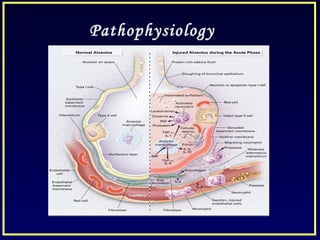
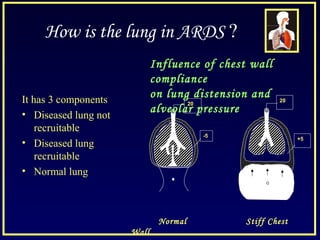
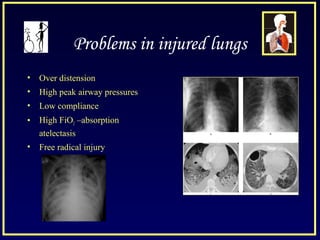
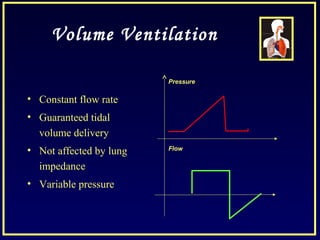
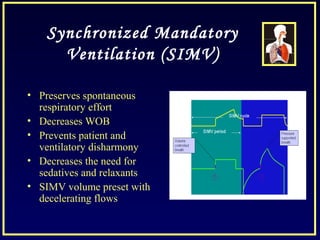
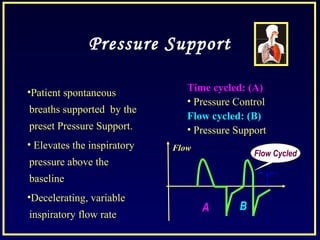
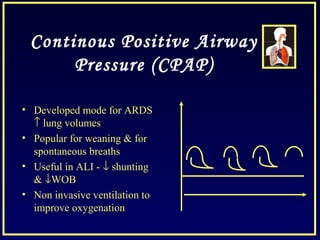
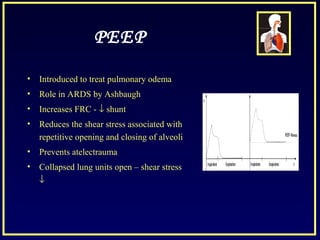
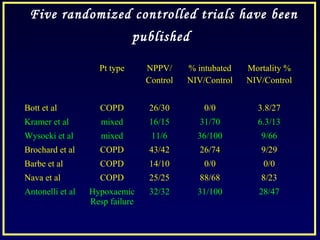
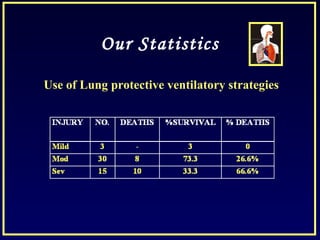
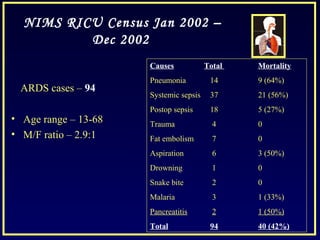
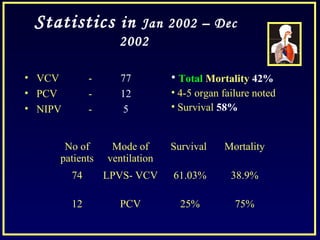
This document discusses various ventilatory strategies for treating ALI/ARDS, including:
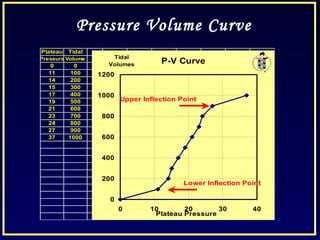
- Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) which reduces atelectasis and improves oxygenation.
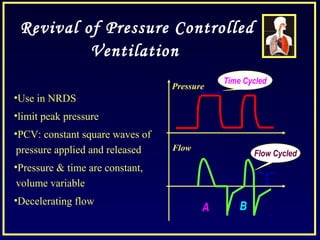
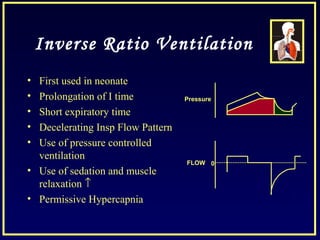
- Controlled mechanical ventilation aims to decrease ventilatory inequalities and distribute flow better while limiting plateau pressure.
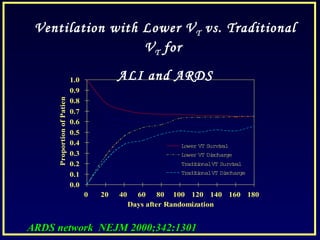
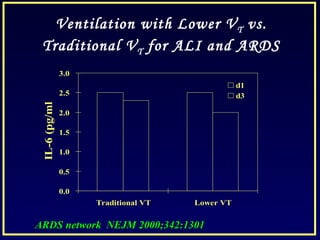
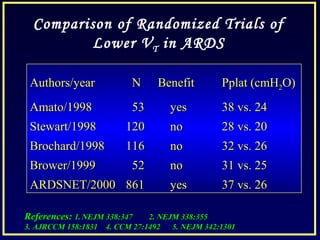
- Low tidal volume ventilation as per the ARDSnet trial reduces mortality compared to conventional tidal volumes.
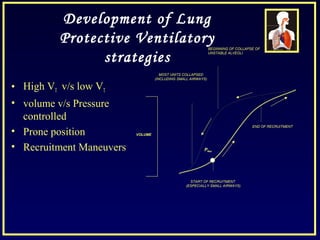
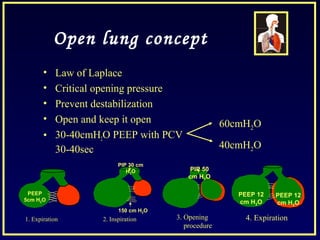
- Recruitment maneuvers use high pressures to reopen collapsed alveoli but can cause barotrauma and hemodynamic instability if not done carefully.
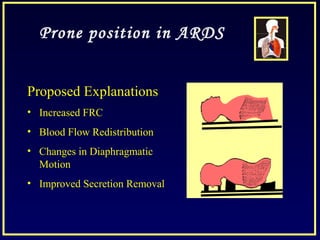
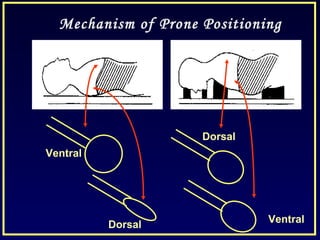
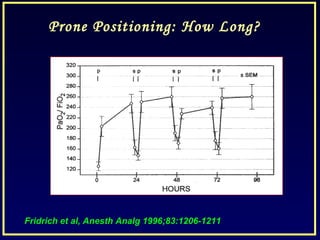
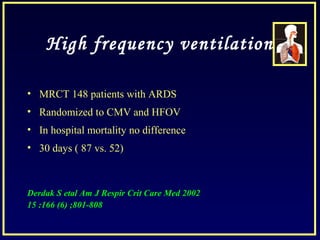
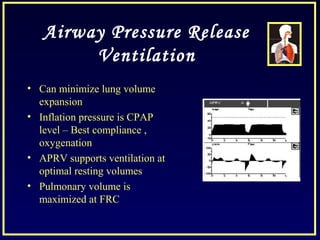
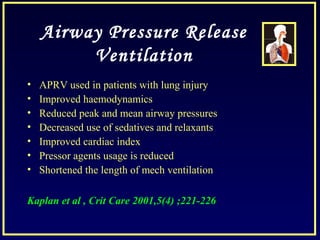
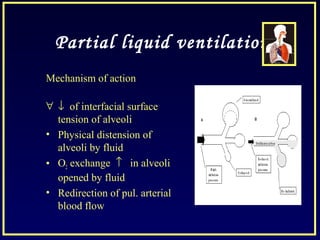
- Other strategies discussed include prone positioning, high frequency ventilation, airway pressure release ventilation and partial liquid ventilation. The goal is