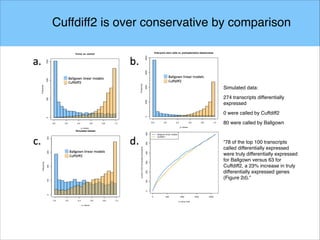
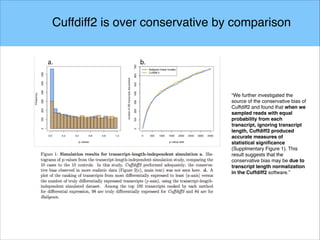
The document discusses the differential analysis of gene regulation using RNA-seq, specifically highlighting the limitations of cuffdiff2 compared to ballgown, which demonstrates greater sensitivity in identifying truly differentially expressed transcripts. The conservative bias of cuffdiff2 is attributed to its normalization for transcript length, affecting its accuracy in statistical significance. Ballgown allows for modeling continuous covariates and has been validated against biological samples, showing improved performance in detecting transcript-SNP pairs.