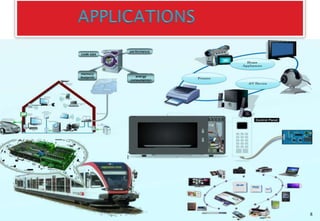
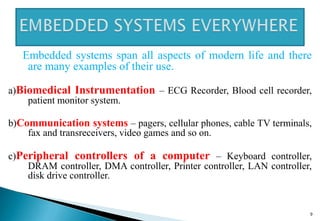
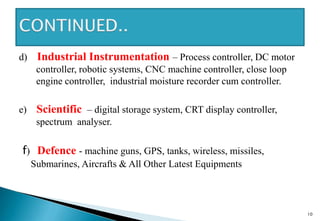
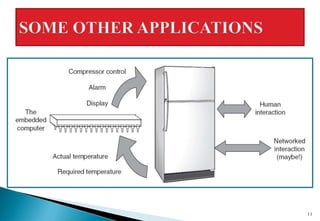
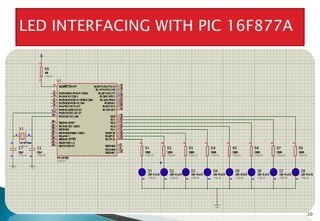
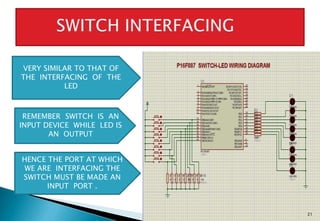
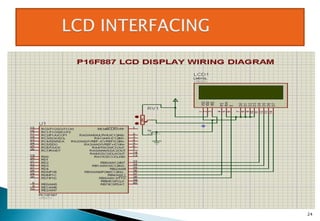
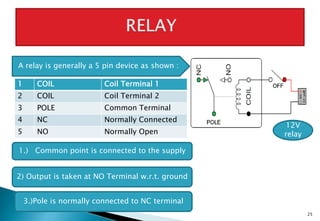
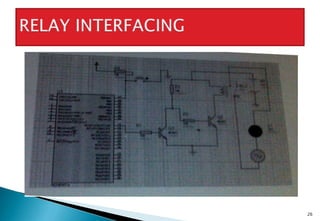
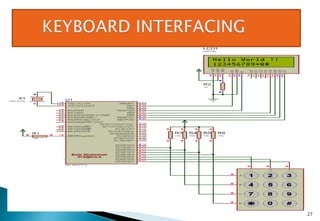
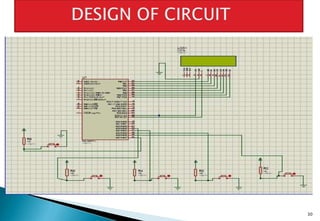
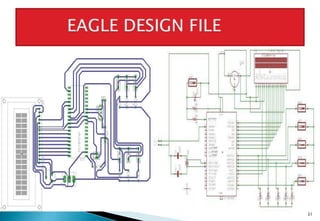
This document discusses embedded systems and provides examples of embedded system applications. It can be summarized as:
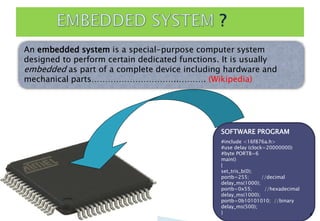
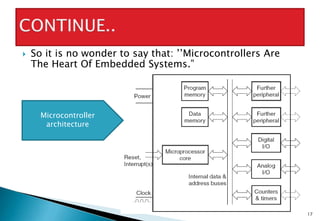
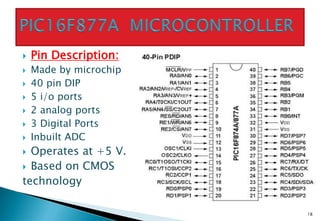
Embedded systems are specialized computer systems designed to perform dedicated functions. They are found in devices ranging from smartphones and appliances to vehicles and industrial equipment. Embedded systems typically have specialized hardware optimized for the specific application and software stored in read-only memory. Microcontrollers, which integrate a processor, memory and input/output peripherals on a single chip, are commonly used as the central processing unit in embedded systems. Examples of embedded systems applications discussed include biomedical devices, industrial controls, and consumer electronics.