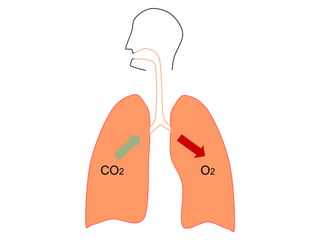
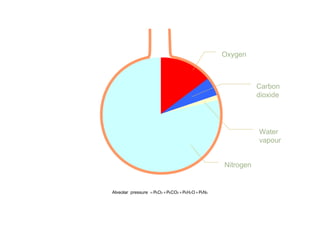
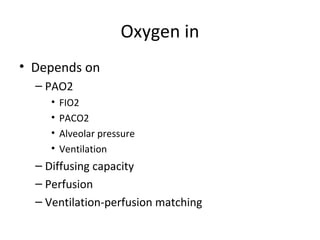
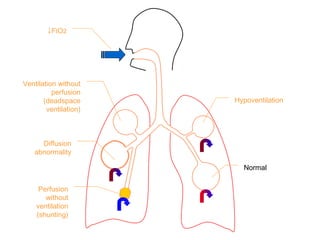
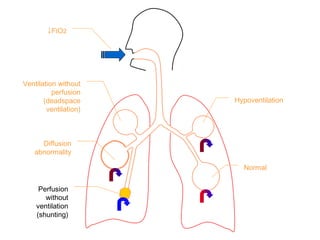
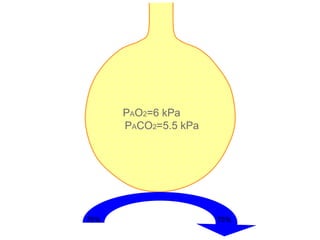
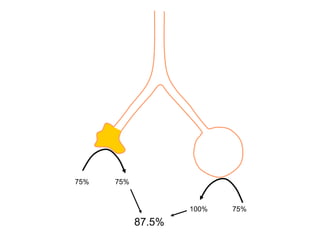
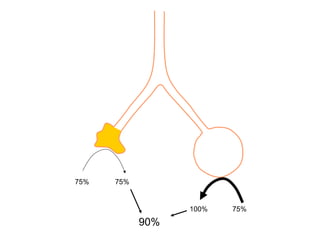
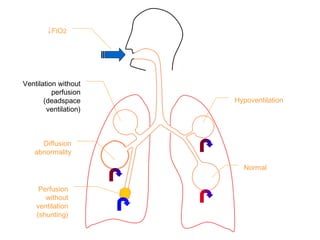
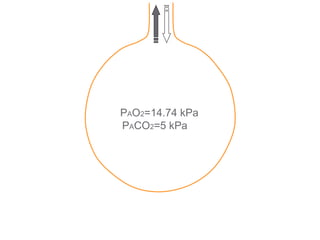
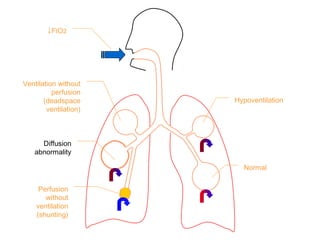
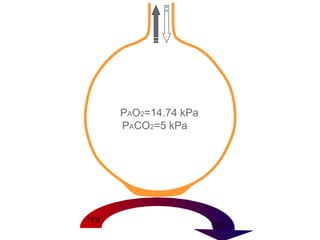
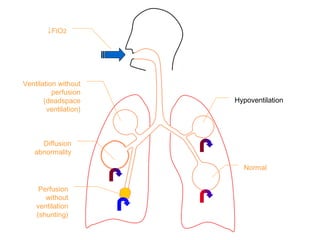
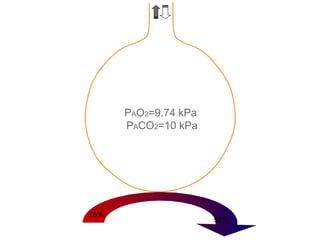
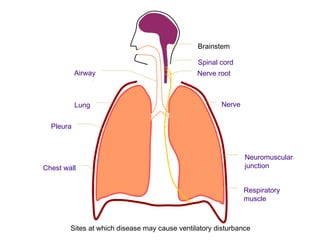
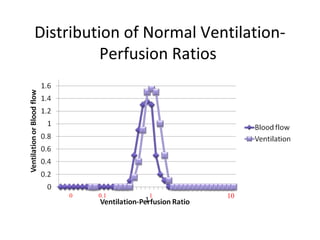
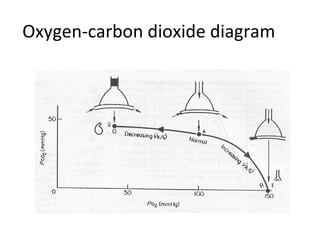
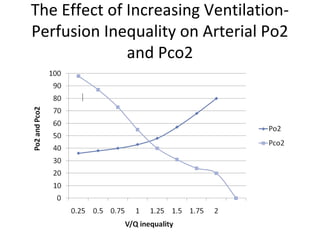
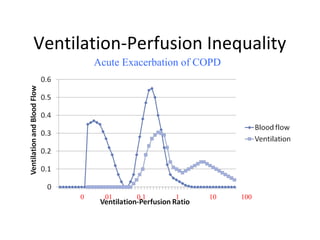
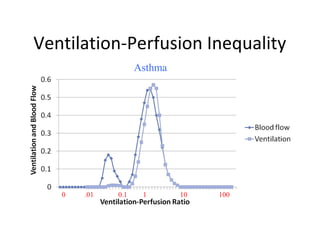
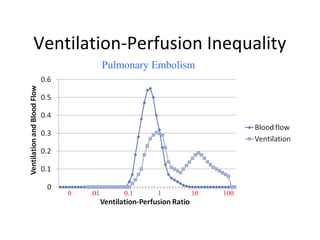
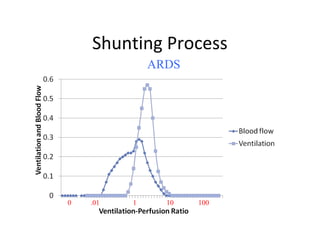
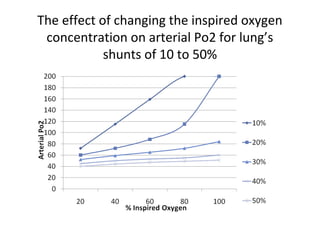
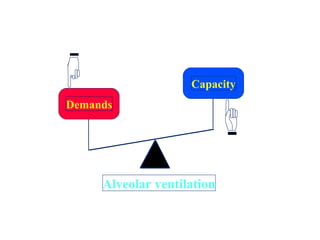
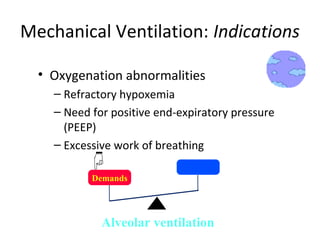
This document summarizes basic respiratory physiology, including how oxygen enters and carbon dioxide exits the lungs. It describes how oxygen in depends on factors like PAO2, diffusing capacity, perfusion, and ventilation-perfusion matching. Carbon dioxide out is largely dependent on alveolar ventilation. Pathophysiology that can affect gas exchange includes decreased FIO2, ventilation without perfusion, diffusion abnormalities, perfusion without ventilation (shunting), and hypoventilation. Shunting can be intra-cardiac or intra-pulmonary due to conditions like pneumonia. The document also discusses ventilation-perfusion inequality in different conditions and sites where disease can cause ventilatory disturbance.