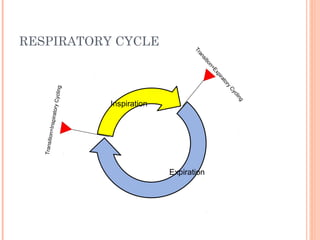
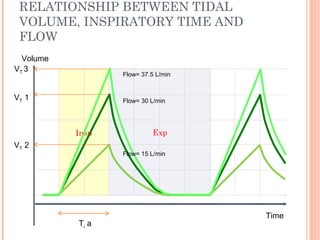
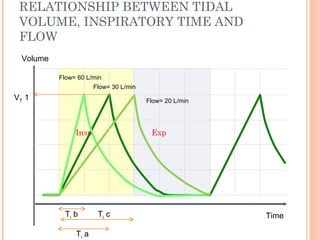
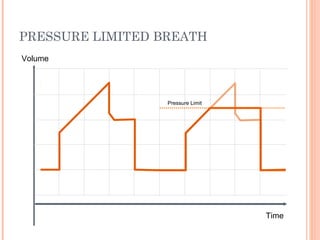
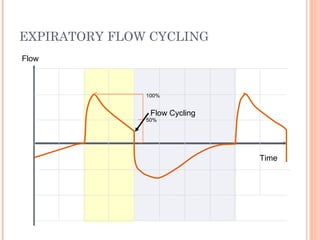
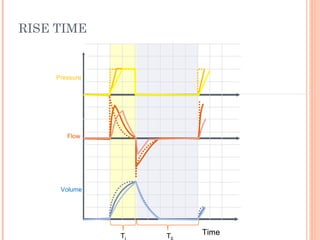
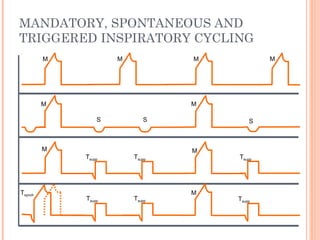
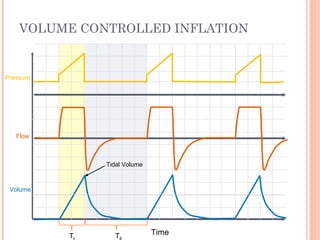
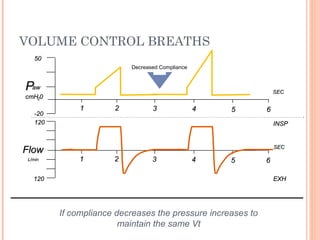
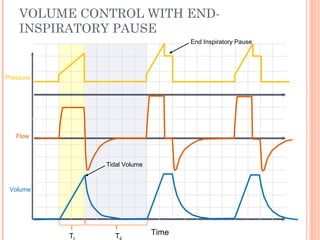
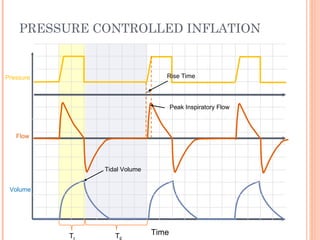
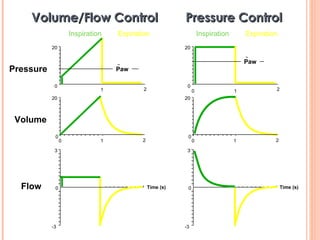
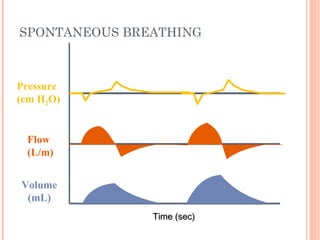
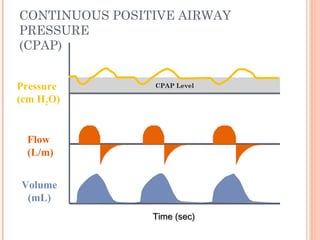
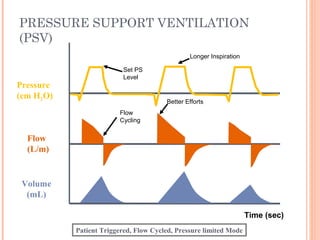
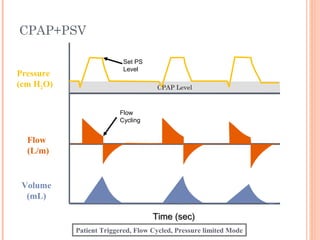
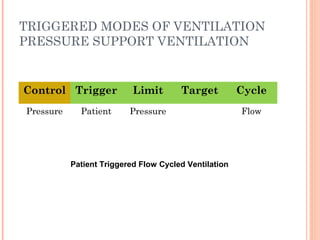
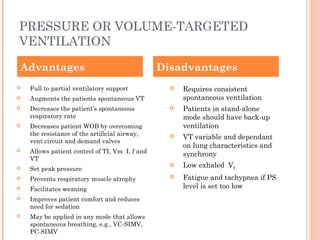
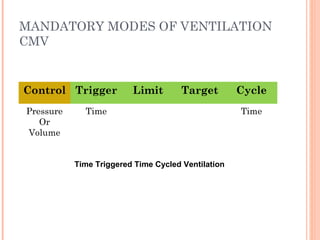
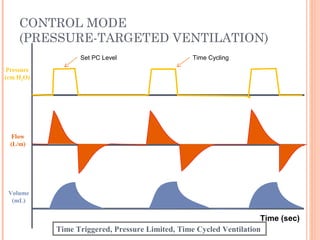
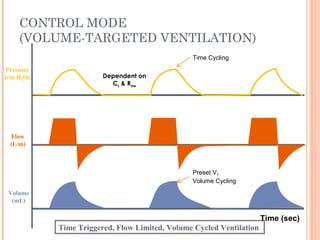
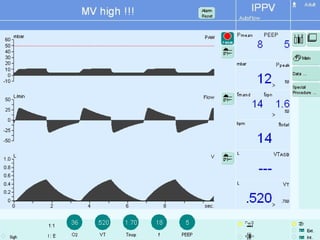
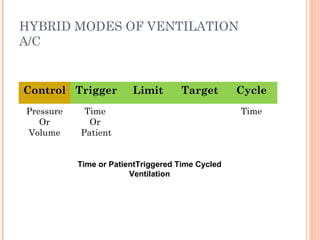
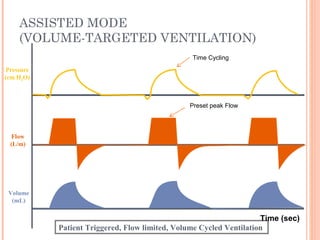
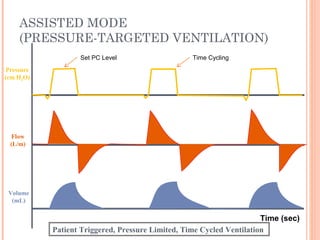
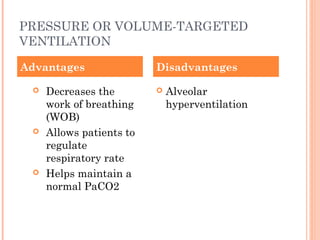
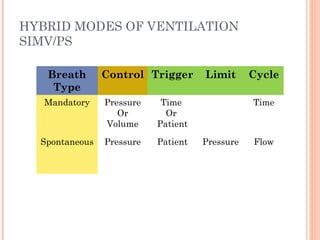
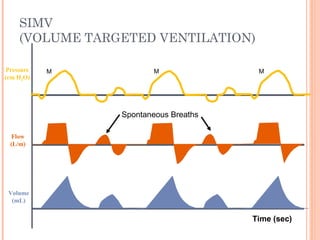
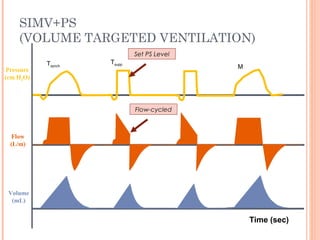
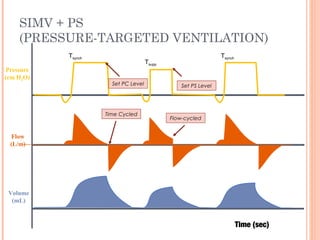
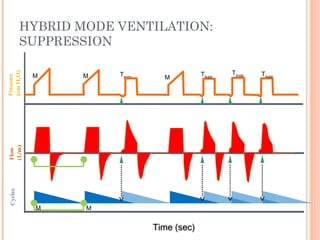
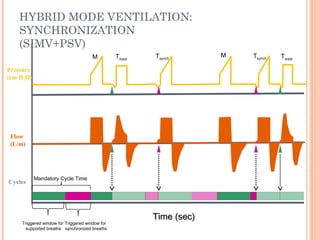
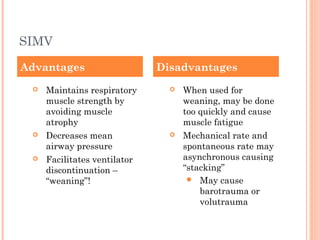
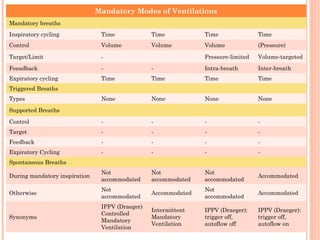
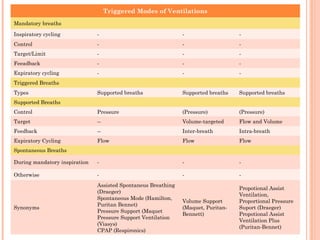
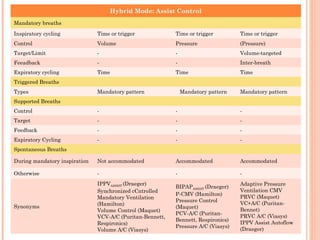
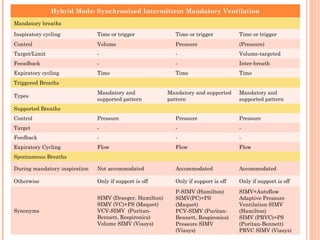
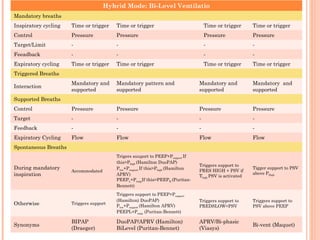
This document discusses various modes of mechanical ventilation. It begins by covering advanced basics related to flow, time, pressure and volume control. It then describes the main categories of ventilation modes: mandatory modes like controlled mandatory ventilation which are time-triggered and time-cycled; triggered modes like CPAP and PSV which are patient-triggered; and hybrid modes like assist-control and SIMV which combine mandatory and spontaneous breaths. For each mode, it provides details on controls, targets, feedback and cycling. The document provides examples of pressure and volume graphs to illustrate different mode functions and interactions. It concludes with tables summarizing the key characteristics of different mandatory, triggered and hybrid ventilation modes.