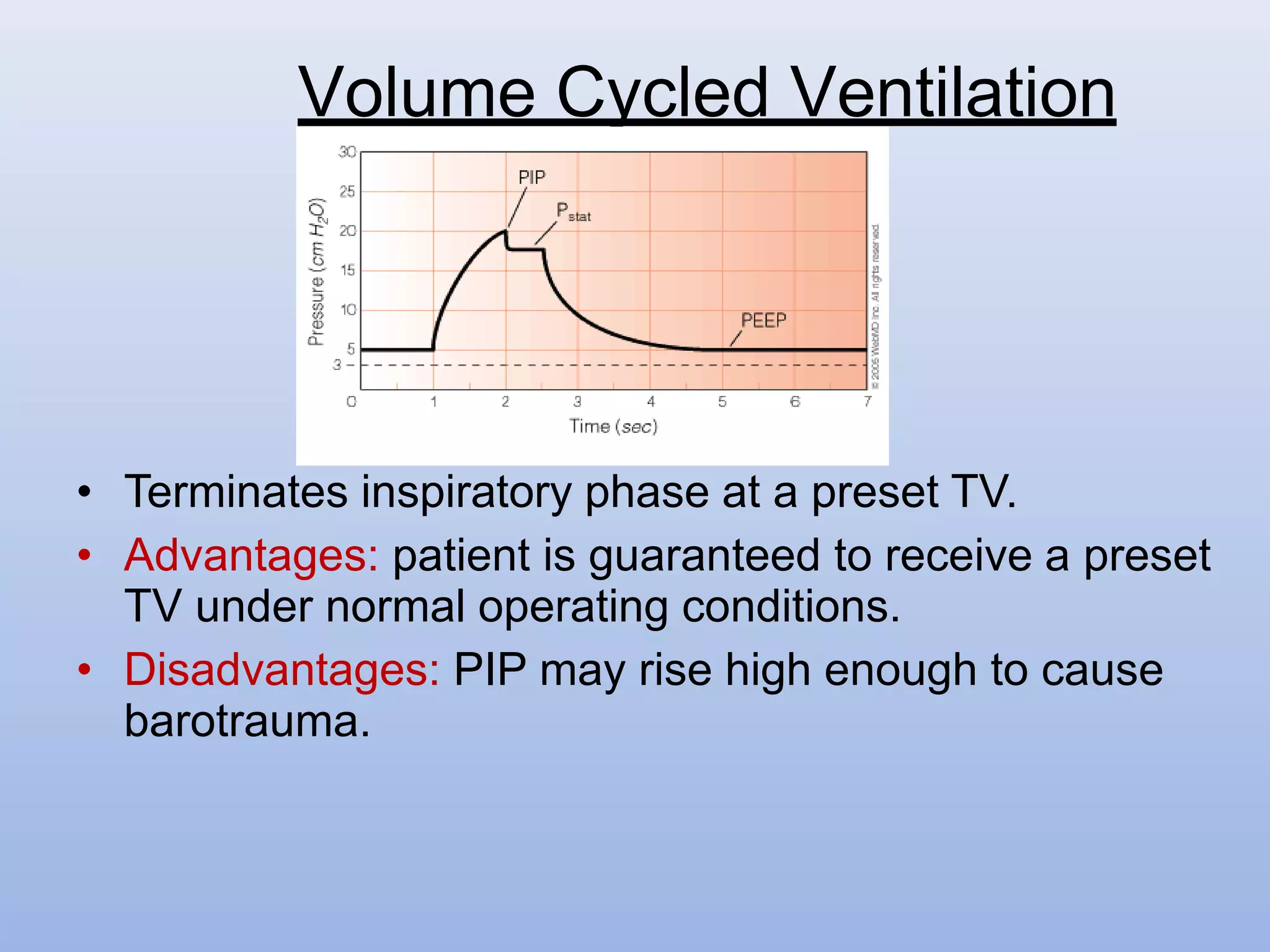
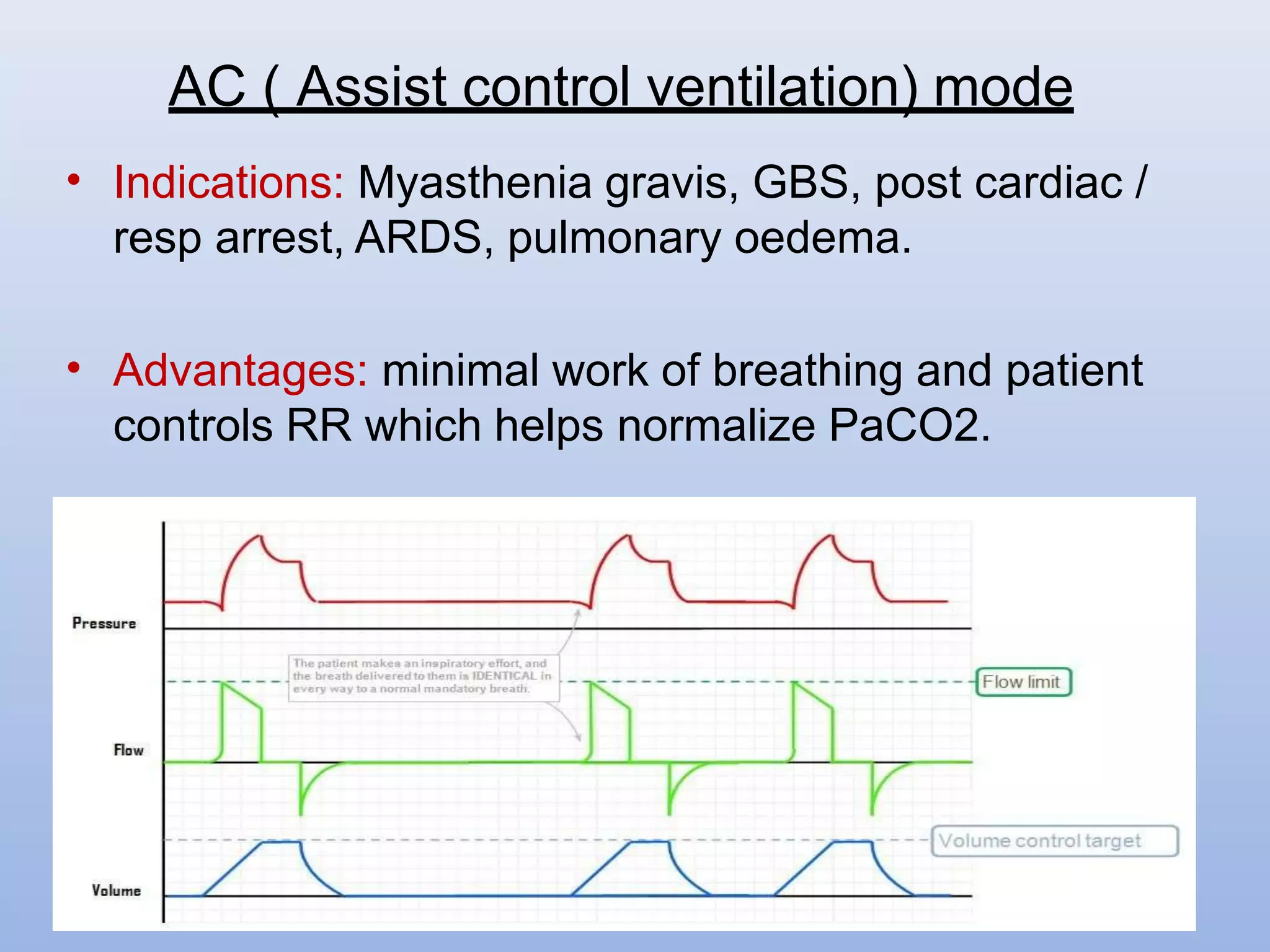
This document provides an overview of various modes of mechanical ventilation. It begins by defining key terms like peak inspiratory pressure, plateau pressure, PEEP, and CPAP. It then describes the basic modes of ventilation: volume-controlled, pressure-controlled, and pressure support. Various advanced modes are also outlined such as SIMV, BiPAP, APRV, and ASV. Factors related to weaning a patient from mechanical ventilation are discussed. Throughout, details are provided on the objectives, physiology, advantages, and disadvantages of each ventilation mode.