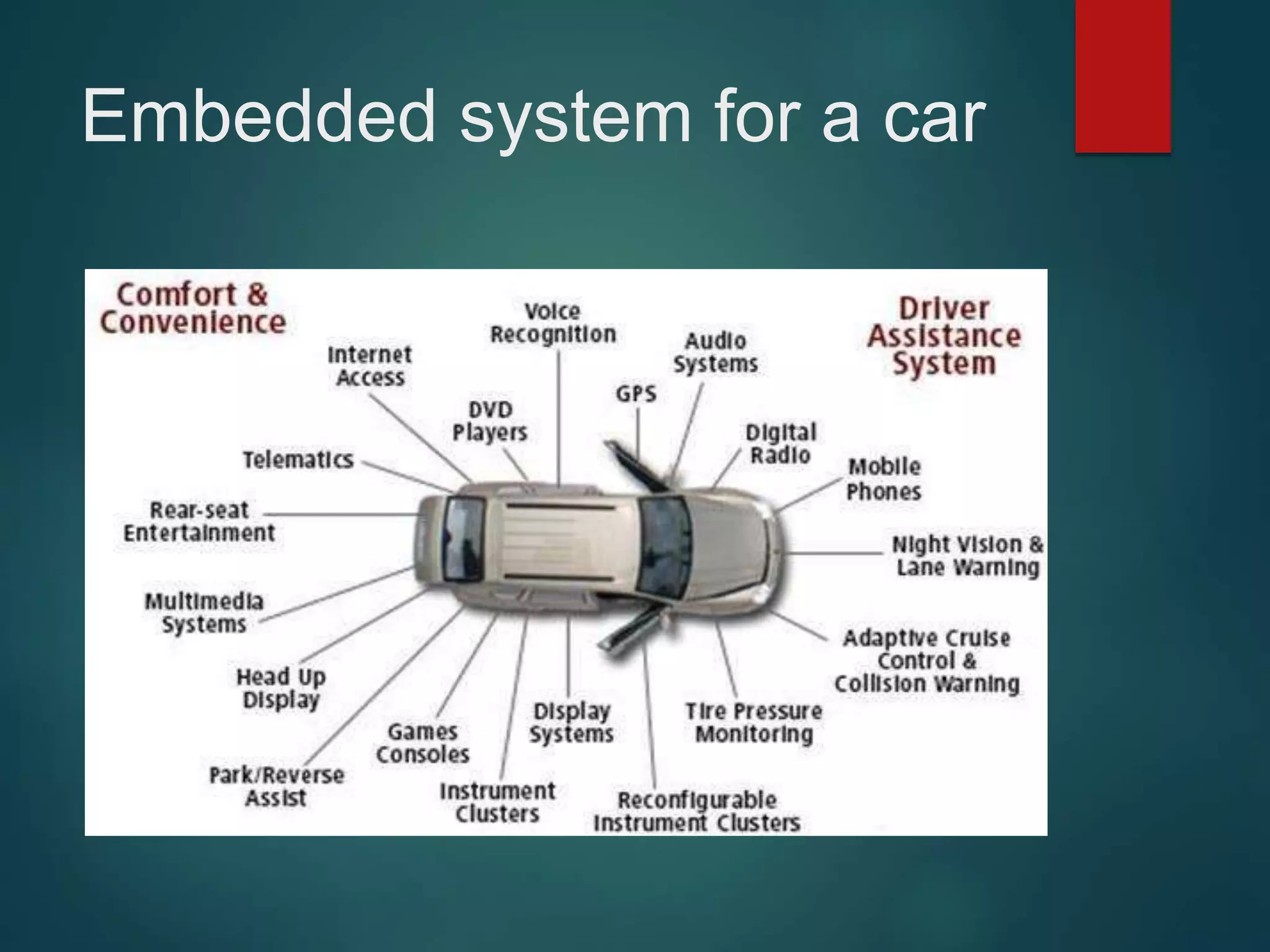
The document discusses embedded systems, defining them as computer hardware integrated with software to perform specific tasks. It highlights the essential components such as processors, features, programming languages, and applications, with a focus on the importance of C and C++ in embedded programming. Additionally, it categorizes embedded systems into real-time systems, mobile systems, and small-scale systems, emphasizing their unique characteristics and requirements.